List of Prime Ministers of Sri Lanka
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Sri Lanka |
|
|
Political parties |
|
|
|
|
Foreign policy |
|
Related issues
|
There have been fourteen Prime Ministers of Sri Lanka since the creation of the position in 1947, prior to the formation of the Dominion of Ceylon. The Prime Minister of Ceylon was the head of the government until 1978. In 1972, the country was named as the Free, Sovereign and Independent Republic of Sri Lanka and the position was known as the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka from then onwards. The Prime Minister also held the unified Ministry of External Affairs and Defence until 1977, when J.R. Jayewardene's government adapted two separate ministries, forming the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
In 1978, Prime Minister J.R. Jayewardene introduced new constitutional changes. The position of the Executive President was introduced, resulting in the powers of the Prime Minister being reduced. The President became the head of state and head of government,[1] and the Prime Minister became a nominal position.[2]
Under the current constitution of Sri Lanka, the Prime Minister is the leader of the Cabinet business and also functions as a deputy to the President. In the event a president dies in office, the Prime Minister becomes the acting president until the Parliament convens to elect a successor or new elections can be held to elect a new president. This was the case in 1993, when President Ranasinghe Premadasa was assassinated and Prime Minister Dingiri Banda Wijetunge took office as President.[3]
On 28 April 2015, the Parliament approved the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka which gives the power of the Government to the Prime Minister, while the President remains the head of state, head of the cabinet, and Commander-in-chief.[4]
Of the fourteen Prime Ministers who have held office since the introduction of the position in 1947, three have held office thrice, and one have held office twice. Five Prime Ministers have gone on to become President of the country. The current Prime Minister of Sri Lanka is Ranil Wickremesinghe, since 9 January 2015.[5]
List of Prime Ministers
- Parties
United National Party Sri Lanka Freedom Party
| № | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) Constituency/Title |
Term of office — Electoral mandates |
Other ministerial offices held while Prime Minister |
Political party of PM (Alliance) |
Government | Refs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | .jpg) |
DS Senanayake දොන් ස්ටීවන් සේනානායක டான் ஸ்டீபன் சேனாநாயக்க (1883–1952) Mirigama |
24 September 1947 |
22 March 1952 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | United National Party | D. S. Senanayake | 3rd | [6] | |
| 1947 | ||||||||||
| The first Prime Minister of Ceylon. The country gained independence from Great Britain during his term of office.[7] | ||||||||||
| 2 | .jpg) |
Dudley Senanayake ඩඩ්ලි සේනානායක டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா (1911–1973) Dedigama |
26 March 1952 |
12 October 1953 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence Minister of Agriculture & Lands & Minister of Health & Local Government |
United National Party | Dudley Senanayake I | 3rd 4th |
[6] | |
| 1952 | ||||||||||
| Appointed as Prime Minister following the death of his father, D. S. Senanayake. His party won at the general elections held in June 1952, and he continued in the office without a re-appointment. Dudley Senanayake resigned in 1953.[8] | ||||||||||
| 3 | .jpg) |
Sir John Kotelawala ජෝන් කොතලාවල ஜோன் கொத்தலாவல CH, KBE, KStJ, CLI (1897–1980) Dodangaslanda |
12 October 1953 |
12 April 1956 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence & Minister of Minister of Transport & Works |
United National Party | Kotelawala | 4th | [6] | |
| — | ||||||||||
| Sri Lanka joined the United Nations under the leadership of Kotelawala.[9] | ||||||||||
| 4 | .jpg) |
S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike සොලමන් බන්ඩාරනායක சாலமன் பண்டாரநாயக்கே (1899–1959) Attanagalla |
12 April 1956 |
26 September 1959 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | Sri Lanka Freedom Party | S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike | 5th | [6] | |
| 1956 | ||||||||||
