Pljevlja
| Pljevlja Пљевља / Pljevlja | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
| Municipality of Pljevlja | |||
| |||
 Pljevlja Location of Pljevlja | |||
| Coordinates: 43°22′N 19°22′E / 43.36°N 19.36°E | |||
| Settlements | 153 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Mirko Đačić (DPS) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 1,346 km2 (520 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2011 census) | |||
| • Total | 19,489 | ||
| • Density | 27/km2 (70/sq mi) | ||
| • Municipality | 30,786 | ||
| Postal code | 84210 | ||
| Area code | +382 89 | ||
| ISO 3166-2 code | ME-14 | ||
| Car plates | PV | ||
| Website | http://www.pljevlja.me/ | ||
Pljevlja (Montenegrin Cyrillic: Пљевља, pronounced [pʎêʋʎa]) is a town and the center of Pljevlja Municipality located in the northern part of Montenegro. The city lies at an altitude of 770 m (2,530 ft). In the Middle Ages, Pljevlja had been a crossroad of the important commercial roads and cultural streams, with important roads connecting the littoral with the Balkan interior. In 2011, the municipality of Pljevlja had a population of 30,786, while the city itself had a population of about 19,489. The municipality borders those of Žabljak, Bijelo Polje and Mojkovac in Montenegro, as well as the republics of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. With a total area of 1,346 km2 (520 sq mi), it is the third largest municipality in Montenegro.
Geography
The city lies at an altitude of 770 m (2,530 ft). The municipality borders those of Žabljak, Bijelo Polje and Mojkovac in Montenegro, as well as the republics of Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. With a total area of 1,346 km2 (520 sq mi), it is the third largest municipality in Montenegro.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
First traces of human life in the region dates to 50,000 and 40,000 BC, while reliable findings show that the Ćehotina River valley was inhabited at latest around 30,000 BC. The oldest traces of human presence in the town area, a flint tool, had been found in the cave under Gospić Peak. The traces of settlements in the later stages of the Stone Age were found in two large archaeological sites called Mališina Stijena and Medena Stijena (around 10,000 stone tools and arms), dating to 12,000–8,000 BC. During the Bronze and Iron Age, since around 2,000 BC up until the Roman conquests, a large number of necropolises with tumuli, as well as fortified settlements rose along the Ćehotina valley, especially around villages of Mataruge, Kakmuža, Hoćevina and Gotovuša. The tumuli found in Ljutići, Gotovuša and Borovica have been archeologically researched.
Illyrian and Roman era
The first attested tribe in the region was called the Pirustae, an Illyrian Pannonian tribe, existed until the Roman invasion in the 1st century AD. The Romans had a town built on the ruins of their town, and it was called Municipium S, located in the Komini neighbourhood. Within the borders of present-day Montenegro, Municipium S is believed to have been the second largest town after Doclea. It was a large trade– and religious center of the Roman province of Dalmatia. A large number of valuable objects including jewellery pieces, glass vases and pottery have been found. The most valuable object is the diatreta or cage cup, a glass vase trimmed with blue glass threads which is considered to be priceless.
Middle Ages
In the Middle Ages, the region of Pljevlja was also a part of nucleus of the Serbian state under the Nemanjić dynasty, until the end of the rule of the Emperor Stefan Dušan. After his death, Pljevlja was under the rule of Serbian autonomous rulers Vojislav Vojinović and Nikola Altomanović. After the defeat of Altomanović 1373 by the joint forces of Serbian lord Lazar Hrebeljanović and Bosnian Ban Tvrtko I, the region of Pljevlja became part of the eastern section of the Kingdom of Bosnia, subsequently part of Sandalj Hranić's province and later the Duchy of Saint Sava.
