USS Winslow (TB-5)
.jpg) USS Winslow (TB-5), photographed circa 1898, with a small "water taxi" rowing past her bow. | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Winslow |
| Namesake: | Rear admiral John Ancrum Winslow |
| Ordered: | 26 July 1894 (authorised) |
| Builder: | Columbian Iron Works and Dry Dock Co., Baltimore, MD |
| Laid down: | 8 May 1896 |
| Launched: | 8 May 1897 |
| Sponsored by: | Miss E. H. Hazel |
| Commissioned: | 29 December 1897 |
| Decommissioned: | 12 July 1910 |
| Struck: | 12 July 1910 |
| Identification: | TB-5 |
| Fate: | sold, January 1920 |
| General characteristics [1] | |
| Class and type: | Foote-class torpedo boat |
| Displacement: | 142 long tons (144 t)[2] |
| Length: | 161 ft 6.75 in (49.2443 m) |
| Beam: | 16 ft (4.9 m) |
| Draft: | 5 ft 9 in (1.75 m) (mean)[2] |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | |
| Complement: | 20 officers and enlisted |
| Armament: |
|
USS Winslow (Torpedo Boat No. 5/TB-5) was a United States Navy torpedo boat noted for its involvement at the First and Second Battle of Cardenas during the Spanish–American War. She was named for Rear Admiral John Ancrum Winslow.
History
The first Winslow (Torpedo Boat No. 5) was laid down on 8 May 1896 at Baltimore, Md., by the Columbian Iron Works; launched on 8 May 1897; sponsored by Miss E. H. Hazel; and commissioned on 29 December 1897 at the Norfolk Navy Yard, Lt. John B. Bernadou in command.
On 6 January 1897, Winslow departed Norfolk and proceeded via New York City to Newport, R.I., where she loaded torpedoes and drilled her crew in torpedo firing before returning to Hampton Roads on the 30th.
During Winslow's seven-week sojourn at Norfolk, the battleship USS Maine (ACR-1) sank in Havana Harbor; and the United States began drifting steadily closer to war with Spain. On 11 March 1897, Winslow steamed out of Norfolk and headed south to Key West, Florida., a base much nearer the probable theater of operations in the approaching conflict. The warship operated from that port through the remainder of March and the first three weeks in April. On Monday, the 25th, President William McKinley reluctantly ratified a joint resolution of Congress which proclaimed that a state of war had existed between the United States and Spain since the previous Thursday.
Battle at Cárdenas
During the next fortnight, the warship patrolled the northern coast of Cuba near Havana, Cárdenas, and Matanzas. On 8 May, she engaged in battle and forced three Spanish gunboats back into the harbor of Cardenas. Early in the morning of 11 May 1898, Winslow left her blockade station off Matanzas and proceeded to Cardenas to replenish her coal bunkers. Upon reporting to USS Wilmington for that purpose, she was ordered to take on a Cuban pilot and scout the entrance of Cardenas Bay for mines. Winslow then entered the bay in company with USRC Hudson. The two ships conducted a meticulous search of the channel, found no mines, and returned to Wilmington around noon to make their report. At this point, the commanding officer of Wilmington decided to take his ship, escorted by Winslow and Hudson, into Cardenas harbor in search of three Spanish gunboats reportedly in port. Winslow marked shoal water to Wilmington's portside and, upon reaching a point about 3,000 yards (2,743.2 m) from the city, sighted a small, gray steamer moored alongside the wharf. The torpedo boat received orders to move in closer to determine whether or not the vessel was an enemy warship.
By 1335, Winslow reached a point approximately 1,500 yards (1,371.6 m) from her quarry when a white puff of smoke from the Spaniard's bow gun signaled the beginning of an artillery duel which lasted one hour and 20 minutes. Winslow immediately responded with her 1-pounders. The Spanish concentrated their efforts on little Winslow, and she soon received a number of direct hits. The first shot to score on the torpedo boat destroyed both her steam and manual steering gear. While her crew tried to rig some type of auxiliary steering system, Winslow used her propellers to keep her bow gun in position to fire. Then, all at once, she swung broadside to the enemy. Almost immediately, a shot pierced her hull near the engine room and knocked the port main engine out of commission. She maneuvered with her remaining engine to evade enemy fire and maintained a steady return fire with her 1 pounders. At this point, Wilmington and Hudson brought their guns to bear on the Spanish ship and shore, and the combined fire of the three American warships put the Spanish gunboat out of action.
