Pays d'états
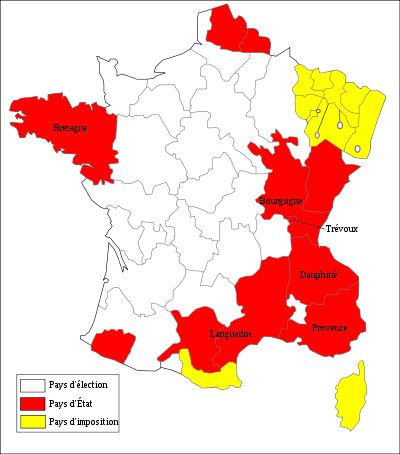
In red, the pays d'états in 1789
Under the Ancien Régime, a pays d'états (French pronunciation: [pei deta]) was a type of généralité, or fiscal and financial region where, in contrast to the pays d'election, an estates provincial or representative assembly of the three orders had retained its traditional role of negotiating the raising of taxes with the royal commissaires or intendants, dividing the tax burden by diocese and parish, and controlling tax collection. The estates also held onto part of the funds thus raised to repair and develop the roads in its province.
According to Roland Mousnier[1] and Bernard Barbiche[2] the pays d'états were:
- Alsace. Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Anjou. Estates suppressed - 15th century
- Artois. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Auvergne. Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Basse-Navarre. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Béarn. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Berry. Estates suppressed - 16th century
- Bigorre. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Bourgogne (Burgundy). Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Bresse. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Bretagne (Brittany). Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Bugey. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Cambrésis. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Charolais. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Corse (Corsica). Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Dauphiné. Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Flandre (Flanders). Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Foix. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Franche-Comté. Estates suppressed - 18th century
- Gévaudan. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Hainaut (Hainault). Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Labourd. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Languedoc. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Limousin. Estates suppressed - 15th century
- Mâconnais. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Maine. Estates suppressed - 16th century
- Marche. Estates suppressed - 15th century
- Marsan. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Nébouzan. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Normandie (Normandy). Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Orléanais. Estates suppressed - 16th century
- Périgord. Estates suppressed - 16th century
- Provence. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Quatre-Vallées. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Quercy. Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Rouergue. Estates suppressed - 17th century
- Soule. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Touraine. Estates suppressed - 16th century
- Velay. Estates suppressed - 1789.
- Vivarais. Estates suppressed - 1789.
Notes and references
See also
- Subdivisions of France under the Ancien Régime
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.