North Carolina State Highway Patrol
| North Carolina State Highway Patrol | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | NCSHP | ||||||
|
Shoulder patch of the North Carolina State Highway Patrol | |||||||
|
North Carolina State Highway Patrol logo | |||||||
|
Trooper badge of the North Carolina State Highway Patrol | |||||||
| Motto |
Esse Quam Videri Latin: To be rather than to seem | ||||||
| Agency overview | |||||||
| Formed | 1 July 1929 | ||||||
| Employees | 2,340 (as of 2008)[1] | ||||||
| Volunteers | 12 (as of 2008) [2] | ||||||
| Legal personality | Governmental: Government agency | ||||||
| Jurisdictional structure | |||||||
| Operations jurisdiction* | Department of Public Safety of in the state of North Carolina, USA | ||||||
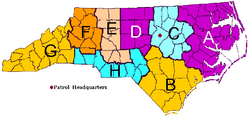 | |||||||
| North Carolina State Highway Patrol Troops | |||||||
| Size | 53,865 square miles (139,510 km2) | ||||||
| Population | 9,061,032 (2007 est.)[3] | ||||||
| Legal jurisdiction | State of North Carolina | ||||||
| Constituting instrument | North Carolina Constitution | ||||||
| General nature | |||||||
| Operational structure | |||||||
| Headquarters | Raleigh, North Carolina | ||||||
| Troopers | 1,517 (as of 2004)[4] | ||||||
| Civilian (uniformed and non w/various titles)s | 212 (as of 2004)[4] | ||||||
| Agency executive | William J. Grey, Commander (Colonel) | ||||||
| Parent agency | North Carolina Department of Public Safety | ||||||
| Sections |
5
| ||||||
| Troop Headquarters |
8
| ||||||
| Facilities | |||||||
| Districts | 54 | ||||||
| Airbases | 4 | ||||||
| Lockups | None (local county jails or state juvenile facilities used) | ||||||
| Helicopters | Bell 206 JetRanger, Bell OH-58A+ and Bell 407 | ||||||
| Dogs and horses | Police tracking/drug sniffing dogs and ceremonial horses | ||||||
| |||||||
| Website | |||||||
| NCSHP website | |||||||
| Footnotes | |||||||
| * Divisional agency: Division of the country, over which the agency has usual operational jurisdiction. | |||||||

The North Carolina State Highway Patrol is the highway patrol agency for North Carolina which has no per-se "state police" agency. The Patrol has jurisdiction anywhere in the state except for federal or military installations. The Highway Patrol was created in 1929 and is a paramilitary organization with a rank structure similar to the armed forces. NCSHP personnel at times conduct formations, inspections, honor guard activities and drill similar to the armed forces drill and ceremonies. Troopers have a reputation in North Carolina for immaculate uniform and grooming standards. The primary mission of the North Carolina State Highway Patrol is to reduce traffic collisions and make the highways of North Carolina as safe as possible.
The Highway Patrol is one of the largest divisions of the North Carolina Department of Public Safety other than the Department of Correction (DOC). The patrol's headquarters is located in the DPS headquarters in Raleigh in the Archdale Building downtown. This department also includes the NC State Bureau of Investigations (SBI), NC Alcohol Law Enforcement (ALE), NC Department of Corrections (DOC), which includes probation and parole (Community Corrections), NC Civil Air Patrol, Emergency Management, NC State Capitol Police, and the NC National Guard.
History
Established in 1929, the NC State Highway Patrol's mission is to reduce collisions and make the highways of North Carolina as safe as possible.[5]
North Carolina, like many Southern states, was distrusted by the federal government from starting a "state police" agency, due to concerns that the department would be used for political motives to intimidate blacks from voting in the late 1920s, at a time when lynchings and Ku Klux Klan activities were on the rise following the end of World War I. The vast majority of the 100 NC Sheriffs also did not want to lose political power to a state police agency. These issues were alleviated by establishment of a traffic enforcement agency to police the ever-expanding highways with the enforcement of motor vehicles laws primarily. The original members of the Highway Patrol were the command staff and they were sent to the Pennsylvania State Police Academy for training. Upon their graduation and return to North Carolina, these men established the first basic school at Camp Glenn, an abandoned World War I Army Camp in Morehead City where Carteret General Hospital is now located. Several extra recruits were brought to the original basic school and were sent home as alternates, in the event that original members quit or were fired. Most of these men were never recalled to duty after 8 weeks of training. Over the years, the agency obtained semi-state police powers with the authority of the Governor to implement it, but this has never been fully done by any NC Governor. Changes in the regulations by the general assembly were made in response to political appointees being names as commander. The changes ensured that the commander of the SHP must meet all trooper requirements, including completion of the grueling basic trooper training school, thus preventing unqualified political appointees from being named commander.
Establishment
″In 1921, 150,558 motor vehicles were registered in North Carolina. By 1929, the number of registered vehicles increased to 503,590. As the number of vehicles increased, so did the number of people killed in traffic accidents: 690 deaths in 1929.
