Republic of Pontus
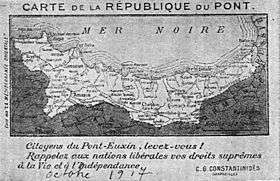
The Republic of Pontus (Greek: Δημοκρατία του Πόντου, Dimokratía tou Póntou) was a proposed Pontic Greek state on the southern coast of the Black Sea, whose territory would have encompassed much of historical Pontos and which is today contained within Turkey's Black Sea Region. The proposed state was discussed at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919, but the Greek government of Eleftherios Venizelos feared the precarious position of such a state and so it was included instead in the larger proposed state of Wilsonian Armenia. Neither state came into existence and the Pontic Greek population was expelled from Turkey after 1922 and resettled in the Soviet Union or Greek Macedonia. This state of events was later formally recognized as part of the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923.
History
Following the Ottoman conquest of the Greek state Trebizond, the region of Pontus remained under Turkish control.
In the early 1830s, the Greek state achieved independence, but with less territory than it holds today. Hellenic nationalists made further claims upon Greek-populated territory elsewhere. The Pontic Greeks in the area had few connections to the Greek state, primarily religious, and so joining with Greece was never strongly considered.[1] At the same time, many Pontic Greeks migrated to Russia, Georgia, and other countries.
In 1904 a secret society, the Pontus Society, was founded in Merzifon whose main purpose was achieving an independent republic of Pontus.[2] The movement gained significant support and during the 1910s and 1920s, the Metropolitan of Trabzon Chrysanthos Filippides, who would later become the Archbishop of Athens, became a major leader in pushing for an independent Republic of Pontus.[3] International societies of Pontic Greeks became connected with the Pontus Society in Merzifon and began significant lobbying efforts to push for an independent Pontic Greek state: most prominently in Russia and the United States.[4] During this period, Leonidas Iasonidis became a primary leader in the movement for the establishment of a Republic of Pontus.[4]
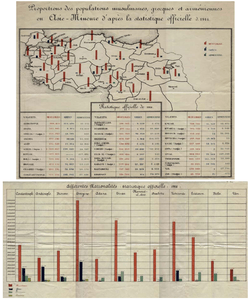
Like Armenians, Assyrians and other Ottoman Greeks, the Greeks of Trebizond province suffered a genocide at the beginning of the 20th century, first by the Young Turks and later by Kemalist forces. In both cases, the reason why, was the fear of the Turks on losing the territory sooner or later to the local indigenous populations of Greeks, Assyrians and Armenians and the policy of turkification. Death marches through Turkey's mountainous terrain, forced labour in the infamous "Amele Taburu" in Anatolia and slaughter by the irregular bands of Topal Osman resulted in hundred of thousands of Pontic Greeks perishing during the period from 1915 to 1922. The Greek population of the city itself was however not targeted directly, as the local authorities refused to supply mass murderer Topal with weapons, and local Turks forced his band out of the city. Also, Muslims of the city protested the arrest of prominent Christians.[5]
Pontic Greeks that escaped the death marches went on to the mountains, with women and kids and started self-defense groups that were protecting the Greek and Armenian population, until the population agreement exchange in 1923. The self-defense groups believed to have saved the lives of more than 60 thousands Pontic Greeks and Armenians.[6][7]
On January 8, 1918, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson enunciated his Fourteen Points towards a post-war order. Point Twelve specified that the non-Turkish nationalities "which are now under Turkish rule should be assured an undoubted security of life and an absolutely unmolested opportunity of autonomous development." This declaration led to significant activity to organize on the part of non-Turkish populations throughout Anatolia, including the Pontus region.[3] In 1918–1919, Greek Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos began a process of financial payment for repatriation of Pontic Greeks who had resettled in Russia during the violence before and during World War I.[4]
Following the Armistice of Mudros which ended World War I hostilities between the Allied powers and the Ottoman Empire, British troops landed in Samsun and occupied much of the region.[2]
At about the same time, with the beginning of the negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919 to decide territorial issues in the Ottoman Empire, Chrysanthos arrived at negotiations to push for an independent Pontus on April 29, 1919. While there he presented an 18-page memorandum of support for the establishment of a Republic of Pontus.[3] The proposed Republic of Pontus was to include the districts of Trabzon, Samsun, Sinop, Amasya and Karahisar and cover much of the northeast Black Sea region of modern Turkey.
At the Conference, Venizelos believed that an independent Republic of Pontus would be too remote for military assistance from Greece and too weak to defend itself against any Turkish attack. For this reason he opposed the creation of a Republic of Pontus and the discussion was largely ended.[8] Later, it was suggested that the district of Trabzon become part of the newly created Armenian state by Venizelos, but this idea did not gain traction with the Allied Powers and violence in the area as a result of the Turkish–Armenian War, the Turkish War of Independence, and the Bolshevik takeover of Armenia soon muted the discussion.[8] In May 1919, the head of the Greek Red Cross for the Pontus region wrote a report indicating that security for the population was very precarious and assistance was necessary.[4]
In 1921 large part of the Orthodox Christian males of Pontus were deported and sent to labour battalions at Erzerum. During this time an "Ad hoc Court of Turkish Independence" in Amasya, which was controlled by the Turkish nationalists of Mustafa Kemal (later Atatürk), sentenced several notable figures to death by hanging. Among them was the former member of the Ottoman parliament, Matthaios Kofidis. They were charged of supporting the Independence movement of Pontus.[9]
Aftermath
A large amount of the Pontic Greek community resettled during the fighting and after the Treaty of Lausanne in 1923 and as part of the Greek and Turkish population exchange. Records find that 182,169 Pontic Greeks were displaced as part of population exchange.[8] Many of the Pontic Greeks left for the Soviet Union, which had been the site of earlier Pontic migrations and thus had family connections. Much of the rest migrated to Greece where they were given full citizenship rights (Pontic Greeks who migrate from Russia today receive similar privileges). In Greece the Pontic migrants were called Póndioi.
See also
References
- ↑ Hionidou, Violetta (2012). ""Abroad I was Greek and in Greece I am a Foreigner": Pontic Greeks from Former Soviet Union in Greece". Journal of Modern Greek Studies. 30 (1).
- 1 2 Shaw, Stanford J.; Ezel Kural Shaw (1977). History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey. London, England: Cambridge University Press.
- 1 2 3 Erimtan, Can (2008). "Hittites, Ottomans and Turks: Ağaoğlu Ahmed Bey and the Kemalist Construction of Turkish Nationhood in Anatolia". Anatolian Studies. 58: 141–171. doi:10.1017/S0066154600008711. JSTOR 20455417.
- 1 2 3 4 Voutira, Eftitia (2011). The 'Right to Return' and the Meaning of Home. Berlin: Lit Verlag.
- ↑ Library Journal Review of Not Even My Name by Thea Halo.
- ↑ people.http://www.impantokratoros.gr/antartiko-pontou.el.aspx/>
- ↑ http://www.hellinon.net/ANEOMENA/AntartikoPontou.htm
- 1 2 3 Freely, John (2010). Children of Achilles: the Greeks in Asia Minor Since the Days of Troy. London: I.B. Taurus.
- ↑ Clark, Bruce (2006). Twice a Stranger: The Mass Expulsion that Forged Modern Greece and Turkey. Cambridge (Massachusetts): Harvard University Press. pp. 112–114. ISBN 9780674023680.