Thyroplasty
Thyroplasty is a phonosurgical technique designed to improve the voice by altering the thyroid cartilage of the larynx (the voice box), which houses the vocal cords in order to change the position or the length of the vocal cords.
Types
There are four different types of thyroplasty procedures described by Isshiki:
- Type 1 thyroplasty – Medialization of the vocal folds (most common surgery for unilateral vocal cord paralysis).
- Type 2 thyroplasty – Lateralization of the vocal folds (in case of airway insufficiency after Laryngeal trauma).
- Type 3 thyroplasty – Shortening of the vocal folds (done to lower the vocal pitch).
- Type 4 thyroplasty – Lengthening of the vocal folds (done to raise the vocal pitch).[1]
Type 1 thyroplasty (medialization thyroplasty)
It is the most commonly used surgical procedure to correct unilateral vocal cord paralysis (a condition where the vocal cord of one side is paralysed).
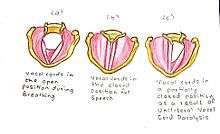
Procedure
In this type of thyroplasty, a rectangular portion of the thyroid cartilage is mobilized and pushed towards the medial side using a piece of silastic block of proper shape under local anesthesia.[2]
Earlier, the piece of the thyroid cartilage was kept along with implant and the stitches were taken, but nowadays, the piece of the thyroid cartilage is cut and removed to avoid complications.

Types of procedures
Currently, there are four types of implant procedures which are used to perform type 1 thyroplasty.
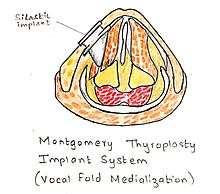
- Montgomery Thyroplasty Implant system
This system was discovered after years of research and the main advantage of this implant system is that it eliminates the process of customizing the implant at the time of surgery.This system consists of different sizes and shapes of shims made of silastic. It has the most proven success rate and the duration of the procedure is slow in comparison to other implant system.The other advantage is that it does not require suturing. It has reduced incidence of trauma.
- VoCoM system (vocal fold medialization)
This system consists of different sizes and shapes of implants made from hydroxyapatite (a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite). It helps in achieving accurate vocal fold medialization. This procedure is technically reversible. But it should be used in candidates of permanent implantation due to its biocompatible clinical use lasting for nearly a decade.
- TVFMI system
This system generally consists of two sizes of implants made out of pure titanium. It has a lot of advantages and the main one is that it reduces the operative time. Titanium is more safe than other implants. It has great biocompatibility. The implants are available in only two variants and they are designed in such a way that they ensure optimal fixation. The implant can be easily made as the titanium sheet is easy to shape. The technique is relatively simple and does not require expensive instruments.
- Gore-Tex Implant system
In this type of implant system, the implant is made of homopolymer of polytetrafluoroethylene in form of minute beads arranged in a fine fiber mesh. It is malleable and can be inserted through a small window.[3]
Indications
- Unilateral vocal cord paralysis where one vocal cord out of the two is paralysed.
- Symptomatic glottic insufficiency (dysphonia, aspiration) which leads to incomplete glottic closure which in turn results in failure to produce proper sound.
- Age-related vocal fold atrophy leading to glottic insufficiency.[4]
Contraindications
- Malignant diseases of the endolaryngeal mucosa.
- Previous history of radiation therapy to the larynx for treatment of laryngeal and hypolaryngeal cancers.
- Poor abduction of the contralateral vocal folds.
Complications
- Airway obstruction is the most common complication.
- Implant migration or extrusion in cases where proper stitches are not taken.
- Wound infection.
- Penetration of the endolaryngeal mucosa.
- Incomplete glottal closure in 10–15% of patients.[5]
Advantages
- The most important advantage is that this procedure is reversible.
- It is long-lasting.
- It can be performed with minimal anesthesia.
- No discomfort to the patient.
Disadvantages
- It is an open procedure.
- It is technically more difficult.
- There may be limited closure of the posterior glottis.
Limitations
- There is increase in average phonation time (from 4.6 seconds to 15 seconds).
- It provides static change to the laryngeal framework but does not have any effect on the dynamic function.[6]
Type 2 thyroplasty (lateralization thyroplasty)
It is a surgical procedure used in conditions like adductor spasmodic dysphonia (a condition in which there is distortion of the voice due to excessively tight closure of the glottis on phonation). Generally, lateralization thyroplasty is intended to prevent this tight closure of the glottis at the terminal stage of phonation by lateralizing the position of the vocal cord. This is a completely mechanical process.
