Pine Barrens tree frog
| Pine Barrens tree frog | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Hylidae |
| Genus: | Hyla |
| Species: | H. andersonii |
| Binomial name | |
| Hyla andersonii Baird, 1854 | |
The Pine Barrens tree frog[1] (Hyla andersonii) is a species of New World tree frog. It is becoming rare due to habitat loss.
Physical characteristics
Hyla andersonii, only about 1–3 inches (25–76 mm) long, is one of the smaller species of tree frogs. Members of the species are predominantly green, with wide, dark stripes. They often have spotted, orange-gold markings on the hidden surfaces of their legs and tend to have large toe pads.
The key to distinguishing the Pine Barrens tree frog from the similar-appearing American green tree frog (H. cinerea) is the white-bordered lavender stripe on each side of the body in the Pine Barrens tree frog. H. cinerea has only a white stripe in this location.
Habitat
H. andersonii is most commonly found in brushy areas, often near peat bogs or shallow ponds. They usually inhabit areas carpeted with thick moss. Adults are terrestrial, but tend to reside near water sources. Unlike most frogs, they are tolerant of low pH levels, and often lay eggs in shallow, acidic ponds. The ideal pH level for H. andersonii eggs is between 3.8 and 5.9.
Distribution
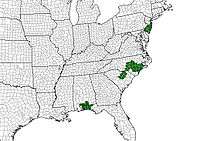
Due to the limited extent of suitable habitats, Hyla andersonii is currently distributed in three disjunct areas in the eastern United States: the New Jersey Pine Barrens; the Sandhills of North and South Carolina; and the Florida panhandle and southern Alabama. Although one specimen of H. andersonii is known from Georgia, a population is not known to currently exist there.[2]
Hyla andersonii is the state frog of North Carolina.[3]
Conservation status
Hyla andersonii was listed as endangered by the US Fish and Wildlife Service between 1977 and 1983, when additional populations were found in Florida.[4] The IUCN has classified it as Near Threatened as of 1996.[5]
References
- ↑ Hyla andersonii, Amphibian Species of the World 5.6
- 1 2 Hammerson (2004). "Hyla andersonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2006. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 5 May 2006. Database entry includes a range map and justification for why this species is near threatened. RangeMap:
- ↑ Horton, Emily. "Pine Barren Tree Frog". NCpedia. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ↑ "Pine Barrens treefrog (Hyla andersonii)". Environmental Conservation Online System. US Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ↑ Hammerson, Geoffrey. "Hyla Andersonii". IUCN Redlist. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hyla andersonii. |
- Animal Diversity Web - Hyla andersonii (Pine Barrens tree frog)
- Pinelands Preservation Alliance - Pine Barrens tree frog photos