Broad-tailed hummingbird
| Broad-tailed hummingbird | |
|---|---|
 | |
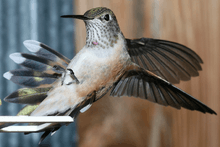
| Adult male at a feeder | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| (unranked): | Cypselomorphae |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Subfamily: | Trochilinae |
| Genus: | Selasphorus |
| Species: | S. platycercus |
| Binomial name | |
| Selasphorus platycercus (Swainson, 1827) | |
The broad-tailed hummingbird (Selasphorus platycercus) is a medium-sized hummingbird, nearly 4 in (10 cm) in length. It is one of seven species in the genus Selasphorus.
Male and female both have iridescent green backs and crowns and a white breast. The male has a gorget (throat patch) that shines with a brilliant pink-red iridescence and a broad, predominantly black tail accented with varying amounts of green, rufous, and occasionally white. The female is much duller with pale rust-colored sides and outer tail feathers banded in rufous, green, black, and white. In flight the male's wings produce a distinct trilling sound diagnostic for this species.[2][3]
The summer range of the broad-tailed hummingbird extends across mountain forests and meadows throughout the Western United States, specifically the central Rocky Mountain region and southwards; the resident birds range from the cordilleran mountain areas of northern Mexico as far south as Guatemala. At summer's end the northerly birds migrate and overwinter in the southern part of their range. This species is somewhat vagrant, especially wintering birds, and is regularly seen in El Salvador where it does not breed. They occur at altitudes ranging from 700–900 m (2,300–3,000 ft) up to 3,350 m (10,990 ft) ASL in the tropical parts of their range.[4]
Broad-tailed hummingbirds consume the typical hummingbird diet of flower nectar[5] and arthropods, which are taken in flight and gleaned from vegetation. Sap from trees and shrubs is used as a nectar substitute.[6]

Nests are small cup of plant fibers woven together and bound to a branch with collected spider webs. The female lays two plain white eggs that she alone will incubate for 16 to 19 days.[6] Young broad-tailed hummingbirds fledge about 23 days after hatching. This species is known to hybridize with other hummingbird species, including black-chinned, white-eared, and Costa's.[3][7]
This species is not considered endangered; it appears to be able to adapt quite well to human-modified habitat and frequents shade coffee plantations.[4]
Footnotes
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Selasphorus platycercus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ "Broad-tailed hummingbird Selasphorus platycercus". Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter. United States Geological Survey (USGS). Retrieved 2008-09-03.
- 1 2 Williamson 2001
- 1 2 Herrera et al. (2006)
- ↑ E.g. Ice-cream-bean (Inga edulis): Herrera et al. (2006)
- 1 2 Calder and Calder 1992
- ↑ Huey (1944)
References
- Herrera, Néstor; Rivera, Roberto; Ibarra Portillo, Ricardo & Rodríguez, Wilfredo (2006): Nuevos registros para la avifauna de El Salvador. ["New records for the avifauna of El Salvador"]. Boletín de la Sociedad Antioqueña de Ornitología 16(2): 1-19. [Spanish with English abstract] PDF fulltext
- Calder, William A., and Lorene Calder (1992). Broad-tailed Hummingbird (Selasphorus platycercus). In The Birds of North America. No. 16 (A. Poole and F. Gill, eds.). The Birds of North America, Inc., Philadelphia, PA.
- Huey, Laurence M. (1944). A hybrid Costa's × Broad-tailed hummingbird. Auk 61(4): 636-637. PDF fulltext
- Williamson, S. L. (2001). A Field Guide to Hummingbirds of North America (Peterson Field Guide Series). Houghton Mifflin. Co., Boston, MA.
External links
- Broad-tailed hummingbird nest with chicks - Birds of North America
- Broad-tailed hummingbird photo gallery