| Bandaranaike changed the official language of the country from English to Sinhalese. He was assassinated before his term of office ended.[10] | ||||||||||
| 5 |  |
Wijeyananda Dahanayake විජයානන්ද දහනායක விஜயானந்த தகநாயக்கா (1902–1997) Galle |
26 September 1959 |
20 March 1960 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | Sri Lanka Freedom Party | Dahanayake | 5th | [6] | |
| — | ||||||||||
| Dahanayake was appointed following the assassination of Bandaranaike. However, following disagreements with the members of his government and party, he was forced to dissolve the parliament.[11] | ||||||||||
| (2) | .jpg) |
Dudley Senanayake ඩඩ්ලි සේනානායක டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா (1911–1973) Dedigama |
21 March 1960 |
21 July 1960 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | United National Party | Dudley Senanayake II | 6th | [6] | |
| March 1960 | ||||||||||
| Senanayake's government was defeated after one month. Senanayake continued to serve as Prime Minister until 21 July 1960. | ||||||||||
| 6 | _(Hon.Sirimavo_Bandaranaike_with_Hon.Lalith_Athulathmudali_Crop).jpg) |
Sirimavo Bandaranayake සිරිමාවො රත්වත්තේ ඩයස් බණ්ඩාරනායක சிறிமா ரத்வத்தே டயஸ் பண்டாரநாயக்கே (1916–2000) |
21 July 1960 |
25 March 1965 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | Sri Lanka Freedom Party | Sirimavo Bandaranaike I | 7th | [6] | |
| July 1960 | ||||||||||
| Sirimavo Bandaranaike was the world's first female prime minister.[12] She was not a member of Parliament at the time of appointment, and was appointed to the Senate on 2 August 1960. | ||||||||||
| (2) | .jpg) |
Dudley Senanayake ඩඩ්ලි සේනානායක டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா (1911–1973) Dedigama |
25 March 1965 |
29 May 1970 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence | United National Party | Dudley Senanayake III | 8th | [6] | |
| 1965 | ||||||||||
| Senanayake was elected Prime Minister for the third time, when his party formed a government with the help of six other parties, after an election which did not give a clear majority to any party. The agriculture sector was given high priority during his term of office.[13] | ||||||||||
| (6) | _(Hon.Sirimavo_Bandaranaike_with_Hon.Lalith_Athulathmudali_Crop).jpg) |
Sirimavo Bandaranayake සිරිමාවො රත්වත්තේ ඩයස් බණ්ඩාරනායක சிறிமா ரத்வத்தே டயஸ் பண்டாரநாயக்கே (1916–2000) Attanagalla |
29 May 1970 |
22 May 1972 |
Minister of External Affairs and Defence & Minister of Planning & Employment |
Sri Lanka Freedom Party | Sirimavo Bandaranaike II | 9th | [6] | |
| 22 May 1972 |
23 July 1977 |
10th | ||||||||
| 1970 | ||||||||||
| Sirimavo Bandaranaike declared the country a republic, and its name was changed from Ceylon to Sri Lanka.[12] Nationalized many companies in the plantation sector and imposed restrictions on several imports. This led to the downfall of the country's economy, and she was defeated in the general elections of 1977, with allegations of corruption which later led to her expulsion from Parliament.[12] | ||||||||||
| 7 | .jpg) |
Junius Richard Jayewardene ජුනියස් රිචඩ් ජයවර්ධන ஜூனியஸ் ரிச்சட் ஜயவர்தனா (1906–1996) Colombo West |
23 July 1977 |
4 February 1978 |
Minister of Defence Minister of Planning & Economic Affairs & Minister of Plan Implementation |
United National Party | Jayewardene | 11th | [6] | |
| 1977 | ||||||||||
| Introduced the Executive Presidency in 1978, and assumed the position of President of Sri Lanka.[14] | ||||||||||
| 8 |  |
Ranasinghe Premadasa රණසිංහ ප්රේමදාස ரணசிங்க பிரேமதாசா (1924–1993) Colombo Central |
6 February 1978 |
2 January 1989 |
Minister of Local Government, Housing & Construction | United National Party | Jayewardene | 11th 12th |
[6] | |
| — | ||||||||||
| Was the first Prime Minister to be appointed after the constitutional changes of 1978, with powers of the position reduced significantly.[15] | ||||||||||
| 9 |  |
Dingiri Banda Wijetunga ඩිංගිරි බණ්ඩා විජේතුංග டிங்கிரி பண்ட விஜேதுங்க (1916–2008) Kandy |
6 March 1989 |
7 May 1993 |
Minister of Finance & Minister of Labour & Vocational Training |
United National Party | Premadasa | 13th | [6] | |
| 1989 | ||||||||||
| Was appointed in a surprise move by the then President, Ranasinghe Premadasa. Wijetunge himself reacted in surprise at the appointment.[3] He resigned from the post on 28 March 1990, but was reappointed two days later, on 30 March 1990. | ||||||||||
