Railway Clearing House
|
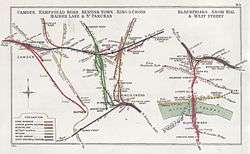
Typical Railway Junction Diagram produced by the RCH. This one shows the location of the RCH offices close to Euston Station. | |
| Abbreviation | RCH |
|---|---|
| Formation | 2 January 1842 |
| Extinction | 8 April 1955 |
| Purpose | Distribution of railway receipts; common standards for railways |
| Location |
|
Region served | United Kingdom |
Membership | Railway companies |
The British Railway Clearing House (RCH) was an organisation set up to manage the allocation of revenue collected by pre-grouping railway companies of fares and charges paid for passengers and goods travelling over the lines of other companies.
History
When passengers travelled between two stations on the same railway, using trains provided by the same company, that company was entitled to the whole of the fare. Similarly, when goods were consigned between two stations on the same railway, using wagons provided by the same company, that company was entitled to the whole of the fee. However, when coaches or wagons owned by a different company were used, that company would be entitled to a proportion of the fare or fee. If the commencement and terminus of the journey were on different railways, a more complicated situation arose: if the two companies involved did not provide through ticketing, the passenger or goods needed to be re-booked at a junction station; if through booking was provided, the receipts collected by the first company needed to be divided between them, usually on a mileage basis. The Railway Clearing House was founded as a means by which these receipts could be apportioned fairly.[1]
The Railway Clearing House commenced operations on 2 January 1842 in small offices at 111 Drummond Street opposite Euston Station, London.[1] These premises were owned by the London and Birmingham Railway, which also provided the initial costs of setting up the organisation.
The founding members, whose first meeting was on 26 April 1842, were: the London and Birmingham Railway; the predecessors of the Midland Railway (the Midland Counties Railway, Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway, and North Midland Railway); the Manchester and Leeds Railway; and the predecessors of the North Eastern Railway (the Leeds and Selby Railway, Hull and Selby Railway, York and North Midland Railway and Great North of England Railway).
This first meeting agreed the principles by which the ongoing activities of the RCH were to be funded. This involved a fixed payment per station served (£5, reduced in 1844 to £2 for stations that were not termini) plus an apportionment of the balance of costs according to the total share of receipts of each participating company. The first manager was Kenneth Morrison, auditor of the London and Birmingham Railway.[2]
By the end of December 1845, more companies had joined: the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway; Chester and Birmingham Railway; the Grand Junction Railway and its allies the North Union Railway and Liverpool and Manchester Railway; the Lancaster and Preston Railway; Manchester and Birmingham Railway; and Newcastle and Carlisle Railway.
The Grand Junction Railway initially refused, because of the £300 pa. cost of using Edmondson tickets, and the Liverpool and Manchester saw no need to join, being isolated from the rest of the railway system.[3]
Owing to expansion, the RCH moved to larger purpose-built premises in Seymour Street (renamed Eversholt Street in 1938)[1] in early 1849, which remained its headquarters for the rest of its existence. By the end of 1850 a further 21 companies had joined, including several of the leading Scottish companies, bringing the total of British railway mileage in the scheme to 55.8%. However it still lacked the Great Western Railway and the companies South of London.
It was soon realised that the RCH provided a neutral meeting point where different railways could discuss points of disagreement and make suggestions which could benefit other railways. Besides meeting rooms, the RCH provided secretarial facilities for these discussions. Conferences between railway managers were arranged, as were conferences between the different railways' departmental heads. In this way, railways moved towards many common practices, without the need for legislation. Unfortunately, the system had a weakness, in that a unanimous vote was required for a recommendation to become compulsory.[2]
In due course, the RCH was given legal status by a private Act of Parliament, the Railway Clearing Act of 25 June 1850.[1] Although initiated by the members' companies themselves, the Bill, in fact, reduced the scope of the RCH, while making it easier to enforce debt collection among members (hitherto not formally regulated). A later attempt, in 1859, via Parliament, to re-extend the powers and potential membership of the RCH, foundered on conflicting interests.
