Square piano
The square piano is a piano that has horizontal strings arranged diagonally across the rectangular case above the hammers and with the keyboard set in the long side, with the sounding board above a cavity in the short side. It is variously attributed to Silbermann and Frederici and was improved by Petzold and Babcock. The English and Viennese square pianos were built in many different designs, including within the action as well as general appearance, from roughly 1760. Because of the competitive industry and relative youth of the instrument design itself, experimentation ensued in the early years, creating a range of moderators (sound-altering effects) and other technical devices (knee levers; hand stops) not seen today. In London, the explosion of the trade is generally attributed to the maker Zumpe. The overwhelming popularity of his instruments was due to inexpensive construction and price. In the 1860s metal frames were developed for square pianos, meaning that higher string tensions and therefore greater volumes were possible; however the size increases meant that the upright piano design was more economical, and so the upright replaced the square as the most common home instrument. Built in quantity through the 1890s in the United States, Steinway's celebrated iron framed over strung squares were more than two and a half times the size of Zumpe's wood framed instruments that were successful a century before. Whilst many view square pianos as a 'proto-piano', because they do not have the range, volume or delicacy of touch available on modern instruments, they have a sound and playability all their own, and should be treated as a different instrument to the modern piano altogether.
Gallery
 Square piano (though this example is not exactly rectangular)
Square piano (though this example is not exactly rectangular) Square piano with open lid
Square piano with open lid Swedish painting of woman playing a square piano.
Swedish painting of woman playing a square piano.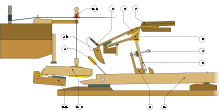 English double action with check, ca.1830 (developed from Geib, 1786
English double action with check, ca.1830 (developed from Geib, 1786 American single action with overdamper, ca.1870 (developed from Petzold, 1809)
American single action with overdamper, ca.1870 (developed from Petzold, 1809) Zumpe single action, 1766
Zumpe single action, 1766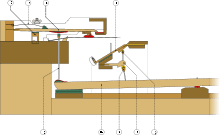 Erard double pilot action, 1790 "Zumpe's second action" ca.1788
Erard double pilot action, 1790 "Zumpe's second action" ca.1788
See also
- Finchcocks, a collection of early keyboard instruments in Kent which has many original square pianos.
References
- Goold, Madeline, Mr. Langshaw's Square Piano, BlueBridge, 280 pages
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Square pianos. |
- Andrew Lancaster Square Pianos
- History of the square piano
- The Square Piano (Virtual Piano Museum)
- Square piano examples and history
- Lucy Coad Square Pianos