Tenuazonic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
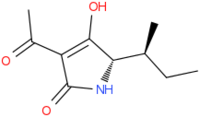
| IUPAC name
(5S)-3-Acetyl-5-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-4-hydroxy-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-2-one[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 610-88-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL511015 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.201 |
| PubChem | 101949 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 197.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.5 |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
* 182 mg kg−1 (Mice, ♂, oral)[2] |
| Pharmacology | |
| Ingested or Inhaled | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Tenuazonic acid is a mycotoxin produced by Alternaria species.[4] It is a powerful eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor.[5]
In 1991 Tenuazonic acid was reported to inhibit skin tumor promotion in mice.[6]
References
- ↑ "Tenuazonic Acid". Cayman Chemical.
- 1 2 Miller, F. A. et al.; Nature, 200 (1963), S. 1338–1339
- ↑ Smith, E. R. et al.; Cancer Chemother. Rep. 52 (1968), S. 579–585.
- ↑ Alisa D. Hocking (Editor), John I. Pitt (Editor) and Robert A. Samson (Editor): Advances in Food Mycology. Springer 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-28385-2; p. 23
- ↑ Dilip K. Arora and Arora K. Arora: Fungal Biotechnology in Agricultural, Food, and Environmental Applications. Marcel Dekker Inc; illustrated edition 2003; ISBN 978-0-8247-4770-1; p. 336
- ↑ Tenuazonic acid page from Fermentek
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/16/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.