Hard palate
| Hard palate | |
|---|---|
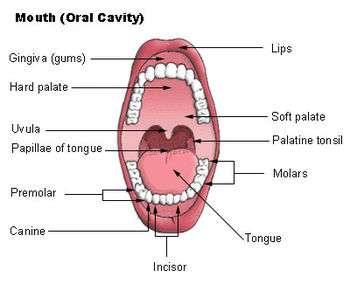 Mouth (oral cavity) | |
 Upper respiratory system, with hard palate labeled at right. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | greater palatine artery |
| Nerve | greater palatine nerve, nasopalatine nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | palatum durum |
| MeSH | A02.835.232.781.324.502.660 |
| TA | A05.1.01.103 |
| FMA | 55023 |
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate of the skull, located in the roof of the mouth. It is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone, and spans the arch formed by the upper teeth.
Structure
The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone. It forms a partition between the nasal passages and the mouth. On the anterior portion of the roof of the hard palate are the plicae, irregular ridges in the mucous membrane that help facilitate the movement of food backwards towards the larynx. This partition is continued deeper into the mouth by a fleshy extension called the soft palate.
Function
The hard palate is important for feeding and speech. Mammals with a defective hard palate may die shortly after birth due to inability to suckle (see Cleft palate below). It is also involved in mastication in many species. The interaction between the tongue and the hard palate is essential in the formation of certain speech sounds, notably palatal consonants such as /j/ and /ɟ/.
Clinical significance
Cleft palate
In the birth defect called cleft palate, the left and right portions of this plate are not joined, forming a gap between the mouth and nasal passage (a related defect affecting the face is cleft lip).
While cleft palate has a severe impact upon the ability to nurse and speak, it is now successfully treated through reconstructive surgical procedures at an early age, where such procedures are available.
Palatal abscesses
The proximity of the dento-alveolar process explains the forming of palatal abscesses and the palatal mucosa and submucosa with its numerous glands and the squamous keratinized epithelium is in correlation with the rich tumoral pathology.[1]
Additional images
-

Mouth
-
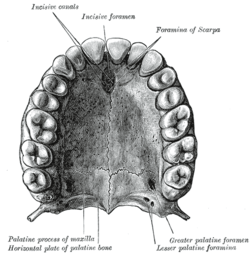
The bony palate and alveolar arch.
-

Base of skull. Inferior surface.
-

Sagittal section of skull.
-
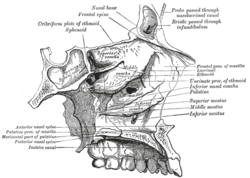
Roof, floor, and lateral wall of left nasal cavity.
-
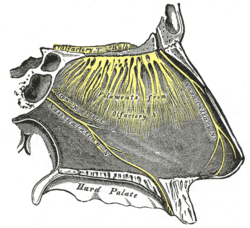
Nerves of septum of nose. Right side.
-
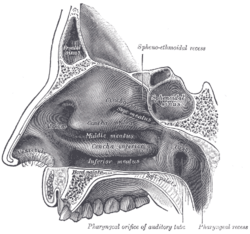
Lateral wall of nasal cavity.
-

Coronal section of nasal cavities.
-

Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx.
See also
References
- ↑ Roman, Alexandru Gabriel; Mițariu, Mihaela Cernușcă; Mițariu, Mihai (June 2012). "Palatul dur — La granița dintre patologia tumorală și cea infecțioasă" [Palate – the border between tumor pathology and the infectious]. Revista de chirurgie oro-maxilo-facială și implantologie (in Romanian). 3 (2): 14–7.