Wahgoshig First Nation
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| (circa 2009: 250 [1]) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Canada – Ontario |
| Abitibi 70 | |
|---|---|
| Indian reserve | |
| Abitibi Indian Reserve No. 70 | |
|
| |
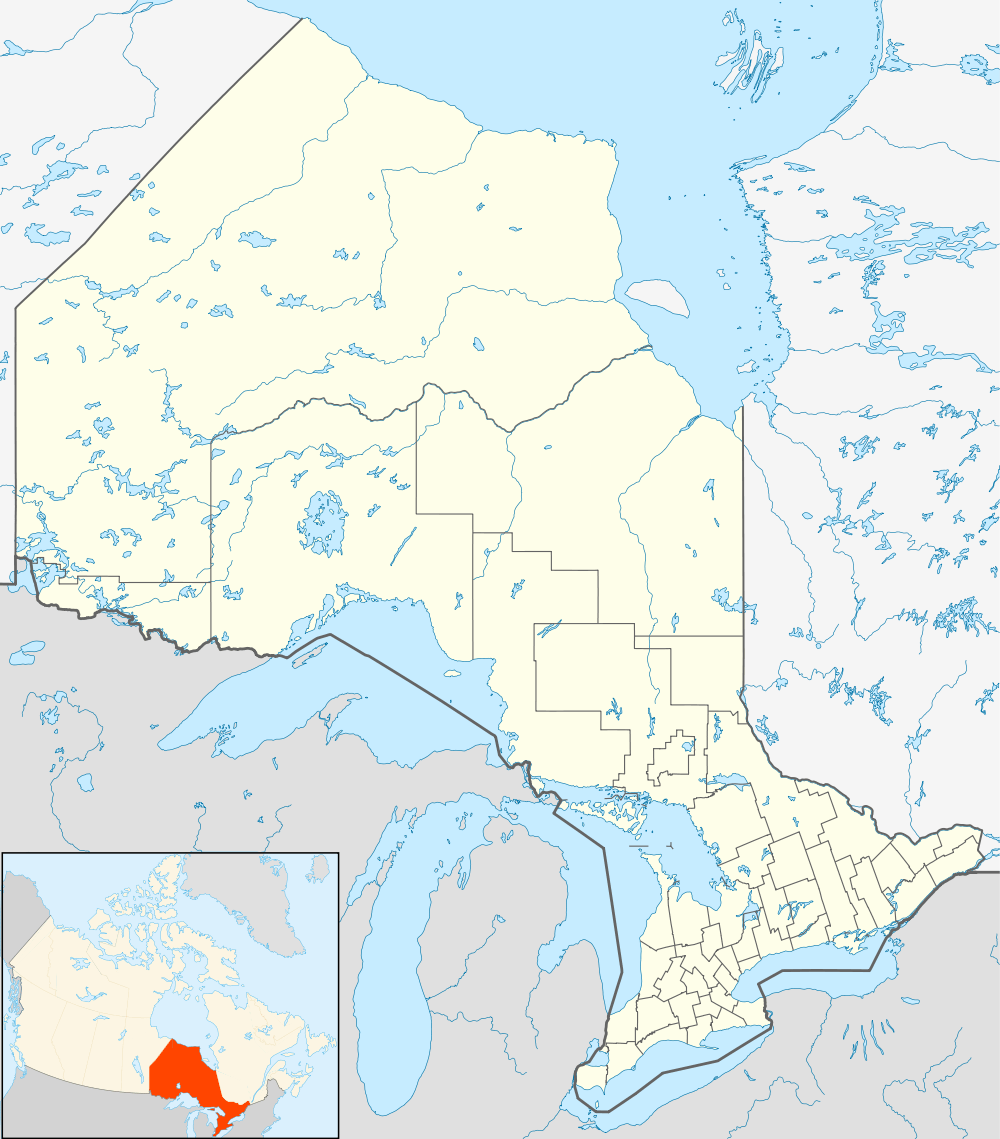 Abitibi 70 | |
| Coordinates: 48°38′N 79°58′W / 48.633°N 79.967°WCoordinates: 48°38′N 79°58′W / 48.633°N 79.967°W | |
| Country |
|
| Province |
|
| District | Cochrane |
| First Nation | Wahgoshig |
| Government | |
| • Chief | Dave Babin |
| • Elder Councillor | Emile Paul Chookomolin |
| Area[2] | |
| • Land | 78.70 km2 (30.39 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[2] | |
| • Total | 126 |
| • Density | 1.6/km2 (4/sq mi) |
| Website |
wahgoshigfirstnation |
Wahgoshig First Nation, formerly known as Abitibi-Ontario Band of Abitibi Indians or simply as Abitibi, is an Anishinaabe (Algonquin and Ojibwa) and Cree First Nation band governments whose reserve communities are located near Matheson in Cochrane District in northeastern Ontario, Canada. They have reserved for themselves the 7,770.1 hectares (19,200.3 acres) Abitibi Indian Reserve No. 70 on the south end of Lake Abitibi. In January, 2008, the First Nation had 270 people registered with the nation, of which their on-reserve population was 121.
