Pudendal nerve
| Pudendal nerve | |
|---|---|
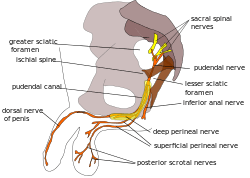 Pudendal nerve, course and branches in a male. | |
| Details | |
| From | Sacral nerves S2, S3, S4 |
| To |
Inferior rectal nerves perineal nerve dorsal nerve of the penis dorsal nerve of the clitoris |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus pudendus |
| TA | A14.2.07.037 |
| FMA | 19037 |
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum.[1]:274 It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may also be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure.
The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve, is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836.
Structure
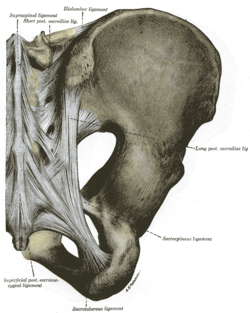
The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle.[2] The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to form the lower cord, and these in turn unite to form the pudendal nerve proper just proximal to the sacrospinous ligament.[3] The three roots are derived from the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth sacral spinal nerves, with the primary contribution coming from the fourth.[2][4]:215[5]:157
The pudendal nerve passes between the piriformis muscle and coccygeus (ischiococcygeus) muscles and leaves the pelvis through the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen.[2] It crosses over the lateral part of the sacrospinous ligament and reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen. After reentering the pelvis, it accompanies the internal pudendal artery and internal pudendal vein upwards and forwards along the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa, being contained in a sheath of the obturator fascia termed the pudendal canal, along with the internal pudendal blood vessels.[6]:8
Inside the pudendal canal, the nerve divides into branches, first giving off the inferior rectal nerve, then the perineal nerve, before continuing as the dorsal nerve of the penis (in males) or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris (in females).[6]:34
Nucleus
The nerve is a major branch of the sacral plexus,[7]:950 with fibers originating in Onuf's nucleus in the sacral region of the spinal cord.[3]
Variation
The pudendal nerve may vary in its origins. For example, the pudendal nerve may actually originate off of the sciatic nerve.[8] Consequently, damage to the sciatic nerve can affect the pudendal nerve as well. Sometimes dorsal rami of the first sacral nerve contribute fibers to the pudendal nerve, and even more rarely S5.[3]
Function
The pudendal nerve has both motor and sensory functions. It does not carry parasympathetic fibers, but does carry sympathetic fibers.[9]:1738
The pudendal nerve supplies sensation to the penis in males and the clitoris in females, through the branches dorsal nerve of penis and dorsal nerve of clitoris.[10]:422 The posterior scrotum in males and the labia in females are also supplied, via the posterior scrotal nerves (males) or posterior labial nerves (females). The pudendal nerve is one of several nerves supplying sensation to these areas.[11] Branches also supply sensation to the anal canal.[6]:8 By providing sensation to the penis and the clitoris, the pudendal nerve is responsible for the afferent component of penile erection and clitoral erection.[12] :147 It is also responsible for ejaculation.[13]
Branches also innervate muscles of the perineum and pelvic floor; namely the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles,[11] the levator ani muscle (including the Iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus, puborectalis and either pubovaginalis in females or pubourethralis in males),[10]:422[14] the external anal sphincter (via the inferior anal branch),[6]:7 and male or female external urethral sphincter.[10]:424–425
As it functions to innervate the external urethral sphincter it is responsible for the tone of the sphincter mediated via acetylcholine release. This means that during periods of increased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle in the external urethral sphincter contracts, causing urinary retention. Whereas in periods of decreased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle in the external urethral sphincter relaxes, allowing voiding of the bladder to occur.[15] (Clarification: Unlike the internal sphincter muscle, the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle, therefore it is under voluntary control of the somatic nervous system.)
