Sajur River
| Sājūr River (Arabic: نهر الساجور) | |
| River | |
| Countries | Turkey, Syria |
|---|---|
| Region | Middle East |
| City | Gaziantep, Manbij |
| Mouth | Euphrates |
| - coordinates | TR 36°39′35″N 38°04′14″E / 36.65972°N 38.07056°ECoordinates: TR 36°39′35″N 38°04′14″E / 36.65972°N 38.07056°E |
| Length | 108 km (67 mi) |
| Basin | 2,042 km2 (788 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 4.1 m3/s (145 cu ft/s) |
| - max | 7 m3/s (247 cu ft/s) |
| - min | 1.4 m3/s (49 cu ft/s) |
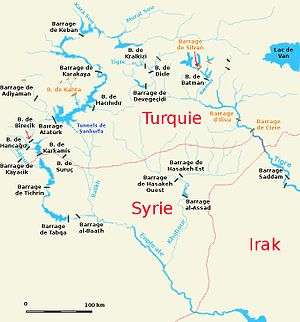 Map (in French) of the Syro–Turkish part of the Euphrates basin with the Sājūr (Sajour) in the left | |
The Sājūr River (Arabic: نهر الساجور [næhr æs sæːˈd͡ʒuːr]) is a 108 kilometres (67 mi) long river originating in Turkey and flowing into the Euphrates in Syria. It is the smallest of the three rivers joining the Euphrates in Syria, and the only one that joins the Euphrates on its right bank. Occupation in the Sājūr basin started in the Lower Palaeolithic period and continues until today.
Course
The Sājūr River is 108 kilometres (67 mi) long, of which 60 kilometres (37 mi) in Turkey and 48 kilometres (30 mi) in Syria.[1] It is fed by two streams which join south of Gaziantep. From there, the Sājūr flows southeast until it crosses the Syro–Turkish border. The river then continues in a roughly easterly direction until it joins the Euphrates on its right bank in the area that is flooded by the Tishrin Dam reservoir.[2] In Syria, the river cuts a valley into the Manbij Plain that is between 20 and 100 metres (66 and 328 ft) below the level of the plain, and up to 500 metres (1,600 ft) wide.[3] Average discharge is 4.1 cubic metres (140 cu ft) per second. Maximum discharge, occurring in the months February and March, is 7 cubic metres (250 cu ft) per second, while minimum discharge, recorded for June–October, is 1.4 cubic metres (49 cu ft) per second.[1][4] Average annual discharge is 0.14 cubic kilometres (0.03 cu mi). Both in terms of length, as well as discharge, the Sājūr is the smallest of the three rivers that join the Euphrates on Syrian soil – the other two being the Balikh and the Khabur.[4][5] The Sājūr is also the only river in Syria that enters the Euphrates on its right bank; both the Balikh and the Khabur flow into the Euphrates on the left bank.[6]
Drainage basin
The Sājūr drains a total area of 2,042 square kilometres (788 sq mi).[4] The Syrian part of the Sājūr basin – the Manbij Plain – has been particularly well-studied. This area is bounded on the north by the Syro–Turkish border and extends as far south as Manbij. To the west, the Manbij Plain is bordered by basalt outcrops; probably the remains of a Pliocene volcano. In the southeast of the plain, limestone outcrops force the Euphrates into the gorge of Qara Quzaq. These outcrops reach a height of 80–100 metres (260–330 ft) over the plain. Reaching heights of 500–520 metres (1,640–1,710 ft) amsl in the north, west and south, the Manbij Plain slopes down to 420 metres (1,380 ft) amsl toward the east. In the western part of the drainage basin, flat grounds with fertile red-brown soils can be found, and this area is suitable for agriculture. Toward the east and along the Sājūr, the plain is dissected by numerous wadis, making these parts of the area less suitable for human occupation and agriculture.[7] The Manbij Plain experiences a continental climate. Average temperatures range from 5 °C (41 °F) in January to 30 °C (86 °F) in July. Annual average precipitation is 300 millimetres (12 in), but ranges from a minimum of 141 millimetres (5.6 in) per year in dry years to 424 millimetres (16.7 in) per year in exceptionally wet years.[8] Although much of the area is cultivated today, combined palaeobotanical, climate and vegetation research suggest that the basin would support a xeric woodland vegetation with open oak forest and Rosaceae (rose/plum family) in the absence of human activity.[9]