A separate organisation, the United Railway Companies' Committee, was formed in 1858, but folded in 1861. It was re-established in June 1867 and became the Railway Companies' Association (RCA) in 1869. There was a certain degree of overlap between the RCA and the RCH, and it was later agreed that the RCA should represent the railways in Parliament, whilst the RCH concentrated on organising the business of railway traffic.[4]
In 1897, the RCH was established as a body corporate.[1] During both World Wars, the railways were placed under government control, and the receipts were pooled and then apportioned in fixed proportions according to pre-war receipts. During these periods, the duties of the RCH were very much reduced, but they continued to provide their secretarial functions.[4] As railway companies amalgamated, so the number of members reduced; until it had just one member, the British Transport Commission (BTC).[5] As part of the Transport Act 1947, the Acts of Incorporation were repealed.[1]
Most of the remaining powers, property, rights and liabilities were transferred to the BTC on 24 May 1954,[1][5] and the RCH was dissolved as a corporate body on 8 April 1955.[5] The BTC then continued the remaining functions of the RCH, still under the name Railway Clearing House. These included the provision of secretarial services and rooms for railway meetings, and meetings between road and rail companies; classification of goods for the setting of rates; the examination and certification of new packaging materials; the registration of rolling stock; the issue of maps and other publications including scales of charges; and the spot-check of wagons and consignments in transit.[6]
Standards

On 22 September 1847, the RCH recommended that Greenwich Mean Time be adopted as the standard time for all railways in the United Kingdom.[7]
The RCH went on to set technical standards for various items, such as goods wagons, to promote standardisation across the rail network. If a wagon was described as an RCH wagon, this meant it had been built to comply with RCH standards.
The RCH set technical standards for cable connections between coaches for the remote operation of systems; they were initially used only for control of train lighting. These cables were known as RCH jumpers, and in the 1970s a system for push-pull trains was developed which used the RCH cable, eliminating the need for a separate control cable to be fitted to intermediate coaches.
The RCH produced Railway Junction Diagrams (RJDs), which show the junctions where two or more railway companies met, and the distances between these junctions and nearby stations and junctions, in order to aid the calculation of mileage-based rates. Starting in 1871 it also issued what has been described as the "most superb series of railway maps ever produced in the United Kingdom."[8]
The RCH had some similarities to the modern Association of Train Operating Companies, and in particular, its Rail Settlement Plan division.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cooke, B.W.C., ed. (December 1954). "The Railway Clearing House". The Railway Magazine. Westminster: Tothill Press. 100 (644): 812.
- ↑ Vaughan, A., (1997) Railwaymen, Politics and Money, London: John Murray
- 1 2 3 Cooke, B.W.C., ed. (June 1958). "The Why and the Wherefore: The Railway Clearing House". The Railway Magazine. Westminster: Tothill Press. 104 (686): 440.
- ↑ Cooke, B.W.C., ed. (March 1955). "Notes and News: The Railway Clearing House". The Railway Magazine. Westminster: Tothill Press. 101 (647): 212.
- ↑ "Daylight Saving Time - Standard time began with the railroads". Retrieved 22 September 2005.
- ↑ Railway Maps and the Railway Clearing House - The David Garnett Collection in Brunel University Library.Uxbridge: Brunel University Library, 1986
- Bagwell, P The Railway Clearing House in the British Economy, 1842-1922, George Allen & Unwin, London (1968)
Diagram sources
- John Airey (1867), Railway junction diagrams, Railway Clearing House
- John Airey (1882), Railway Junction Diagrams (4 ed.), Railway Clearing House
- Railway Junction Diagrams, Railway Clearing House, 1895
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Railways Junctions Diagram 1914. |
- Edward Walford (1878), "XXVI. Somers Town and Euston Square", Old and New London, 5, pp. 340–355, contemporary description of the Railway Clearing House
- Winchester, Clarence, ed. (5 July 1935), "The Railway Clearing House", Railway Wonders of the World, pp. 711–716, contemporary description of the work of the Railway Clearing House
Coordinates: 51°31′53″N 0°08′09″W / 51.5315°N 0.1357°W