Ottoman era
In 1465, the Ottoman Empire conquered Pljevlja. During the Ottoman offensive, the fortress of Kukanj, the residence of Stjepan Vukčić Kosača, was destroyed. Fearing an onslaught, many merchants, almost all feudal land owners and wealthier population fled from Pljevlja, seeking refuge in the Republic of Venice, Republic of Ragusa, or further north into the Kingdom of Hungary or Austrian Empire. In Turkish, the town was known as Taşlıca ("rocky").
In the Ottoman defter (census book) of 1475/76, the majority of local inhabitants were Eastern Orthodox Christian, numbering some 101 households. The town was expanded into a kasaba, a larger Ottoman city without a fortress. The 15th and 16th centuries were a period of much construction in the city: in 1465 the Holy Trinity Monastery was founded, in 1569 Husein-paša's mosque was built and during the 16th century the city got a sewage system. When the center of Sanjak of Herzegovina was moved to Pljevlja from Foča in 1572, the city started to change rapidly: urban housing increased: 72 houses in 1468, 150 in 1516, 300 in 1570; in the 17th century Pljevlja had around 650 houses in the city center and over 400 in the surrounding area. The first Muslim religious school (madrasa), was built in the 17th century; water-works were constructed in the 18th century. The Russian consul visited Pljevlja in the 19th century and wrote that Pljevlja was a very beautiful oriental city with gardens and fountains, mosques and churches and over 800 houses in the city center (7,000 citizens) which made Pljevlja the second largest city in the Herzegovina Sanjak besides Mostar. After two big fires that burned the city center to the ground, the city's economy was ruined. That was the reason for displacing the center of Herzegovina to Mostar in 1833. After 1833 the city stagnated in both an economic and cultural sense.
Modern history
In 1875, after a failed uprising, mass emigration took place around Pljevlja in the direction of Užice, Valjevo and the Drina river basin.[1]
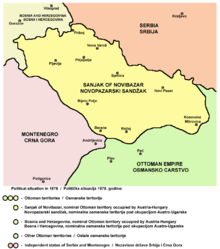
In 1879, according to special Convention between Austria-Hungary and Ottoman Empire, western parts of the Sanjak of Novi Pazar were put under dual jurisdiction. Administration remained in Turkish hands, with Austro-Hungarian military presence in the cities of Pljevlja, Prijepolje and Priboj. Some 5,000 Austro-Hungarian soldiers and other personal with their wives and children came to Pljevlja. That was a beginning of a new era for the city because Austrians transformed Pljevlja into a modern western city with hotels, bookstores, theater and cultural events. The first modern drug store was opened in 1879, a photo store in 1892, hospital in 1880 and beer factory in 1889 (Šećerović beer factory). The Pljevlja Gymnasium was established in 1901. Austrians withdrew from the town in 1908 and it was restored to full Ottoman control.
Since 1880, Pljevlja was the center of the newly formed Sanjak of Pljevlja (in Turkish: Taşlıca Sancağı) which existed until 1912 when the city was captured from the Ottoman Empire during the First Balkan War of 1912–1913. Serbian and Montenegrin armies captured Pljevlja on the same day. In 1913 Pljevlja became a part of Kingdom of Montenegro, and after World War I, in 1918, it became a part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, which Montenegro joined.
From 1929 to 1941, Pljevlja was part of the Zeta Banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. At the beginning of the Second World War Pljevlja, like the rest of Sandžak, was occupied by NDH Ustaše forces. Notable Muslims from Pljevlja, Bijelo Polje and Prijepolje wrote to Pavelić and expressed their loyalty to the Independent State of Croatia allegedly in the name of all Muslims of Sandjak.[2] By September 1941 Ustaše left Sandžak which was occupied by Italian forces within Italian governorate of Montenegro. The Battle of Pljevlja, fought on 1 December 1941 between attacking Partisans and the Italian Pljevlja garrison, was the biggest battle of the Uprising in Montenegro. In April 1942 Italians established a battalion of Sandžak Muslim militia in Metaljka, near Čajniče, composed of about 500 Muslims from villages around Pljevlja and Čajniče. A little later a command post of Sandžak Muslim militia was established in Bukovica, near Pljevlja. Since the end of 1943 Pljevlja belonged to the German occupied territory of Montenegro and after the war to Yugoslav Socialist Republic of Montenegro.