Clinical significance
Anesthesia
A pudendal nerve block, also known as a saddle nerve block, is a local anesthesia technique used in a obstetric procedure to anesthetize the perineum during labor.[16] In this procedure, an anesthetic agent such as lidocaine is injected through the inner wall of the vagina about the pudendal nerve.[17]
Damage
The pudendal nerve can be compressed or stretched, resulting in temporary or permanent neuropathy. Irreversible nerve injury may occur when nerves are stretched by 12% or more of their normal length.[6]:655 If the pelvic floor is over-stretched, acutely (e.g. prolonged or difficult childbirth) or chronically (e.g. chronic straining during defecation caused by constipation), the pudendal nerve is vulnerable to stretch-induced neuropathy.[6]:655 Pudendal nerve entrapment, also known as Alcock canal syndrome, is very rare and is associated with professional cycling.[18] Systemic diseases such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis can damage the pudendal nerve via demyelination or other mechanisms.[6]:37 A pelvic tumor (most notably a large sacrococcygeal teratoma), or surgery to remove the tumor, can also cause permanent damage.[19]
Unilateral pudendal nerve neuropathy inconsistently causes fecal incontinence in some, but not others. This is because crossover innervation of the external anal sphincter occurs in some individuals.[6]:34
Imaging
The pudendal nerve is difficult to visualize on routine CT or MR imaging, however under CT guidance, a needle may be placed adjacent to the pudendal neurovascular bundle. The ischial spine, an easily identifiable structure on CT, is used as the level of injection. A spinal needle is advanced via the gluteal muscles and advanced within several millimeters of the ischial spine. Contrast (X-ray dye) is then injected, highlighting the nerve in the canal and allowing for confirmation of correct needle placement. The nerve may then be injected with cortisone and local anesthetic to confirm and also treat chronic pain of the external genitalia (known as vulvodynia in females), pelvic and anorectal pain.[20][21]
Nerve latency testing
The time taken for a muscle supplied by the pudendal nerve to contract in response to an electrical stimulus applied to the sensory and motor fibers can be quantified. Increased conduction time (terminal motor latency) signifies damage to the nerve.[22]:46 2 stimulating electrodes and 2 measuring electrodes are mounted on the examiner's gloved finger ("St Mark's electrode").[22]:46
History
The term pudendal comes from Latin pudenda, meaning external genitals, derived from pudendum, meaning "parts to be ashamed of".[23] The pudendal canal is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Alcock documented the existence of the canal and pudendal nerve in a contribution about iliac arteries in Robert Bentley Todd's "The Cyclopaedia of Anatomy and Physiology".[24]
Additional images
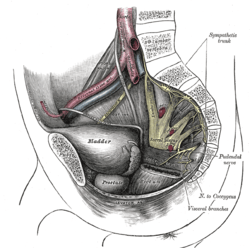 The male pelvis, showing the pudendal nerve (centre right)
The male pelvis, showing the pudendal nerve (centre right) Schematic showing the structures innervated by the pudendal nerve
Schematic showing the structures innervated by the pudendal nerve Diagram of the course of the pudendal nerve in the male pelvis
Diagram of the course of the pudendal nerve in the male pelvis
See also
References
- ↑ AMR Agur; AF Dalley; JCB Grant (2013). Grant's atlas of anatomy (13th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-60831-756-1.
- 1 2 3 Standring S (editor in chief) (2004). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (39th ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-443-06676-4.
- 1 2 3 Shafik, A; el-Sherif, M; Youssef, A; Olfat, ES (1995). "Surgical anatomy of the pudendal nerve and its clinical implications". Clinical Anatomy. 8 (2): 110–5. doi:10.1002/ca.980080205. PMID 7712320.
- ↑ Moore, Keith L. Moore, Anne M.R. Agur ; in collaboration with and with content provided by Arthur F. Dalley II ; with the expertise of medical illustrator Valerie Oxorn and the developmental assistance of Marion E. (2007). Essential clinical anatomy (3rd ed.). Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-6274-8.
- ↑ Russell RM (2006). Examination of peripheral nerve injuries an anatomical approach. Stuttgart: Thieme. ISBN 978-3-13-143071-7.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Wolff BG et al., eds. (2007). The ASCRS textbook of colon and rectal surgery. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-24846-3.
- ↑ TL King; MC Brucker; JM Kriebs; JO Fahey (2013). Varney's midwifery (Fifth ed.). Jones & Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-1-284-02542-2.
- ↑ Nayak, Soubhagya R.; Madhan Kumar, S.J.; Krishnamurthy, Ashwin; Latha Prabhu, V.; D'costa, Sujatha; Jetti, Raghu (November 2006). "Unusual origin of dorsal nerve of penis and abnormal formation of pudendal nerve—Clinical significance". Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger. 188 (6): 565–566. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2006.06.011.
