Predigerkloster
The Predigerkloster was a monastery of the Dominican Order, established around 1234 and abolished in 1524, in the imperial city of Zürich, Switzerland. Its church, the Predigerkirche, is one of the four main churches in Zürich, and was first built in 1231 as a Romanesque church of the then Dominican monastery. In the first half of the 14th century it was converted, the choir between 1308 and 1350 rebuilt, and a for that time unusually high bell tower built, regarded as the highest Gothic edifice in Zürich.[1]
_-_Innenhof_-_Zentralbibliothek_2011-08-22_15-02-16_ShiftN.jpg)
History
Early years
The city of Zürich supported at that time the popular mendicant orders by attributing them free plots in the suburbs and asked to support the construction of the city wall in return. In the east of the area, the city's fortification was built in the late 11th or 12th century. The first Dominican monks settled, according to the chronicler Heinrich Brennwald, outside of the city walls of medieval Zürich at Stadelhofen in 1230 AD, and in 1231 was first mentioned that in Zurich was a new monastery under construction. In the Schweizerchronik of 1513, Heinrich Brennwald calls for the arrival of the Dominicans in Zurich the year 1230. In two documents from 1231 a Dominican oratorio is mentioned.[2] In 1232 a sale of land to Hugo von Ripelin, then the paddock prior, is mentioned.[3] Initially, against the resistance of the Grossmünster canons, the Dominican's inclusion in Zürich was granted in 1233/1235, because they tirelessly drove the little foxes in the vineyard of the Lord.[4]
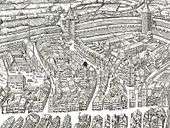
Located at the medieval Neumarkt quarter, the commonly named Predigerkloster was mentioned for the first time in 1234 AD as a monastery of the Dominican Order. The monastery consisted of a Romanesque church in the same place as the today's Predigern church, and the three-winged building complex attached to the north of the church. In 1254 the establishment of a cemetery at Zähringerstrasse was allowed tp the so-called "prayer" (used for Dominican monks, the 'blackfriars') abbey, and repealed in 1843.[5] The monastery was built at the edge of the city on a flat terrace between the now subterranean Wolfbach and the as of today Hirschengraben road. The monastery area was delimited by a wall from the urban environment. Remnants of this wall were found in 1995 on the present Predigerplatz square. The hospital was erected in the west, beyond the Wolfbach stream at the location of today's Spitalgasse, before the Dominicans settled in Zürich. In the decades in which the convent was built, the new fortifications, which is depicted on the Murerplan of 1576, was built at that location. The Neumarkt quarter arose at the same time and was settled increasingly by Beguines. Among other things, the orthogonal structure of the monastery, the town fortifications and the Chorgasse and Predigergasse lane are evidence, and especially the latter is important for this quarter; it leads from Neumarkt in a straight line to the southern portal, which was the main entrance to the church. The northern part of the convent was predominantly used for agricultural purpose.[2]
Influence
The order purchased 28 houses in the 13th and early 14th century, and was in close connection to the city nobility and landed gentry in Zürich and the surrounding area, among them the Bilgeri family (Grimmenturm) and the House of Rapperswil, where they received after their expulsion to 1348 to asylum in Rapperswil. Memorial measurement had to be held until the 14th century at Grossmünster, because thus the most income was achieved. Until the Reformation in Zürich, all income obtained with the funerals had also to be delivered to the Grossmünster abbey.[6]
Because of his great appointment district in the province of the order Teutonia , the convent influenced almost throughout the German-speaking Switzerland. He was in charge of the pastoral care of the women monasteries Oetebach and Winterthur-Töss as well as the urban communities of the women Beguines, who lived nearby the Dominican and Franciscan mendicant in separate quarters outside the convents. After the founding of the Dominican convents in Bern, Chur and Zofingen, remained the pastoral care of the canton of Zürich, the counties of Baden and Uznach, the cantons Obwalden, Nidwalden and Zug as well as parts of Glarus, Uri and Gaster, and the border areas around Schwarzwald and Klettgau.[6] In 1259 Count Rudolf IV von Rapperswil, Countess Elisabeth's father, donated certain duties and lands "in den Widen" for the construction of the Dominikanerinnenkloster Maria Zuflucht. Initially, the Dominican nuns were supported by the Dominican convent in Zürich, because its close relationship to the House of Rapperswil. After the founding of the monastery, the Dominican monks in Chur took over the pastoral assistance of the monastic community in Weesen.[7]
Decline

