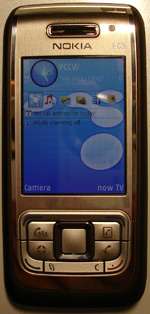
Nokia E65
 | |
| Manufacturer | Nokia |
|---|---|
| Compatible networks | Quad-band EGSM, WCDMA (3G) |
| Availability by country | Released 14 February 2007 |
| Predecessor | Nokia E70 |
| Successor | Nokia E66 |
| Form factor | Slide |
| Dimensions | 105 mm × 49 mm × 15.5 mm |
| Operating system | S60 platform third edition on Symbian OS |
| CPU | ARM 9, 222 MHz |
| Memory | microSD (TransFlash), up to 2 GB (hot-swappable), 256 MB card included, ~45 MB SDRAM - 20 MB free memory |
| Battery | 3.7 V 950 mAh lithium-polymer, |
| Display | Portrait 2,2" QVGA 181 ppi 240 × 320 TFT screen 24 bits (16 million) colors |
| Rear camera | 2 MP, 1600 × 1200 pixels, |
| Connectivity |
GPRS Class 32, 107 kbit/s HSCSD Yes EDGE Class 32, 296 kbit/s; DTM Class 11, 177 kbit/s 3G Wireless LAN Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g, Bluetooth (v. 1.2), Infrared port, USB (Pop-port) |
The Nokia E65 is a smartphone in the Eseries range, a S60 platform third edition device[1] with slide action. It shared many of the features of the N95 (quad band GSM, 3G, wifi, bluetooth) released around the same time, but thinner, lighter and without the GPS. It was followed fairly quickly by the E66, which was very similar but gained an FM radio, a newer release of S60, A2DP bluetooth, GPS and 3.2 mpixel camera.
Key features
- Conference calling, voice recording, notepad, integrated handsfree speaker, talking ringtones, and Nokia Team Suite
- SMS, MMS with distribution lists, instant messages, and email
- One Touch keys for conference calls, mute/unmute, and contacts
- Quad-band GSM/GPRS giving coverage on up to five continents
- 3G
- 802.11b/g integrated Wi-Fi
- Symbian S60 3rd edition
- Available in black, mocca brown, red, pink and "periwinkle" blue
Operating frequency
- Quad-band: EGSM 850/900/1800/1900
- W-CDMA 2100
- Voice over IP (VoIP) calls via integrated WLAN (IEEE 802.11g and 802.11b standards)
Size
- Volume: 74 cm3 (4.5 cu in)
- Weight: 115 g (4.1 oz)
- Dimensions: 105 mm × 49 mm × 15.5 mm
Display
- Active-matrix QVGA color display (240 × 320 pixels) with color support for up to 16 million colors
- Display contrast and brightness control
- Display size 2.2 in (56 mm)
User interface
- S60 3rd Edition, built on the Symbian operating system
- One Touch keys for mute/unmute, contacts, and conference calling
- Five-way Nokia NaviTM key with two customizable soft keys, power key that can be used as profile key, and My Own key
- S60 edit key located on the side of the device
- Volume keys on the side of the device
Imaging

- Take snapshots with the 2-megapixel camera (no built-in flash)
Messaging
- Read email with attachments: supports POP/IMAP, SMTP, and IMAP4 with idle protocols
- Instant messaging client (OMA IMPS 1.2)
- Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS, ver. 1.2) for text, voice clips, video clips, and still images ok
- SMS and MMS with distribution lists
- Predictive text input T9
Multimedia
- Video and audio streaming (3GPP & RealMedia)
- Music player (MP3/AAC) and media player
- Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) digital rights management (DRM) 1.0 with forward lock
Memory functions
- Up to 650 MB user memory
- MicroSD memory card support (up to 4 GB maximum size)
Applications
- Java MIDP 2.0-based games and applications
- Attachment viewers for documents, spreadsheets, and presentations
- Symbian V9 games and applications
Connectivity
- Dual Transfer Mode (MSC 9)
- Bluetooth 1.2 wireless technology
- Pop-Port connector carrying USB and audio
- IrDA with transfer rate up to 115 kbit/s
- WiFi 802.11b/g
- Nokia standard "tube" power connector
Browsing
- HTML Nokia browser
- XHTML browser (HTTP stack)
Data transfer
- EGPRS multi-slot class 32 for 5 + 3 (receive + transmit) timeslots (up to 6 timeslots total for maximum download speeds of up to 296 kbit/s)
- Multi-slot class 32 is also supported with GPRS for a maximum downlink rate of 67 kbit/s
- Remote and local (peer-to-peer) synchronization of calendar, contacts, notes and to-do list via Bluetooth technology, IR, or USB connectivity cable
Personal information management (PIM)
- Calendar with weekly view, contacts, to-do list, and notepad for short notes all viewable while managing a phone call
Voice features
- One Touch keys for direct access to contacts, mute/unmute, and conference calling
- Voice dialing
- Voice commands for menu short cuts, keypad lock, and profiles
- Voice recording to record your own notes or conversations
- Talking ringtones mix the name of the caller with the ringtone so you know who's calling without looking at the screen
- Integrated handsfree speaker
- Supported speech codecs: EFR, FR, AMR NB, HR
- Conference calling
Digital services
- Over the air (OTA) downloads for ringtones, contacts, email, WAP, MMS, operator logos, and user group icons
- Image upload/download
- Smart content upload/download
- Downloadable instrumental MIDI ringing tones
Other features
- Add-on solutions enable integration into enterprise private branch exchange (PBX) infrastructure
- Ambient light sensor on front (sometimes mistaken for a forward-facing camera)
- Backlit keypad (activated when ambient light is low)
- User-upgradeable firmware using Nokia's software updater on a Windows PC.
Sales package contents
- Nokia E65 handset
- Nokia Battery BL-5F
- Nokia Travel Charger AC-4
- Nokia Headset HS-5 (black)
- Nokia Connectivity Cable CA-53
- Nokia Carrying Pouch CP-18
- Nokia MicroSD card (256 MB) (Asia Pacific only)
| Battery | Talk time | Standby time | ||||
| GSM | WCDMA | VoIP | GSM | WCDMA | GSM/WCDMA and WLAN | |
| BL-5F | Up to 3–6 hours | Up to 1.8–2.5 hours | Up to 2 | Up to 7–11 days | Up to 8–14 days | Up to 4–5 days |
Operation times vary depending on the network and usage.
Known issues
Many users have experienced problems with the SIM connecting to the network after using the phone for some time. Most of them had to bring the phone to the Nokia center to get their phone repaired or replaced. The cause seems to be a design problem in the SIM container on the chassis of the phone. The SIM container is mainly built of a thin metal foil, which in time tends to bend, thus disconnecting the SIM from the mobile phone's SIM contacts. The problem can apparently be solved just by putting a bit of paper between the metal foil and the SIM, enabling it to make contact. There's also difficulties in making connection to WLAN networks which use EAP-PEAP and MSchapV2 protocols if you update the phone's firmware (this is true as for firmware version 3.0633.69) Other users experience problems with the phone connecting to third party GPS devices over Bluetooth. This seems to be a compatibility flaw in the Nokia Bluetooth stack of Nokia Maps as these devices do connect well when used with Google Maps on the E65.
References
- ↑ Cha, Bonnie (22 March 2007). "Nokia E65 Review". CNET.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nokia E65. |