Pit (botany)
Pits are parts of plant cell walls which allow the exchange of fluids. In the case of pressure changes in the cell lumen pit aspiration can occur.
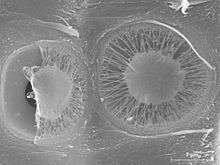
Bordered pits (Picea abies)
Types
- bordered pits: between tracheids or vessel elements
- half-bordered pits: between parenchyma cells and tracheids or vessel elements
- simple pits: between parenchyma cells
See also
The cell wall is not totally complete around the cell. It is interrupted by narrow pores carrying fine strands of cytoplasm, which interlink the contents of the cells. They are called plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma). They form a protoplasmic continuum called symplast which consists of a canal, lined by plasma membrane. It has a simple or branched tubule known as desmotubule. The desmotubule is an extension of endoplasmic reticulum. Plasmodesmata serve as a passage for many substances to pass through. It is also believed that they have a role in the relay of stimuli.
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wood anatomy. |
- Andreas Bresinsky, Christian Körner, Joachim W. Kadereit, Gunther Neuhaus, Uwe Sonnewald: Strasburger – Lehrbuch der Botanik. Begründet von E. Strasburger. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2008 (36. Aufl.) ISBN 978-3-8274-1455-7
- Dietger Grosser: Die Hölzer Mitteleuropas – Ein mikrophotographischer Holzatlas, Springer Verlag, 1977. ISBN 3-540-08096-1
- Rudi Wagenführ: Holzatlas, 6. neu bearb. und erw. Aufl., Fachbuchverlag Leipzig im Carl Hanser Verlag, München, 2007. ISBN 978-3-446-40649-0
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.