Sakhalin–Hokkaido Tunnel
The Sakhalin–Hokkaido Tunnel (or potentially bridge) is a proposed connection to link the Russian island of Sakhalin with the Japanese island of Hokkaido. Cost estimates by Russia in the year 2000 put the project to span the 45-kilometre (28-mile) strait at $50 billion.[1]
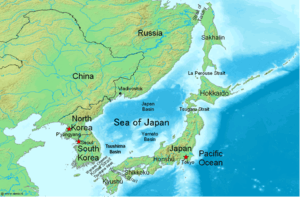
Overview
On 16 January 2009, the Russian Vice-Minister of Transport, Andrei Nedossekov, confirmed that proposals are now under consideration in regards to the Sakhalin–Hokkaido Tunnel. His decision to invite Japanese companies to bid to become consortium members of a wide array of Russian rail infrastructure work, particularly the Sakhalin Tunnel (or bridge) to the Russian mainland could be taken as a nod towards future rail cooperation between Russia and Japan.[2]
The tunnel would span roughly 40–45 km between Sakhalin's Cape Crillon (in Russia) to Hokkaido's Cape Sōya (in Japan). In comparison, the completed 53.85 km (33.46 mi) Seikan Tunnel links the Japanese islands of Honshu and Hokkaido. A further tunnel or bridge in the north of Sakhalin to the Russian mainland would also have to be created. Already a proposal for the Sakhalin Tunnel, has been announced by the Russian Government. Once on the Russian mainland, the rail link could connect to the rest of the Russian (and hence European) rail network, allowing for gauge changes. Running south, from Hokkaido, the line would connect with the Seikan Tunnel between Hokkaido and Honshu, currently the longest undersea tunnel in the world. This would allow connections to the rest of the Japanese rail network.
The project could be seen as an alternative to the Japan–Korea Undersea Tunnel, as Russia is already under way with planning and construction of many of the necessary linkages on the Russian side, whilst the tunnel itself would be considerably shorter than that between Japan and Korea.
As well as the great cost and engineering difficulty, there may be political problems, particularly in regards to the Kuril Islands dispute between Russia and Japan. The Japanese government's initial reaction has been cool towards the idea.[1]
Russian officials again raised the idea of a bridge or tunnel to connect Sakhalin with Hokkaido in 2013.[3][4] When combined with a potential bridge between Sakhalin and the Russian mainland, if built, it would be one of the final fixed links needed for a continuous rail corridor between Europe and Japan.[5]
Gauges
The railways on the Russian mainland use the 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) Russian gauge, while the Sakhalin Railway is, as of 2016, being gradually converted from the original Japanese 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge to the Russian gauge. Japanese railways use 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) and 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) gauge. It is unclear what rail gauge would be used for the proposed tunnel and associated infrastructure.
- Breaks of gauge: in Wakkanai area, Hokkaido, 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in)/1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in).
- Sakhalin-Hokkaido Tunnel
- Track gauge: 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in)
- Loading gauge: 4.1m wide and 6.15m tall
- Electrification: 25kV 50Hz AC overhead lines
- Hokkaido network:
- Track gauge: 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in)
- Loading gauge: Japanese Shinkansen
See also
References
- 1 2 "Plan for Tunnel to Sakhalin Unveiled". St Petersburg Times. 28 November 2000.
- ↑ "Sakhalin link proposed". Railway Gazette International. 16 January 2009.
- ↑ "Sakhalin Seeks Japan's Help for Bridge to Sakhalin and Hokkaido". RIA Novosti. 25 April 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ↑ "Russian Far East railway project may extend to Hokkaido". The Asahi Shimbun. 4 June 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ↑ "Russia's Far East Envoy Unveils Giant Sakhalin Bridge Plan". RIA Novosti. 18 July 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2014.