History
Occupation of the Sājūr river basin started as early as the Lower Palaeolithic period, as evidenced by Acheulean stone artefacts. Middle Palaeolithic artefacts have been found as well.[10][11]
Economy
Both Turkey and Syria use water from the Sājūr for irrigation purposes. Since the 19th century, occupation in and cultivation of the Sājūr basin have steadily increased, especially in the western, more fertile part of the area. The introduction of motorized pumps has led to a considerable decrease of the groundwater table, with the effect that many wells have dried up.[12] Turkey has built the Kayacık Dam on the Ayfinar Deresi, one of the two streams that join to form the Sajur. This 45-metre (148 ft) high dam creates a reservoir with a surface area of 11 square kilometres (4.2 sq mi). From this reservoir, an area of 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) is irrigated.[13] A dam with a planned reservoir capacity of 0.0098 cubic kilometres (0.0024 cu mi) is under construction on the Syrian part of the Sajour.[14] The city of Aleppo disposes part of its wastewater into the Sājūr drainage system.[15]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Kolars & Mitchell 1991, p. 109
- ↑ Rawlinson 1880, pp. 137–138
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1985, p. 8
- 1 2 3 Besançon & Sanlaville 1985, p. 15
- ↑ Kolars & Mitchell 1991, pp. 108–109
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1981, p. 5
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1985, pp. 7–8
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1985, p. 13
- ↑ Moore, Hillman & Legge 2000, p. 50
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1981, p. 14
- ↑ Muhesen 2002, p. 102
- ↑ Besançon & Sanlaville 1985, p. 14
- ↑ Kayacik Dam, www.dsi.gov.tr, retrieved 23 February 2011
- ↑ Daoudy 2005, p. 84
- ↑ Kaisi, Yasser & Mahrouseh n.d., p. 259
References
- Besançon, J.; Sanlaville, P. (1981), "Aperçu géomorpholoqique sur la vallée de l' Euphrate syrien", Paléorient (in French), 7 (2): 5–18, doi:10.3406/paleo.1981.4295
- Besançon, Jacques; Sanlaville, Paul (1985), "Le milieu géographique", in Sanlaville, Paul, Holocene settlement in north Syria: résultats de deux prospections archéologiques effectuées dans la région du nahr Sajour et sur le haut Euphrate syrien, BAR International Series (in French), 328, Oxford: B.A.R., pp. 7–40, ISBN 0-86054-307-2
- Daoudy, Marwa (2005), Le partage des eaux entre la Syrie, l'Irak et la Turquie. Négociation, sécurité et asymétrie des pouvoirs, Moyen-Orient (in French), Paris: CNRS, ISBN 2-271-06290-X
- Kaisi, A.; Yasser, M.; Mahrouseh, Y. (n.d.), Syrian Arab Republic Country Report (PDF), pp. 251–264, retrieved 26 July 2010
- Kolars, John F.; Mitchell, William A. (1991), The Euphrates River and the Southeast Anatolia Development Project, Carbondale: SIU Press, ISBN 978-0-8093-1572-7
- Moore, A.M.T.; Hillman, G.C.; Legge, A.J. (2000), Village on the Euphrates. From foraging to farming at Abu Hureyra, Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-510807-8
- Muhesen, Sultan (2002), "The Earliest Paleolithic Occupation in Syria", in Akazawa, Takeru; Aoki, Kenichi; Bar-Yosef, Ofer, Neandertals and Modern Humans in Western Asia, New York: Kluwer, pp. 95–105, doi:10.1007/0-306-47153-1_7, ISBN 0-306-47153-1
- Rawlinson, George (1880), The Seven Great Monarchies of the Ancient Eastern World, 2, New York: J.W. Lovell, OCLC 288418703