Scheduled bank
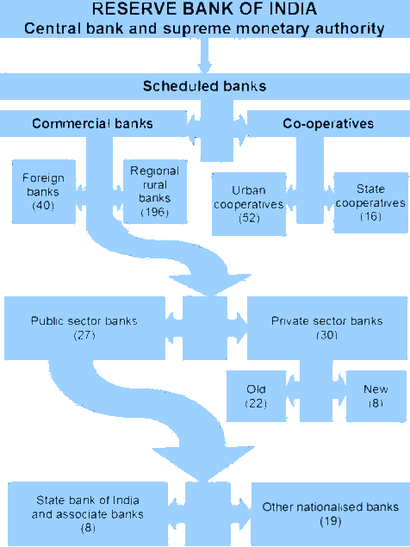
Structure of the organised banking sector in India.
A scheduled bank, in India, refers to a bank which is listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. Banks not under this Schedule are called non-scheduled banks.[1] Scheduled banks are usually private, foreign and nationalised banks operating in India. However, cooperative banks are allowed to seek scheduled bank status if they satisfy certain criteria.[2] A scheduled bank is eligible for loans from the Reserve Bank of India at bank rate. They are also given membership to clearing houses.[3]
Classification
The further classification of scheduled banks is as follows:[1]
- Scheduled commercial banks
- Nationalised banks
- State Bank of India and its associates
- Regional Rural Bank (RRBs)
- Foreign banks
- Other Indian private sector banks
- Scheduled State Co-operative Banks
- Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks
- Foreign Private Banks
See also
References
- 1 2 "Business Financing: Banks". Government of India. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "Urban co-operative banks permitted to seek scheduled status". Live Mint. 27 September 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "Bharatiya Mahila Bank included in second schedule to RBI Act". Live Mint. 21 May 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
Further reading
- "Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934: The Second Schedule" (PDF). Reserve Bank of India. p. 91-100.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.