| 10 |  |
Ranil Wickremesinghe රනිල් වික්රමසිංහ ரணில் விக்ரமசிங்க (1949–) Gampaha |
7 May 1993 |
19 August 1994 |
United National Party | Wijetunga | 13th | [6] | ||
| — | ||||||||||
| Appointed as the Prime Minister[16] when Wijetunge was appointed as the President of Sri Lanka, following the assassination of the former President, Ranasinghe Premadasa. | ||||||||||
| 11 |  |
Chandrika Kumaratunga චන්ද්රිකා බණ්ඩාරනායක කුමාරතුංග சந்திரிகா பண்டாரநாயக்கே குமாரதுங்கா (1945–) Gampaha |
19 August 1994 |
12 November 1994 |
Sri Lanka Freedom Party (People's Alliance) |
Wijetunga | 14th | [6] | ||
| 1994 | ||||||||||
| Served as the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka for a short period, before contesting in the presidential elections in 1994 and being elected as president.[17] | ||||||||||
| (6) | _(Hon.Sirimavo_Bandaranaike_with_Hon.Lalith_Athulathmudali_Crop).jpg) |
Sirimavo Bandaranayake සිරිමාවො රත්වත්තේ ඩයස් බණ්ඩාරනායක சிறிமா ரத்வத்தே டயஸ் பண்டாரநாயக்கே (1916–2000) National List |
14 November 1994 |
9 August 2000 |
Sri Lanka Freedom Party (People's Alliance) |
Kumaratunga | 14th | [6] | ||
| — | ||||||||||
| Sirimavo Bandaranaike was appointed as the Prime Minister when Chandrika Kumaratunga was appointed as the President of Sri Lanka. She resigned in 2000.[12] | ||||||||||
| 12 |  |
Ratnasiri Wickremanayake රත්නසිරි වික්රමනායක ரத்னசிறி விக்கிரமநாயக்க (1933–) Kalutara |
10 August 2000 |
7 December 2001 |
Sri Lanka Freedom Party (People's Alliance) |
Kumaratunga | 14th 15th |
[6] | ||
| 2000 | ||||||||||
| Wickremanayake assumed the office of the Prime Minister following the resignation of Sirimavo Bandaranaike.[2] | ||||||||||
| (10) |  |
Ranil Wickremesinghe රනිල් වික්රමසිංහ ரணில் விக்ரமசிங்க (1949–) Colombo |
9 December 2001 |
6 April 2004 |
United National Party | Kumaratunga | 16th | [6] | ||
| 2001 | ||||||||||
| Wickremesinghe's term of office ended early when the then president Chandrika Kumaratunga dismissed his government and called for a general election in 2004.[18] | ||||||||||
| 13 |  |
Mahinda Rajapaksa මහින්ද රාජපක්ෂ மகிந்த ராசபக்ச (1945–) Hambantota |
6 April 2004 |
19 November 2005 |
Ministry of Highways | Sri Lanka Freedom Party (United People's Freedom Alliance) |
Kumaratunga | 17th | [6] | |
| 2004 | ||||||||||
| Appointed as Prime Minister of the Cabinet that was formed after the elections following the dismissal of Wickremesinghe's government by President Chandrika Kumaratunga. He won the presidential elections in 2005 and assumed the office of the President of Sri Lanka.[19] | ||||||||||
| (12) |  |
Ratnasiri Wickremanayake රත්නසිරි වික්රමනායක ரத்னசிறி விக்கிரமநாயக்க (1933–) National List |
19 November 2005 |
21 April 2010 |
Sri Lanka Freedom Party (United People's Freedom Alliance) |
Rajapaksa | 17th | [6] | ||
| — | ||||||||||
| Appointed as Prime Minister when Rajapaksa assumed the office of the President of Sri Lanka.[2] | ||||||||||
| 14 |  |
D. M. Jayaratne දිසානායක මුදියන්සේලාගේ ජයරත්න திசாநாயக்க முதியன்சேலாகே ஜயரத்ன (1931-) National List |
21 April 2010 |
9 January 2015 |
Minister of Buddhasasana & Religious Affairs | Sri Lanka Freedom Party (United People's Freedom Alliance) |
Rajapaksa | 18th | [6] | |
| 2010 | ||||||||||
| Appointed as Prime Minister after the parliamentary election held in April 2010 was won by the incumbent Freedom Party. | ||||||||||
| (10) |  |
Ranil Wickremesinghe රනිල් වික්රමසිංහ ரணில் விக்ரமசிங்க (1949–) Colombo |
9 January 2015 |
Incumbent | Minister of National Policies and Economic Affairs | United National Party |
Sirisena | 18th | [6] | |
| 2015 | 19th | |||||||||
| Appointed as Prime Minister by President Maithripala Sirisena after winning 2015 presidential election and was re-elected in the 2015 parliamentary election. | ||||||||||
Living former Prime Ministers
| Prime Minister | Term of office | Date of birth |
|---|---|---|
| Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga | 1994–1994 | 29 June 1945 |
| Mahinda Rajapaksa | 2004–2005 | 18 November 1945 |
| Ratnasiri Wickremanayake | 2005–2010 | 5 May 1933 |
| Disanayaka Mudiyanselage Jayaratne | 2010–2015 | 4 June 1931 |
The most recent death of a former Prime Minister was that of Dingiri Banda Wijetunga (1989–1993) on 21 September 2008, aged 92.