Traffic control was of such concern that in 1929 the General Assembly passed an act authorizing the establishment of a State Highway Patrol. The new organization was given statutory responsibility to patrol the highways of the state, enforce the motor vehicle laws, and assist the motoring public.
The organization was designed as a division of the State Highway Commission. The Highway Commission initially sent ten men (later designated as a captain and nine lieutenants) to Pennsylvania to attend the training school of the Pennsylvania State Police. Their mission was to study law, first aid, light adjustments, vehicle operation, and related subjects for use in North Carolina's first Patrol School.″[6]
The SHP was transferred to the department of Revenue until in 1941[7] becoming part of the newly formed NC Department of Transportation, but was again transferred to the newly formed Department of Crime Control and Public Safety in the mid-1970s. This agency more recently became the Department of Public Safety, which expanded to absorb other agencies including the Department of Motor Vehicles, State Bureau of Investigation and other state departments dealing with statewide law enforcement.
An office was established in Raleigh to serve as state headquarters, and a district office was established in each of the nine state DOT highway districts. A lieutenant and three patrolmen were assigned to each district. All patrolmen were issued Harley Davidson motorcycles and the lieutenants drove Model A Ford Coupes. The Patrol commander was issued a Buick automobile. The new patrolmen and command staff made a cross-state introductory riding tour on July 1, 1929 to show off the new agency's personnel to the state. On the following day, the first officer death occurred when Patrolman George I. Thompson who was driving his motorcycle in the procession was killed in a traffic collision in Anson County (see below for line-of-duty deaths) [8]
Growth
In 1931, the General Assembly increased the Patrol to 67 members and reduced the number of lieutenants to six. The Patrol was increased in size in 1933 to 121 members. Patrolmen were relieved of gasoline inspection duties and given responsibilities for issuing driver licenses and enforcing the new driver license laws.
Without vehicular radios, patrolmen were issued 2 rolls of dimes each week so they could phone in for calls on a regular basis. Though the legislature authorized the patrol to establish a one-way statewide radio system in 1937, it had many areas of no reception (dead spots), especially in the far eastern coastal areas and more so in the rugged western mountains. The system was flawed in that patrolmen could not answer back. Poor reception made it hard for patrolmen to tell which patrolman was being called, even when they could hear the radio. If dispatchers could not locate a patrolman, they would call certain selected stores, gas stations and post offices in the particular patrolman's district and ask the employees or personnel to watch for and to flag the patrolman down the next time he was seen passing by and to tell him to call in. If patrolmen arrested a violator, they would have minor offenders follow them to the justice of the peace office or courthouse. If they physically arrested a violator, the patrolmen would hide their motorcycle in brush and drive an offender to the local jail in his own vehicle.
All patrolmen were assigned individual vehicles in 1937, and over the passing decades, numerous executive, legislative, and administrative changes have occurred since the Patrol's creation. The duties and responsibilities have varied, different ranks have been designated, and the organizational structure has been modified to improve efficiency, to address the needs of the state and in response to changing technology. Examples included an expanded air wing after World War II, implementation of two-way radios, use of helicopters, abolition of fixed-wing aircraft, use of breath testing devices, K-9 dog units, body armor, pursuit vehicles such as Mustangs and Camaros, speed measurement instruments such as the "whammy" in the 1950s, later RADAR, VASCAR and LIDAR and more recently computerized dispatch through in-vehicle terminals.
In World War II, a number of Patrolmen who had served in World War I were recalled to active duty and others enlisted, taking leave of absence from the SHP. Many others had served in the Guard or Reserves. Patrolmen assisted the military by being alert for saboteurs and spies by reporting suspicious activity to the FBI. Deserters and AWOLS were also arrested. By 1946, all personnel on military status had returned to duty with the Patrol.
As of 2008, the North Carolina State Highway Patrol had an authorized strength of over 1,800 sworn law enforcement officers.
In 2008, the NC State Highway Patrol arrested 23,199 people for Driving While Impaired, seized $10 million worth of drugs, and investigated 1,081 fatalities on North Carolina highways. The Motor Carrier unit fined thousands of truck drivers for various violations.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ NCDPS Website
- ↑ Volunteers in Police Service Website
- ↑ http://www.census.gov/popest/states/NST-ann-est.html 2007 Population Estimates
- 1 2 USDOJ Statistics
- ↑ North Carolina State Highway Patrol Website http://www.nccrimecontrol.org/Index2.cfm?a=000003,000014
- ↑ https://www.ncdps.gov/Index2.cfm?a=000003,000014,000721
- ↑ http://www.dor.state.nc.us/aboutus/ncdor.html
- ↑ North Carolina State Highway Patrol Website http://www.nccrimecontrol.org/Index2.cfm?a=000003,000014,000721
- ↑ NC Department of Crime Control & Public Safety Website