WCW World Heavyweight Championship
| WCW World Heavyweight Championship | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The Big Gold Belt represented the WCW World Heavyweight Championship in 1991 and then from 1994–2001 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Promotion |
WCW (January 11, 1991 – March 23, 2001) WWF (March 26, 2001 – December 9, 2001) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Date established | January 11, 1991 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Date retired |
December 9, 2001 (unified with the WWF Championship) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Past design(s) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other name(s) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
The WCW World Heavyweight Championship was a professional wrestling world heavyweight championship originally used in World Championship Wrestling (WCW) and later, the World Wrestling Federation (WWF, now WWE). It was the original world title of the World Championship Wrestling promotion, spun off from the NWA World Heavyweight Championship. It existed in WCW from 1991 to 2001.
Following the acquisition of WCW by the WWF in March 2001, it became one of two world titles in the WWF, with its name being immediately abbreviated to the WCW Championship and finally, the World Championship in November. It continued to complement the then-WWF Championship until the following month, when both titles were unified to create the Undisputed WWF Championship. The Undisputed title retained the lineage of the WWF Championship, and the World Championship was retired.
Ric Flair was the first holder of the WCW World Heavyweight Championship, with Chris Jericho being the last.[1] The title was the second of six to be represented by the historic Big Gold Belt, first introduced in 1986.
History
Formation
In December 1988, Turner Broadcasting purchased Jim Crockett Promotions, which had promoted under the name "NWA World Championship Wrestling". While the promotion remained a member of the National Wrestling Alliance (NWA), the use of the NWA name was gradually reduced on televised programming, in favor of the name "World Championship Wrestling", or "WCW". On January 11, 1991, Ric Flair defeated Sting to win the NWA World Heavyweight Championship and was recognized as the WCW World Heavyweight Champion. The new championship was not initially represented by its own title belt, and WCW continued to use the NWA World Heavyweight Championship title belt. Because of this, WCW regularly claimed the NWA World Heavyweight Championship lineage for its own championship.
Big Gold Belt
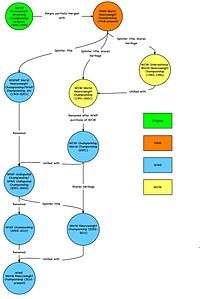
On July 1, 1991, a creative disagreement with WCW Executive Vice President Jim Herd led to Flair leaving WCW for Vince McMahon's World Wrestling Federation. When Herd refused to return Flair's $25,000 deposit (that was left with the NWA), Flair kept the "Big Gold Belt" that had represented the NWA World Heavyweight Championship. WCW was forced to use a belt owned by Dusty Rhodes from the defunct Championship Wrestling from Florida with a gold-colored plate tacked on with the words "WCW World Heavyweight Champion", which was awarded to Lex Luger after he defeated Barry Windham in a cage match for the vacant championship at 1991's Great American Bash. Shortly after the Bash, a new, original WCW World Heavyweight Championship belt was created.
In late 1991, the Big Gold Belt was used for the revived NWA World Heavyweight Championship, a co-promotional gimmick between WCW and New Japan Pro Wrestling. In September 1993, WCW left the NWA for good over a dispute regarding the other NWA members demanding that NWA world champion be available for booking, and due to the use of the NWA World Heavyweight Championship on syndicated programming recorded months in advance. By fall 1993, Rick Rude was appearing at the "Disney Tapings" as the NWA World Heavyweight Champion, despite the fact that in regards to the storyline, Flair, who had returned to WCW and regained the NWA title, was still champion. After leaving the NWA, WCW kept the Big Gold Belt, and it was renamed the WCW International World Heavyweight Championship.
Unification
At Starrcade in December 1993, Flair won the WCW World Heavyweight Championship, by defeating Vader. WCW decided to unify the WCW World Heavyweight Championship (represented by the new belt) and International Championship (represented by the "Big Gold Belt"), by having Flair wrestle Sting in June 1994. Flair won and the WCW International Heavyweight Championship belt replaced the old WCW World Heavyweight Championship belt, while the International Heavyweight Championship itself was dropped.
During Hollywood Hogan's runs as champion in 1996–1997 and again in 1998–1999 (ie from his second to his fifth reign as champion), as part of the New World Order (nWo) storyline, the title was spray painted each time with the "nWo" initials and often announced during Hogan's title defenses as the nWo/WCW World Heavyweight Championship, while referred to by nWo members only as the nWo World Heavyweight Championship.
Acquisition by the WWF
In March 2001, the World Wrestling Federation (WWF, now WWE) purchased the assets of World Championship Wrestling. Soon after, "The Invasion" took place and four of WCW's championships were defended on WWF programming including the WCW World Heavyweight Championship, which became known as the "WCW Championship". The WWF carried over the title, along with the United States Heavyweight Championship, Cruiserweight Championship, and the WCW Tag Team Championship.
After the "Invasion" concluded at Survivor Series in 2001, the title was rebranded as the "World Championship". The title was then unified with the WWF Championship at Vengeance, where Chris Jericho defeated The Rock and Stone Cold Steve Austin to win the World Championship and the WWF Championship respectively. As a result, Jericho was the last World Champion,[2][3] and he became the first Undisputed WWF Champion.[4]
Reigns
See also
- NWA World Heavyweight Championship
- WCW International World Heavyweight Championship
- World Heavyweight Championship (WWE)
- WWE World Championship
References
- ↑ WCW World Championship. WWE.com. Retrieved on 2013-09-05.
- ↑ WCW World Champion – Chris Jericho at WWE.com
- ↑ WCW World Heavyweight Championship history, from Wrestling-Titles.com
- ↑ "WWWF/WWF/WWE World Heavyweight Title". Wrestling-titles.com. Retrieved 2007-03-18.