Procedure
An incision is made at midline of the thyroid cartilage. A silicon wedge is used to fix the incised thyroid cartilage in the newly abducted position.
Modified technique
A specially deviced titanium bridge is used instead of silicon wedge. Nowadays, instead of one titanium bridge, two titanium bridges are used for permanent fixation of the thyroid cartilage.
Indications
- The only known indication for type 2 thyroplasty is adductor spasmodic dysphonia, a condition characterized by involuntary movements of muscles of the larynx during speech.
Contraindications
Type 3 thyroplasty (relaxation thyroplasty)
This procedure is generally done to lower the vocal pitch by shortening the thyroid ala.
Procedure
In this thyroplasty, the relaxation of the vocal cords is done by antero-posterior shortening of the thyroid ala.
Indications
- It is most commonly indicated in males with high-pitch voices and those who are resistant to voice therapy.
- In people with spasmodic dysphonia.
- In people who have stiff vocal folds with high-pitched breathy voices.
Type 4 thyroplasty (stretching thyroplasty)
Procedure
This procedure is done to elevate the vocal pitch. This procedure consists of lengthening of the thyroid cartilage. It includes cricothyroid approximation.
Indications
- It is done in people with bow-shaped vocal folds.
- Androphonia (condition characterized by low vocal pitch).[8]
Combination
In some specific conditions, different types of thyroplasties are combined for the desired results.
Medialization thyroplasty with arytenoid adduction (rotation technique)
Purpose
The main purpose of this combination is the medialization of the entire vocal cord (anterior and posterior).
Indications
- Open posterior glottis.
- In people with high vagal paralysis.
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis with lateralized arytenoid.
- Non-rotating aarytenoid.
Medialization thyroplasty with arytenoid adduction (fixation technique)
Purpose
- Medial vocal cord fixation.
Indications
- Arytenoid fracture where there is anterior dislocation of the arytenoid cartilage.
- In cricoarytenoid joint ankylosis where there is failed arytenoid adduction.
Medialization thyroplasty (type 1) with stretching thyroplasty (type 4)
Purpose
- The main purpose of this combination is stretching of the vocal cord with medialization of the affected side.
Indications
- Unilateral superior laryngeal nerve weakness.
Medialization thyroplasty (type 1) with relaxation thyroplasty (type 3)
Purpose
- The main aim of this combination is relaxation and increased mass of one vocal cord.
Indications
- In males with high-pitched, presbyphonic voice.
Bilateral medialization thyroplasty
Purpose
- Medialization of both the vocal cords.
Indications
- Open anterior glottis.
- In presbyphonia where there is bilateral vocal cord weakness.
- When there is bilateral loss of muscle mass.
- Tremor-induced abductor spasmodic dysphonia (AbSD).
Bilateral relaxation thyroplasty
Purpose
- Relaxation of both the vocal cords.
Indications
- In males who have an overly high-pitched voice.
- Stable abductor spasmodic dysphonia (AbSD)[9]
References
- ↑ Sataloff, Robert T.; Chowdhury, Farhad; Portnoy, Joel E.; Hawkshaw, Mary J.; Joglekar, Shruti (30 September 2013). Surgical Techniques in Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery: Laryngeal Surgery. JP Medical Ltd. p. 208. ISBN 9789350906521.
- ↑ Remacle, Marc; Eckel, Hans Edmund. Surgery of Larynx and Trachea. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540791362.
- ↑ Remacle, Marc; Eckel, Hans Edmund. Surgery of Larynx and Trachea. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 59. ISBN 9783540791362.
- ↑ Bailey, Byron J. Atlas of Head & Neck Surgery--otolaryngology (Second ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 636. ISBN 9780781729079.
- ↑ Flint, Paul W.; Haughey, Bruce H.; Robbins, K. Thomas; Thomas, J. Regan; Niparko, John K.; Lund, Valerie J.; Lesperance, Marci M. Cummings Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 930–945. ISBN 9780323278201.
- ↑ Lin, Harrison W.; Roberts, Daniel S.; Harris, Jeffrey P. Cummings Review of Otolaryngology. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9780323427999.
- ↑ Hathiram, Bachi T.; Khattar, Vicky S. Atlas of Operative Otorhinolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery: Voice and Laryngotracheal Surgery. JP Medical Ltd. ISBN 9789350904824.
- ↑ "Phonosurgery Phonosurgery" (PDF).
- ↑ Remacle, Marc; Eckel, Hans Edmund. Surgery of Larynx and Trachea. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540791362.