In 2008, some members of the municipal assembly of Pljevlja threatened a secession from Montenegro following the Montenegrin recognition of Kosovo.[3]
Culture
Culture and education are all present throughout history of Pljevlja and its region. The first educational life,churches and monasteries,as well as in the mosques some time later. The Holy Trinity Monastery (Pljevlja) is the richest treasury of cultural and spiritual life of the Orthodox Serbs from the Middle Ages to the present times. The school in the Holy Trinity Monastery has been working continuously since the 16th century. In 1823, a primary school in Pljevlja started working. The school in Dovolja monastery worked since the 18th century. The very important date in the history of education in Pljevlja is the opening of the Pljevaljska Gymnasium in 1901. The Heritage Museum Pljevlja is a treasure trove of rich historical and cultural heritage of the city and region.
Main features of the town include:
- Heritage museum Pljevlja
- Pljevlja Gymnasium
- Holy Trinity Monastery
- Husein-paša's Mosque and Sahat–kula
- Municipium S, archaeological site
- Stećci (monoliths)
- Saint Petka’s Church
- Hadži Zekerijah's Mosque
- Rizvan Čauš Mosque
- Church of St. Elijah, Pljevlja|Church of St. Elijah
- Hadži Alija's Mosque
- Šećerović's House
- Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul

- Husein-paša's Mosque and the Sahat-kula (Clock Tower)
- Husein-paša's Mosque with the tallest minaret (42m) in the Balkans
 Old Čaršija in Pljevlja
Old Čaršija in Pljevlja
Economy

Pljevlja is also one of the main economic engines of Montenegro. The only thermal power plant in Montenegro, which provides 45% of the electric power supply for Montenegro, is situated outside Pljevlja as well as the biggest coal mine with 100% of the coal production in Montenegro. Zinc and lead can be found in Šuplja stijena mine. The richest municipality with forest in Montenegro is Pljevlja and its lumber industry. Agriculture is widespread in the whole municipality. Pljevaljski sir (Pljevlja's cheese, from Пљеваљски сир) is considered a delicacy. There is big potential for ecological and winter tourism.
Demographics
Pljevlja is the administrative center of Pljevlja municipality, which has a population of 35,806. The town of Pljevlja itself has 19,136 citizens, and is the only town in the municipality with a population of over 1,000. The municipality has a majority of Serbs.
Population of Pljevlja (Town):
- March 3, 1981 - 16,792
- March 3, 1991 - 20,887
- November 1, 2003 – 21,337
- April 15, 2011 – 19,489
Ethnicity in 2011
| Ethnicity | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Serbs | 17,569 | 57.07% |
| Montenegrins | 7,494 | 24.34% |
| Bosniaks | 2,128 | 6.91% |
| Muslims by nationality | 1,739 | 5.65% |
| Albanians | 17 | 0.06% |
| Croats | 16 | 0.05% |
| Other | 115 | 0.42% |
| not declared | 1448 | 4.62% |
| no data | 205 | 0.55% |
| Total | 30,786 | 100% |
Transport
The main transit road connections are:
- to Belgrade in Serbia
- to Podgorica and the rest of Montenegro across a bridge over Tara river
- to Sarajevo in Bosnia and Herzegovina
References
- ↑ Jovan Cvijić, Balkansko poluostrvo i južnoslovenske zemlje, Belgrade: Zavod za izdavanje udžbenika, 1966, pp. 151-152.
- ↑ Knežević, Danilo (1969). Prilog u krvi: Pljevlja 1941-1945. Opštinski odbor SUBNOR-a.
- ↑ Скупштина Црне Горе о демонстрацијама (in Serbian). Rts.rs. 2008-10-15. Retrieved 2010-04-28.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pljevlja. |

