Rail transport in France
| Rail transport in France | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 TGV at Paris-Est station | |||||
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | SNCF | ||||
| Infrastructure company | SNCF | ||||
| Major operators | Thalys, Lyria, Eurostar, RATP, Elipsos, ECR | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 1,122 million (2014)[1] | ||||
| Passenger km | 83.9 billion (2014)[1] | ||||
| Freight | 32 billion tonne-km (2014)[1] | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 29,901 kilometres (18,580 mi) [2] | ||||
| Double track | 16,445 km (10,218 mi) | ||||
| Electrified | 15,140 km (9,410 mi) | ||||
| High-speed | 1,876 km (1,166 mi) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) | ||||
| High-speed | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| 25 kV AC | 9,113 km (5,663 mi) | ||||
| 1500 V DC | 5,905 km (3,669 mi) | ||||
| other | 122 km (76 mi) | ||||
| Features | |||||
| No. tunnels | 1,300[3] | ||||
| Tunnel length | 540 km (340 mi) | ||||
| Longest tunnel | 50.5 km (31.4 mi) (Channel Tunnel) | ||||
| Longest bridge | 2.178 km (1.353 mi) (Saint-André-de-Cubzac bridge) | ||||
| No. stations | 3,054 (2009).[4] | ||||
| Highest elevation | 1,593m (Yellow Train) | ||||
| |||||
Rail transport in France is operated mostly by SNCF, the French national railway company. France has the second largest European railway network, with a total of 29,901 kilometres of railway.[2] However, the railway system is a small portion of total travel, accounting for less than 10% of passenger travel.[5]
Since 1981, the SNCF has operated the TGV service, a high-speed rail network which has been consistently expanded in subsequent years.
France is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for France is 87.
History
The history of rail transport in France dates from the first French railway in 1832.
Exploitation
Since Legrand Star rail plan of 1842, French railway is highly polarized by Paris.
Traffic is concentrated on the main lines: 78% of activity is done on 30% of the network (8,900 km) when the 46% smaller lines (13,600 km) only drive 6% of the traffic.[6] The 366 largest stations (12%) make 85% of passenger activity, and the smallest 56% of stations take only 1.7% of traffic.[7]
Freight transport
Freight transport has declined since the early 1980s.[8] Today the network is predominantly passenger centric.
Since January 1 2007, the freight market has been open to conform to European Union agreements (EU Directive 91/440). New operators had already reached 15% of the market at the end of 2008.[9]
Passenger transport
Short and middle distance
The Transport express régional (TER) is directed by the administrative Regions of France. They contract with the SNCF for lines exploitation.
Long distance
The SNCF directly manage this class of trains. The TGV is used on the most important destinations, while Intercités carriages are still used for other lines.
Network
The French railway network, as administered by SNCF Réseau, as of June 2007, is a network of commercially usable lines of 29,213 kilometres (18,152 mi), of which 15,141 km (9,408 mi) is electrified. 1,876 km (1,166 mi) of those are high speed lines (LGV), 16,445 km (10,218 mi) dispose of two or more tracks. 5,905 km (3,669 mi) are supplied with 1,500 V DC, 9,113 km (5,663 mi) with 25 kV AC at 50 Hz. 122 km (76 mi) are electrified by third rail or other means.[2]
1,500 V is used on the south, and HSR lines and the northern part of the country use 25 kV electrification.
Trains drive on the left, except in Alsace and Moselle where tracks were first constructed while those regions were part of Germany.
Rail links to adjacent countries
- Same gauge
- Belgium — voltage change 25 kV AC/3 kV DC (except high-speed line to Brussels, same voltage)
- Germany — voltage change 25 kV AC/15 kV AC
- Great Britain via the Channel Tunnel — voltage change 25 kV AC/750 V DC third rail (except high-speed line to London, same voltage)
- Italy — voltage change 25 kV AC/3 kV DC (except high-speed line, same voltage)
- Luxembourg — same voltage
- Monaco — same voltage
- Spain via the LGV Perpignan-Figueres — same voltage
- Switzerland — voltage change 25 kV AC or 1,5 kV DC/15 kV AC
- Break-of-gauge, 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in)/1,668 mm (5 ft 5 21⁄32 in)
- Spain (on conventional tracks) — voltage change 1,5 kV DC/3 kV DC
- No rail link to Andorra
Current status
The French non-TGV intercity service (TET) is in decline, with old infrastructure and trains. It is likely to be hit further as the French government is planning to remove the monopoly that rail currently has on long-distance journeys by letting coach operators compete.[10]
Travel to the UK through the Channel Tunnel has grown in recent years, and from May 2015 passengers have been able to travel direct to Marseille, Avignon and Lyon. Eurostar is also introducing new Class 374 trains and refurbishing the current Class 373s.
The International Transport Forum described the current status of the French railways in their paper "Efficiency indicators of Railways in France":[11]
- The success of the TGV is undeniable (Crozet 2013). Work started in September 1975 on the first high-speed rail (HSR) line, between Paris and Lyon, and it was inaugurated in September 1981. New high-speed lines were opened in 1989 (towards the south-west), in 1993 (towards the north), etc. The high-speed network now covers 2,000 km, and will reach over 2,600 km in 2017 with the opening of the four lines currently being built.
- The regionalisation of intercity and local services was tested in 1997 and fully deployed in the early 2000s. Since then, TERs (regional express trains) have seen traffic rise steeply (50% between 2000 and 2013) as, to a lesser extent, have services in the Ile de France region (25%).
- Rail freight has been far less successful. The French network carried 55 billion tonne-km in 2001, but this figure scarcely reached 32 billion tonne-km in 2013. This weak performance contrasts sharply with the ambitious public policy of the last fifteen years. The Grenelle Environment Forum (2007–2010) oversaw the deployment of a costly freight plan that was no more effective than its predecessors.
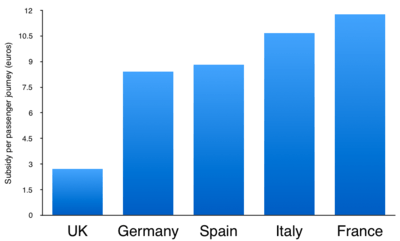
Subsidies
Like roads, the French railways receive rail subsidies from the state in order to operate. Those amounted to €13.2 billion in 2013.[11]
Material
Alstom is the manufacturer of the TGV, and is behind many regional train models (Régiolis, SNCF Class Z 26500 ... )
See also
- Transport in France
- Narrow gauge railways in France
- Rail transport in Europe
- Rail transport by country
References
- 1 2 3 "Railway Statistics – 2014 Synopsis" (PDF). Paris, France: International Union of Railways, IUC. 2014. Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- 1 2 3 RFF Website "Network inventory"
- ↑ http://www.assemblee-nationale.fr/rap-oecst/tunnels/r2388.asp#_Toc483033395
- ↑ La Gare Contemporaine p94, Fabienne Keller
- ↑ "Transport in France". International Transport Statistics Database. iRAP. Archived from the original on December 20, 2008. Retrieved 2009-02-17.
- ↑ Audit sur l'état du réseau national français p3, Robert Rivier & Yves Putallaz, 2005 September 7
- ↑ Gares et Connexion p20
- ↑ Pourquoi le fret ferroviaire va-t-il si mal en France ? Autour du plan Véron (Fret 2006) Pierre Zembri 2004
- ↑ http://www.senat.fr/rap/r08-220/r08-2207.html
- ↑ "France's loss-making inter-city services at a crossroads".
- 1 2 "Efficiency indicators of Railways in France" (PDF).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rail transport in France. |
