Seipp's day gecko
| Seipp‘s day gecko | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Lacertilia |
| Family: | Gekkonidae |
| Subfamily: | Gekkoninae |
| Genus: | Phelsuma |
| Species: | P. seippi |
| Binomial name | |
| Phelsuma seippi Meier, 1987 | |
 | |
Seipp's day gecko (Phelsuma seippi Meier, 1987) is a diurnal species of geckos. It lives in north Madagascar and typically inhabits rainforests and dwells on trees. Seipp's day gecko feeds on insects and nectar.
Description
This lizard belongs to the medium-sized day geckos. It can reach a total length of about 14 cm. The body colour of this slender and long-snouted gecko is green or yellowish green. There are several small red or rust-coloured spots on the back which may form dorsal striping. A rust coloured eye stripe extends from the nostril to above the ear opening. A red v-shaped marking may be present on the head. Typical for this species are several v-shaped stripes on the throat. The ventral side is light pink.
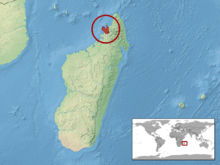
Distribution
This species inhabits northwest Madagascar. It can also be found on the islands Nosy Bé and Nosy Komba.
Habitat
Phelsuma seippi is restricted to the native rainforests and avoids bright sun light. It live on trees both in the forest and along its edges.
Diet
These day geckos feed on various insects and other invertebrates. They also like to lick soft, sweet fruit, pollen and nectar.
Behaviour
This Phelsuma species is often found in pairs on a tree. Juveniles mainly inhabit surrounding low shrubs.
Reproduction
The females lay a pair of eggs and hide them on the ground under foliage or wood or they may lay their eggs on trees under loose bark. At a temperature of 28 °C, the young will hatch after approximately 45–50 days. The juveniles measure 40 mm.
Care and maintenance in captivity
These animals should be housed in pairs in a well planted terrarium. The temperature should be between 25 and 28 °C. The humidity should be maintained between 75 and 100%. In captivity, these animals can be fed with crickets, wax moth larvae, fruit flies, mealworms and houseflies.
References
- ↑ Glaw, F.; Rabibisoa, N.; Rakotondrazafy, N.A. & Ratsoavina, F. (2011). "Phelsuma seippi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.1. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- Henkel, F.-W. and W. Schmidt (1995) Amphibien und Reptilien Madagaskars, der Maskarenen, Seychellen und Komoren. Ulmer Stuttgart. ISBN 3-8001-7323-9
- McKeown, Sean (1993) The general care and maintenance of day geckos. Advanced Vivarium Systems, Lakeside CA.