Oranit
Oranit
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| ||
 Oranit | ||
| Coordinates: 32°7′45.5″N 34°59′42.76″E / 32.129306°N 34.9952111°ECoordinates: 32°7′45.5″N 34°59′42.76″E / 32.129306°N 34.9952111°E | ||
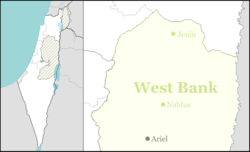
| Region | West Bank | |
| District | Judea and Samaria Area | |
| Founded | 1983 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Local council (from 1990) | |
| • Head of Municipality | Shlomi Langer | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 2,069 dunams (2.069 km2 or 511 acres) | |
| Population (2015)[1] | ||
| • Total | 8,495 | |
| Name meaning | Little pine | |
| Website | http://www.oranit.org.il/ | |
Oranit (Hebrew: אֳרָנִית) is an Israeli settlement and local council located in the Seam Zone, straddling the Green Line. It is surrounded by Horshim forest to the west, Rosh HaAyin and Kfar Qasim to the southwest, Sha'arei Tikva to the east, and Khirbet Abu Salman to the northeast. In 2015 it had a population of 8,495.
The international community considers Israeli settlements illegal under international law, though Israel disputes this.[2]
History
In April 1983, the Israeli government approved the establishment of Oranit, one of three settlements planned for "western Samaria".[3]
According to Amnesty International the majority of the land of the neighboring Palestinian village of 'Izbat Salman was lost when Oranit was established, with most of the remainder being effectively lost when the West Bank barrier was built to encompass Oranit and enough surrounding land for future expansion of the settlement.[4] The UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East has estimated that three Palestinian villages in the vicinity lost 3,000 dunams of land with the creation of Oranit settlement. Thirty Palestinian farmers were initially given access to their farmland through the gates of the settlement. This right was soon withdrawn for security reasons and the settlement has since expanded onto this Palestinian farmland.[5]
In 1985, the first residents moved in. In 1990, Oranit achieved local council status. In 2009, Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu imposed a 10-month freeze on construction in Oranit and other Israeli settlements in the West Bank.[6] Building inspectors of the Israeli military's civil administration issued a stop-work order, sending home a crew of Palestinian laborers who had been employed at a building site in Oranit.[6]
According to Zvika Ma-Yafit, former mayor of Oranit, the town maintains good relations with nearby Kafr Qasim and the two towns have cooperated on environmental projects such as the development of a joint sewage system. Many residents of Kafr Qasim work in Oranit as gardeners and handymen.[7] He says the motive for moving to Oranit is not ideological but quality of life.[8]
Demographics
According to a 2009 survey, the population is young and evenly divided between men and women. Around 15% of the population is Orthodox, two-thirds of whom live in the town's religious neighborhood. Oranit ranked 8 out of 10 on the Israeli socio-economic scale.[9]
Education and culture

In an educational project at MultiCenter, a computer center at Park Afek industrial zone, Jewish and Arab youngsters from Oranit, Rosh Ha'ayin and Kafr Qasim created a computer model for a virtual city of coexistence. According to the project director, the children learn about each other's language and culture, discuss strategies for promoting tolerance and avoiding violence, and use a program developed by MultiCenter to create a virtual dream city, complete with a map, logo and charter.[10]
Community facilities include a public swimming pool and tennis courts.[8]
Notable residents
- Shai Piron[11] (b. 1965), Israeli politician (Yesh Atid) and former Minister of Education
References
- ↑ "List of localities, in Alphabetical order" (PDF). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ↑ "The Geneva Convention". BBC. 2009-12-10.
- ↑ Nakhleh, Issa. "Encyclopedia of the Palestine Problem".
- ↑ "Enduring occupation Palestinians under siege in the West Bank". Amnesty International. 4 June 2007. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Impact of the First Phase of the Security Barrier on the Qalqiliya, Tulkarmand Jenin districts". United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East. 1 July 2003. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- 1 2 Mitnick, Joshua (December 1, 2009). "In Israeli settlements, residents and builders push back on 10-month freeze". Christian Science Monitor.
- ↑ 'Quality of life' is theme for bedroom community of Oranit
- 1 2 Golden, Tim (July 3, 2002). "Dreams of Land Collide as Israeli Settlers Grow in Numbers". New York Times.
- ↑ "Local Authorities in Israel 2009, Publication #1451 - Municipality Profiles - Oranit" (PDF) (in Hebrew). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2011-09-07.
- ↑ Fisher-Ilan, Allyn (February 1, 2001). "Youngsters build virtual coexistence". Jerusalem Post.
- ↑
External links
- Official website (Hebrew)