- ↑ Neill, editor-in-chief, Jimmy D. (2006). Knobil and Neill's physiology of reproduction (3rd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-12-515400-3.
- 1 2 3 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- 1 2 Ort, Bruce Ian Bogart, Victoria (2007). Elsevier's integrated anatomy and embryology. Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 978-1-4160-3165-9.|page=Neurovascular Bundles of the Perineum
- ↑ Babayan, Mike B. Siroky, Robert D. Oates, Richard K. (2004). Handbook of urology diagnosis and therapy (3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-4221-4.
- ↑ Penson, David F. (2002). Male Sexual Function: A Guide to Clinical Management. Annals of Internal Medicine.
- ↑ Guaderrama, Noelani M.; Liu, Jianmin; Nager, Charles W.; Pretorius, Dolores H.; Sheean, Geoff; Kassab, Ghada; Mittal, Ravinder K. (October 2005). "Evidence for the Innervation of Pelvic Floor Muscles by the Pudendal Nerve". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 106 (4): 774–781. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000175165.46481.a8.
- ↑ Fowler, CJ; Griffiths, D; de Groat, WC (June 2008). "The neural control of micturition". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9: 453–66. doi:10.1038/nrn2401. PMC 2897743
 . PMID 18490916.
. PMID 18490916. - ↑ Lynna Y. Littleton; Joan Engebretson (2002). Maternal, Neonatal, and Women's Health Nursing, Volume 1. Cengage Learning. p. 727.
- ↑ Satpathy, Hemant K.; et al. Isaacs, Christine; et al., eds. "Transvaginal Pudendal Nerve Block". WebMD LLC. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ Mellion MB (January 1991). "Common cycling injuries. Management and prevention". Sports Med. 11 (1): 52–70. doi:10.2165/00007256-199111010-00004. PMID 2011683.
- ↑ Lim, Jit F.; Tjandra, Joe J.; Hiscock, Richard; Chao, Michael W. T.; Gibbs, Peter. "Preoperative Chemoradiation for Rectal Cancer Causes Prolonged Pudendal Nerve Terminal Motor Latency". Diseases of the Colon & Rectum. 49 (1): 12–19. doi:10.1007/s10350-005-0221-7.
- ↑ Calvillo O, Skaribas IM, Rockett C.; Skaribas; Rockett (2000). "Computed tomography-guided pudendal nerve block. A new diagnostic approach to long-term anoperineal pain: a report of two cases". Reg Anesth Pain Med. 24 (4): 420–3. doi:10.1053/rapm.2000.7620. PMID 10925942.
- ↑ Hough DM, Wittenberg KH, Pawlina W, Maus TP, King BF, Vrtiska TJ, Farrell MA, Antolak SJ Jr.; Wittenberg; Pawlina; Maus; King; Vrtiska; Farrell; Antolak Jr (2003). "Chronic perineal pain caused by pudendal nerve entrapment: anatomy and CT-guided perineural injection technique". Am J Roentgenol. 181 (2): 561–7. doi:10.2214/ajr.181.2.1810561. PMID 12876048.
- 1 2 G.A. Santoro, A.P. Wieczorek, C.I. Bartram (editors) (2010). Pelvic floor disorders imaging and multidisciplinary approach to management. Dordrecht: Springer. ISBN 978-88-470-1542-5.
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "Pudendum". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 28 February 2014.
- ↑ Oelhafen, Kim; Shayota, Brian J.; Muhleman, Mitchel; Klaassen, Zachary; Tubbs, R. Shane; Loukas, Marios (September 2013). "Benjamin Alcock (1801-?) and his canal". Clinical Anatomy. 26 (6): 662–666. doi:10.1002/ca.22080. PMID 22488487.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pudendal nerve. |
- Anatomy figure: 41:04-11 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inferior view of female perineum, branches of the internal pudendal artery."
- figures/chapter_32/32-2.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- figures/chapter_32/32-3.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- Cross section image: pelvis/pelvis-female-17 - Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
- Diagnosis and treatment at www.nervemed.com
- www.pudendal.com
- Pudendal nerve entrapment at chronicprostatitis.com
- CT sequence showing a pudendal nerve block.