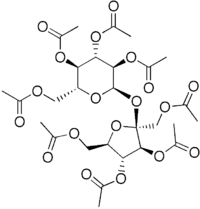
Sucrose octaacetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acetic acid [(2S,3S,4R,5R)-4-acetoxy-2,5-bis(acetoxymethyl)-2-[ [(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-triacetoxy-6-
(acetoxymethyl)-2-tetrahydropyranyl]oxy]-3-tetrahydrofuranyl] ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| 126-14-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.339 |
| PubChem | 31340 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H38O19 | |
| Molar mass | 678.59 g/mol |
| Appearance | needles |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 at 16 °C |
| Melting point | 86.5 °C (187.7 °F; 359.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) at 1 mmHg |
| slightly soluble in water | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, benzene, chloroform[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Sucrose octaacetate is an acetylated derivative of sucrose. It is used commercially and industrially in a variety of applications. It is used as an inert ingredient in pesticides and herbicides. As of December 2005, sucrose octaacetate was determined by the EPA to be usable as an inert ingredient in pesticides due to its low toxicity.[2]
Sucrose octaacetate has been approved by the FDA as a food additive. It has a bitter taste which has led to its use as bitterant and an aversive agent. The chemical has also been used to determine tasters from non-tasters in mice.[3]
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 3–506, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Inert Reassessment: Sucrose Octaacetate (CAS Reg. No. 126-14-7)
- ↑ Intermediate sucrose octa-acetate sensitivity suggests a third allele at mouse bitter taste locus Soa and Soa-Rua identity - Harder et al. 17 (4): 391 - Chemical Senses
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/16/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.