The extremely ambitious dimensions of the Domnican's Baroque church were designed the early 14th century. But already in the 1330s, the construction was set, and remained unfinished for years. The second phase of the plant building ended in a much more honest construction, and it was saved much substance of the Romansque building, for example, almost the entire Romanesque transept remained.[2] Historical events are the explanation for that change. The revolution of 1336 that Rudolf Brun and his entourage brought to power,[8] was followed by a period of economic uncertainty reaching its peak with the plague of 1348/49, the persecution and killing of the Jewish citizens of the so-called Synagogengasse in 1349,[9] as well as the "Zürich night of murder" (Mordnacht) by 1350, a failed counter coup of Brun's opposition under the son of Johann I (Habsburg-Laufenburg), Johann II. Unlike the Franciscan and the Augustinian orders, the Preachers in Zürich pleaded to the Pope, another opponent of the political situation in Zürich, and therefore, the convent was forced to leave the city for several years. His exile led to Winterthur and Kaiserstuhl and finally to Rapperswil, those counts were the most prominent opponents of Brun's regime. This development represents the beginning of the general decline of the Zürich Dominican convent.[2]
Within the city, as the other "mendicant" orders, the Predigern have been reduced to the function of area pastors.[10][11] The convent was distablished on 3 December 1524, worship in the church was discontinued, and the buildings and income of the monastery were assigned to the adjoining Heilig-Geist-Spital.[1][8][2]
Buildings of the convent


The former convent buildings were also used after the abolition of the monastery by the hospital. After the construction of the new hospital in 1842, they became the so-called "Versorgungsanstalt" where chronically ill, old, incurable mental patients were housed; the contemporaries complained unsustainable states that were solved in 1870, when the Burghölzli sanatory was built.[8] The convent buildings were sold in 1873 to the city of Zurich, which used it to house destitute citizens. When the old convent building burned down on 25 June 1887, whose ruins were dismantled in the same year, and the open space was used for celebrations.[1][2]
On 28 June 1914, the citizens of Zürich agreed to the establishment of the Central Library (German: Zentralbibliothek), that was completed according to the plans by Hermann Fietz in 1917.[2] So the cantonal library was outsourced, however in 1919 moved back and again moved, to make room for the as of today Staatsarchiv Zürich; therefore since 1982, the premise is used for the library, in particular for the so-called Musikabteilung.[8]
See also
Literature
- Dölf Wild, Urs Jäggin, Felix Wyss: Die Zürcher Predigerkirche – Wichtige Etappen der Baugeschichte. Auf dem Murerplan beschönigt? – Untersuchungen an der Westfassade der Predigerkirche. Amt für Städtebau der Stadt Zürich, Zürich 2006.[2]
- Dölf Wild: Stadtmauern. Ein neues Bild der Stadtbefestigungen Zürichs (= Stadtgeschichte und Städtebau in Zürich. Schriften zu Archäologie, Denkmalpflege und Stadtplanung. 5). Schrift zur Ausstellung im Haus zum Haus zum Rech, Zürich, 6. Februar bis 30. April 2004. Amt für Städtebau, Baugeschichtliches Archiv, Zürich 2004, ISBN 3-905384-05-1.
- Dölf Wild: Das Predigerkloster in Zürich. Ein Beitrag zur Architektur der Bettelorden im 13. Jahrhundert. Monographien der Kantonsarchäologie Zürich 32, Hochbaudepartement der Stadt Zürich, Amt für Städtebau, Archäologie, Zürich 1999, ISBN 978-3-905647-89-1.[12]
- Walter Baumann: Zürichs Kirchen, Klöster und Kapellen bis zur Reformation. Verlag Neue Zürcher Zeitung (NZZ), Zürich 1994, ISBN 978-3-8582-3508-4.
- Martina Wehrli-Johns: Geschichte des Zürcher Predigerkonvents (1230–1524). Mendikantentum zwischen Kirche, Adel und Stadt. Hans Rohr, Zürich 1980, ISBN 978-3-8586-5061-0.
References
- 1 2 3 "Geschichte Kirche" (in German). Predigerkirche Zürich. Retrieved 2014-12-19.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Dölf Wild, Urs Jäggin, Felix Wyss (2006-12-31). "Die Zürcher Predigerkirche – Wichtige Etappen der Baugeschichte. Auf dem Murerplan beschönigt? – Untersuchungen an der Westfassade der Predigerkirche." (in German). Amt für Städtebau der Stadt Zürich. Retrieved 2014-12-27.
- ↑ Urs Järmann (February 2013). "Projekt # 13303 Restaurierung Predigerchor, Zürich" (PDF) (in German). Henauer Gugler. Retrieved 2014-12-25.
- ↑ Leonhard Meister (1786). "Geschichte von Zürich, von ihrem Ursprung bis zum Ende des XVI. Jhd." (in German). Google books, Orell Füssli Zürich. Retrieved 2014-12-26.
- ↑ "Der ehemalige "Prediger"- Friedhof" (in German). Gang dur Alt-Zürich. Retrieved 2014-12-19.
- 1 2 Martina Wehrli-Johns: Geschichte des Zürcher Predigerkonvents (1230–1524). Mendikantentum zwischen Kirche, Adel und Stadt. Hans Rohr, Zürich 1980, ISBN 978-3-8586-5061-0.
- ↑ Alfred Ehrensperger. "Der Gottesdienst im Appenzellerland und Sarganserland-Werdenberg: vor, während und nach der Reformation bis ca. 1700" (in German). Theologischer Verlag Zürich. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- 1 2 3 4 Meinrad Sutter, Agenes Hohl Otto Sigg, Thomas Weibel, Reto Weiss, Josef Zweifel, Werner Reich (photos). "Kleine Zürcher Verfassungsgeschichte 1218–2000" (PDF) (in German). Staatsarchiv Zürich. Retrieved 2014-12-29.
- ↑ "Auf den Spuren der mittelalterlichen Synagoge von Zürich: Archäologische Untersuchungen im Haus Froschaugasse 4." (in German). Stadt Zürich. 2002-08-08. Retrieved 2014-12-19.
- ↑ "Zürcher Kantorei zu Predigern" (in German). kantorei.ch. Retrieved 2014-12-25.
- ↑ "Predigern" (in German). kirche-zh.ch. Retrieved 2014-12-25.
- ↑ "Das Predigerkloster in Zürich" (in German). Stadt Zürich, Amt für Städtebau. January 1999. Retrieved 2014-12-29.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Predigerkloster (Zürich). |
Coordinates: 47°22′26″N 8°32′43″E / 47.3738°N 8.5454°E