Oswego River (New York)
| Oswego River | |
| River | |
 The Oswego River as it passes through the city of Oswego. | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | New York |
| Counties | Onondaga, Oswego |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Seneca River |
| - right | Oneida River |
| City | Oswego |
| Source | |
| - elevation | 357 ft (109 m) [1] |
| - coordinates | 43°12′5″N 76°16′50″W / 43.20139°N 76.28056°W [2] |
| Mouth | Lake Ontario |
| - location | Oswego |
| - elevation | 245 ft (75 m) [1] |
| - coordinates | 43°27′54″N 76°30′50″W / 43.46500°N 76.51389°WCoordinates: 43°27′54″N 76°30′50″W / 43.46500°N 76.51389°W [2] |
| Basin | 5,122 sq mi (13,266 km2) |
| Discharge | for Oswego |
| - average | 6,912 cu ft/s (196 m3/s) [3] |
| - max | 37,000 cu ft/s (1,048 m3/s) (March 28, 1936)[3] |
| - min | 261 cu ft/s (7 m3/s) (September 18, 1985)[3] |
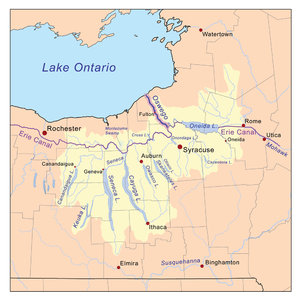 The Oswego drainage basin, with the Oswego River highlighted
| |
The Oswego River /ɒsˈwiːɡoʊ/ is a river in upstate New York in the United States. It is the second-largest river (after the Niagara River) flowing into Lake Ontario. James Fenimore Cooper’s novel The Pathfinder, or The Inland Sea is set in the Oswego River valley.[4]
The name Oswego is a Mohawk name that means "flowing out", or specifically, "small water flowing into that which is large".[5]
Description
James Fenimore Cooper described the Oswego in these words:
The Oswego is formed by the junction of the Oneida and the Onondaga,[note 1] both of which flow from lakes; and it pursues its way, through a gently undulating country, some eight or ten miles, until it reaches the margin of a sort of natural terrace, down which it tumbles some ten or fifteen feet, to another level, across which it glides with the silent, stealthy progress of deep water, until it throws its tribute into the broad receptacle of the Ontario.[6]
River course
The Oswego River starts at the confluence of the Oneida River (flowing from Oneida Lake) and the Seneca River (flowing from Seneca Lake, Cayuga Lake, and Montezuma Marsh). The river drains an area of 5,122 square miles (13,266 km2), as large as the states of Rhode Island and Delaware together, comprising most of the Finger Lakes region of upstate New York.
At its mouth at Lake Ontario, the river divides the City of Oswego just as it divides the City of Fulton a few miles upstream.
Oswego Canal
"Canalized" for part of its length as the Oswego Canal, the Oswego River also serves as a part of the New York State Canal System, providing a route from the Erie Canal to Lake Ontario. This section of the canal was completed in 1827, two years after completion of the Erie Canal. In 1917, as part of a general overhaul of the canal system, the Oswego Canal was deepened and refurbished. The canal is now 14 feet (4.3 m) deep and has an overhead clearance of 20 feet (6.1 m).
Pollution
The Oswego River was listed as a Great Lakes Areas of Concern in The Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement between the United States and Canada until it was formally delisted on July 21, 2006.[7]
Sportfishing
The river is known for its steelhead run in the early spring, followed by a salmon run in early autumn. The river is stocked annually by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation with 140,000 Chinook salmon and 20,000 steelhead.[8]
See also
Notes
- ↑ The river downstream of Onondaga Lake is now considered to be the Seneca before it meets the Oneida.
References
- 1 2 Google Earth elevation for GNIS coordinates.
- 1 2 "Oswego River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "04249000 Oswego River at Lock 7, Oswego NY, Water Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1934–2013. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- ↑ "Oswego." The Columbia Gazetteer of the World Online. New York: Columbia University Press, 2005. http://www.columbiagazetteer.org/ . Accessed: February 14, 2008
- ↑ Beauchamp, William Martin (1907). Aboriginal Place Names of New York (New York State Museum Bulletin, Volume 108). New York State Education Department. p. 171. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- ↑ James Fenimore Cooper, The Pathfinder, Chapter 3
- ↑ "Oswego River AOC, US EPA". Retrieved March 28, 2013.
- ↑ NYS Department of Environmental Conservation. "Oswego River". Dec.ny.gov. Retrieved February 20, 2015.
External links
- Information and Boater's Guide to the Oswego River and NYS Canal
- New York State Barge Canal information
- Where to Fish, Oswego County