Timeline
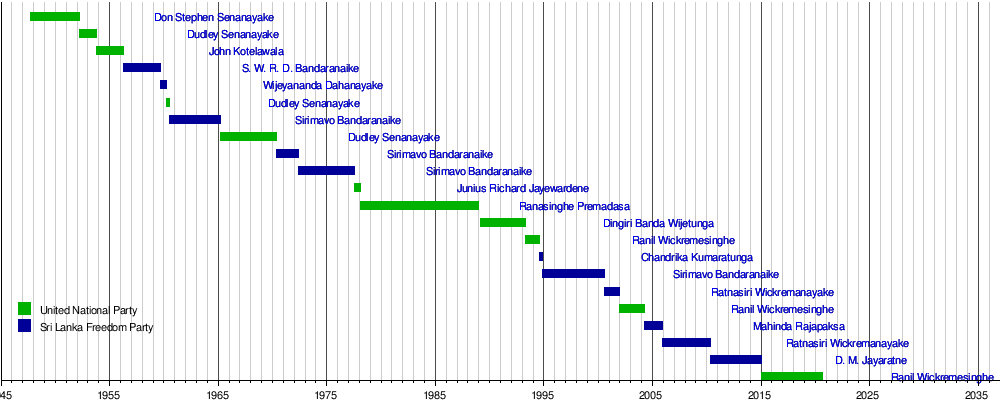
See also
Notes
- The Parliament was known as the "House of Representatives" during the period of 1947–1972
- In 1972, the country was named "Free, Sovereign and Independent Republic of Sri Lanka", and the Parliament was named as the National State Assembly.
- Under the constitutional changes of 1978, the country was renamed as the "Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka", and the Parliament was referred to as "Parliament of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka".
References
- General
- "Former Prime Ministers" (.html). Official Website of the Government of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- "Handbook of Parliament - Prime Ministers" (.jsp). The Parliament of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- "PMs of Sri Lanka" (.htm). Prime Minister's Office. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- Specific
- ↑ V. Jayanth (2003-11-15). "Sri Lanka's executive presidency". The Hindu. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- 1 2 3 V.S. Sambandan (2005-11-22). "Ratnasiri Wickremanayake appointed Sri Lankan Premier". The Hindu. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- 1 2 M.B. Dassanayake (2008-09-22). "Dingiri Banda Wijetunga - the journey to greatness". Daily News. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka: 19A to the Constitution passed in parliament".
- ↑ Wanniarachchi, Lakruwan. "Sri Lanka's new president gets down to mending ties". 10 January 2015. Business Insider AFP. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 "Prime Ministers". Parliament.lk. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "Senanayake, Don Stephen (1884–1952)". The History Channel. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ Buddhika Kurukularatne (2007-06-19). "Dudley – the reluctant Prince". Daily Mirror. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ K. T. Rajasingham (2001-11-17). "Sri Lanka: The Untold Story". Asia Times Online. Retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ "Bandaranaike, Solomon West Ridgeway Dias". history.com. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ "Short Term". Time. 1959-12-14. Retrieved 2008-10-11.
- 1 2 3 4 "Sirimavo Bandaranaike: First woman premier". BBC News. 2000-10-10. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ Neville de Silva. "A Prime Minister who knew his onions". UK Lanka Times. Retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ "Former Sri Lanka president dies, leaves mixed legacy". CNN. 1996-11-01. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ Barbara Crossette (1988-12-21). "MAN IN THE NEWS: Ranasinghe Premadasa; Sri Lankan At the Top". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- ↑ "Profile: Ranil Wickramasinghe". BBC News. 2005-11-22. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ "Hon Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga (1994–2005)". The official website of the Government of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka". The History Channel. Retrieved 2008-10-04.
- ↑ "President's Profile". The President's Fund of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 2008-10-04.