Psiphon
 | |
| Developer(s) | Psiphon Inc. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2004 (1.0), 1.6 (2008) 2009 (2.X), 2011 (3.x) |
| Stable release |
2.X, 3.X
/ 2012 |
| Repository |
bitbucket |
| Operating system | Windows, Android |
| Type | Internet censorship circumvention |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website |
psiphon |
Psiphon is an Internet censorship circumvention that uses a combination of secure communication and obfuscation technologies (VPN, SSH, and HTTP Proxy). The Psiphon codebase is developed and maintained by Psiphon Inc which operates systems and technologies designed to assist Internet users to securely bypass the content-filtering systems used by governments to impose censorship of the Internet. Psiphon is specifically designed to support users in countries considered to be "enemies of the Internet".[1]
The original concept for Psiphon (1.0) was developed by the Citizen Lab at the University of Toronto, building upon previous generations of web proxy software systems, such as the "SafeWeb"[2] and "Anonymizer" systems.
In 2007 Psiphon Inc was established as an independent Ontario corporation that develops advanced censorship circumvention systems and technologies. Psiphon Inc and the Citizen Lab at the Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto occasionally collaborate on research projects, through the Psi-Lab partnership.[3]
Psiphon currently consists of three separate but related open source software projects:
- 3.X – A cloud based run-time tunneling system.[4]
- 2.X – A cloud-based secure proxy system.[5]
- 1.X – The original home based server software (released by the Citizen Lab in 2004, rewritten and launched in 2006). Psiphon 1.X is no longer supported by Psiphon Inc. or the Citizen Lab.[6]
History
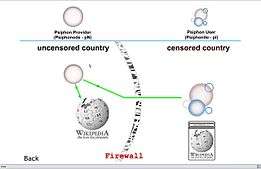
The original concept for Psiphon envisioned an easy-to-use and lightweight Internet proxy, designed to be installed and operated by individual computer users who would then host private connections for friends and family in countries where the Internet is censored. According to Nart Villeneuve "The idea is to get (users) to install this on their computer, and then deliver the location of that circumventor, to people in filtered countries by the means they know to be the most secure. What we're trying to build is a network of trust among people who know each other, rather than a large tech network that people can just tap into."[7] Psiphon 1.0 was launched by the Citizen Lab on 1 December 2006 as open source software.[8]
In Early-2007, Psiphon inc was established as a Canadian corporation independent of the Citizen Lab and the University of Toronto. The original code (1.6) was made available under the GNU General Public License. In 2008, Psiphon was awarded the Netexplorateur award by the French Senate.[9] In 2009, Psiphon was recognized with The Economist Best New Media Award by Index on Censorship.[10] In 2011, Psiphon 1.X was officially retired and is no longer actively supported by Psiphon Inc., or the Citizen Lab.[6]
In 2008, Psiphon inc was awarded two sub-grants via the Internews operated SESAWE (Open Internet) project(s).[8][11] The source of funding came from the European Parliament and the US State Department Internet Freedom program, administered by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (DRL).[12] The objective of these grants was to develop Psiphon into a scalable circumvention solution capable of supporting large numbers of users across different geographic regions. The core development team grew to include a group of experienced security and encryption software engineers that previously developed Ciphershare, a secure document management system.[13]
In 2010, Psiphon inc began providing services to the Broadcasting Board of Governors (US), US Department of State, and the British Broadcasting Corporation. Psiphon inc currently (2015) operates on the basis revenues generated from commercial operations.
In 2012, Psiphon inc began development of a mobile version of Psiphon 3 for use with phones running Android.[14]
See also
References
- ↑ http://en.rsf.org/internet-enemie-egypt,36679.html
- ↑ "SafeWeb's Holes Contradict Claims". Wired. 2002-02-12.
- ↑ "Ronald Deibert | Director, The Canada Centre for Global Security Studies and the Citizen Lab, Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto". Deibert.citizenlab.org. 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "psiphon / Psiphon Circumvention System — Bitbucket". Bitbucket.org. 2011-06-14. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "psiphon in Launchpad". Launchpad.net. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- 1 2 "Psiphon - Total Delivery Solution for the Censored Internet". Psiphon.ca. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ Boyd, Clark (2004-03-10). "Bypassing China's net firewall". BBC News. Retrieved 2007-03-28.
- 1 2 "Psiphon - Total Delivery Solution for the Censored Internet". Psiphon.ca. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "Psiphon, un logiciel anticensure, « Netxplorateur de l'année »" (in French). Rue89. 2008-02-14. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "FREEDOM OF EXPRESSION AWARD 2009 RECIPIENTS ANNOUNCED". Index on Censorship. 2009-04-21. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "is now offline". Sesawe.net. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "Promises We Keep Online: Internet Freedom in the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) Region". State.gov. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "CipherShare - High Performance, Secure Document Management and Collaboration". Provensecuritysolutions.com. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ↑ "Psiphon - Total Delivery Solution for the Censored Internet". Psiphon.ca. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
External links
- Official website
- Software jumps China's firewall for news from Tibet
- BBC: Web censorship 'bypass' unveiled
- Canadian software touted as answer to Internet censorship abroad
- Computerworld: Liberation software designed on basis of trust
- Reuters: Canada experts find path round Internet firewalls
- Al Jazeera's Listening Post story about psiphon on YouTube
- Index on Censorship – Psiphon wins Economist New Media award at Freedom of Expression awards 2009