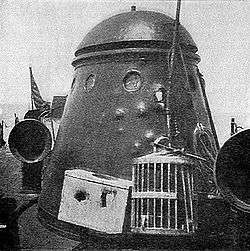
All but disabled, Winslow requested Hudson to tow her out of action. The revenue cutter approached the stricken torpedo boat and rigged a tow line between the two ships. As Hudson began to tow Winslow out to sea, one of the last Spanish shells to strike the torpedo boat hit her near the starboard gun and killed Ensign Worth Bagley who had been helping to direct the warship's maneuvers by carrying instructions from the deck to the base of the engine room ladder. Ens. Bagley had the dubious distinction of being the first naval officer killed in the Spanish–American War; and in memory of his sacrifice and devotion to duty, USS Bagley (TB-24), USS Bagley (DD-185), USS Bagley (DD-386) and USS Bagley (FF-1069) each carried the name USS Bagley.
Badly damaged, Winslow was towed clear of the action. Her commanding officer and a number of others in her crew were wounded. Lt. Bernadou saw that the dead and wounded were transferred to Hudson, and he then left the ship himself after turning command over to Chief Gunner's Mate George F. Brady, who—along with Chief Gunner's Mate Hans Johnsen and Chief Machinist Thomas C. Cooney—later received the Medal of Honor and was promoted to warrant officer.
The day following the engagement, Winslow arrived at Key West for temporary repairs there and at Mobile, Ala. She returned to Key West for 10 days before sailing north on 16 August. After brief stops at Port Royal, S.C., and at Norfolk, Va., the ship reached New York on 27 August and was placed out of commission at the New York Navy Yard on 7 September 1898 to begin more extensive repairs.
Post Spanish–American War
But for a short voyage to Philadelphia in mid-October, Winslow remained inactive until early in 1901, first at New York, in a decommissioned status, and later at the Norfolk Navy Yard where she was officially listed as "in reserve." In any event, the torpedo boat had returned to full commission by 30 June 1901 and, assigned to the Naval Torpedo Station at Newport, spent the next three years training naval officers and enlisted men in the techniques of torpedo firing and helping them to polish their skills in gunnery and shipboard engineering. In all probability, she also participated in some of the work done to improve the "automotive" torpedo.
Information on her activities between July 1904 and February 1906 is extremely sketchy, but she probably spent the majority of that time either in reserve or out of commission at New York. Whatever the case, Winslow was recommissioned at the New York Navy Yard on 16 February 1906 and steamed south to Norfolk, where she was placed in the Reserve Torpedo Flotilla. Sometime during fiscal year 1909, she was transferred to Charleston, S.C., though she remained in reserve.
On 1 June 1909, the torpedo boat was turned over to the Massachusetts Naval Militia at Charlestown. She moved north to Boston where she served as a school ship for volunteer seaman of the local naval militia until the following November. On 2 November 1909, the Massachusetts Naval Militia returned Winslow to the Navy, and she was placed in reserve at the Boston Navy Yard until the summer of 1910. On 12 July 1910, Winslow was placed out of commission at Boston, and her name was struck from the Navy list. In January 1911, she was sold to H. Hanson of New York City.
References
- ↑ "USS Winslow (TB-5)". Navsource.org. Retrieved July 8, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Table 10 - Ships on Navy List June 30, 1919". Congressional Serial Set. U.S. Government Printing Office: 714. 1921.
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
- Additional technical data from Gardiner, Robert (1979). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Conway Maritime Press. p. 160. ISBN 0-85177-133-5.
External links
- Photo gallery of Winslow at NavSource Naval History