History
The first recorded reference to the native people about Lake Abitibi was in The Jesuit Relations in 1640.[3] They were a nomadic group of hunter-gatherers, whose traditional territory straddled a large segment of what is now northeastern Ontario and northwestern Quebec. Their hunting and trapping grounds extended and still extend east and northeast of Long Sault to Pierre, Harris, and Montreuil Lakes in Ontario, and on a parallel line into Quebec and as far east as Amos. The southernmost limit of the territory was a little south of Kirkland Lake in Ontario and Rouyn In Quebec. Cochrane, Ontario is the approximately western boundary.
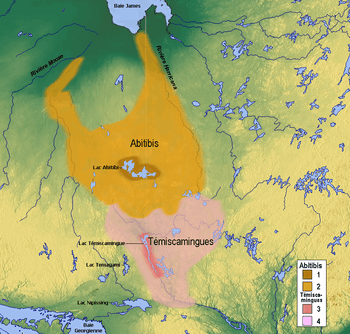
The Abitibi Indian Reserve No. 70 was created when the James Bay Treaty (Treaty 9) was signed at the Hudson's Bay Company post on Lake Abitibi in Quebec on June 7, 1906. It encompasses 19,239 acres (7,786 ha), or 30 square miles (78 km2). However, the treaty commissioners revealed that they were only authorized to negotiate with the Anishinaabe whose hunting grounds were in Ontario. The Abitibi Indians who were part of the same group, but whose hunting territory lay within Quebec, were told that negotiations for a reserve for them would occur later, but the Quebec government stalled that process for a considerable time after a treaty was signed with the Ontario band.
Two years after the signing of the James Bay Treaty the Canadian federal government still had not been able to get Quebec to set aside a reserve for the Quebec Indians. It then arranged with the Quebec government to bring them under Treaty 9, which meant that they would receive annuities and would share in the revenues allocated to Abitibi 70, and income from this reserve was, and still is, divided on a per capita basis. This is the origin of much of the economic disparity that Wahgoshig First Nation contends with today; due to the way disbursements are set up through the federal government's intervention into their affairs, the Wahgoshig people receive only a minor share of any revenue that they may generate from natural resources on Wahgoshig Reserve. This has proved to be a disincentive towards developing the on-reserve natural resources.
Until 1972, the Department of Indian Affairs in Quebec administered the affairs of both the Abitibi-Dominion Band of Abitibi Indians (located in Quebec) and the Abitibi-Ontario Band of Abitibi Indians. From 1972 onward, Indian Affairs in Sudbury, Ontario, took over the affairs of the Abitibi-Ontario band. In 1979, the Abitibi-Dominion Band changed its name to Abitibiwinni First Nation, and the Abitibi-Ontario Band became Wahgoshig First Nation.
Governance
The Wahgoshig First Nation have a Custom Electoral system of government. Elected officials have 3-year term. The current elected officials consists of Chief David Babin and five Councillors: Lindy Black, George Sackaney, Denis Tremblay Sr, Edward Black and Paul McKenzie. Their term began on November 21, 2008.
As a signatory to Treaty 9, the First Nation is a member of the Wabun Tribal Council, a Regional Chief's Council who is a member of the Nishnawbe Aski Nation, a Tribal Political Organization representing majority of First Nations in Northern Ontario. However, the Wahgoshig First Nation is a political member of the Algonquin Anishinabeg Nation Tribal Council since November 2000, together with other nations which Wahgoshig First Nation maintained strong historical ties.
There is an on-reserve village that occupies about 25 ha of the 70 ha flat land. West of the village, the land becomes undulating and it contains many wet swampy areas - ideal moose habitat. Moose, bears, grouse and other game are quite abundant in the area.
The reserve is served by Highway 101, which provides access to the 5.8 km long reserve road, approximately 50 km east of Matheson, Ontario, within a few miles of the western Quebec border. The north end of the reserve meets the south shore of Lake Abitibi, which separates the two provinces.
| Canada census – Wahgoshig First Nation community profile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | |||
| Population: | 114 (-10.2% from 2001) | ||
| Land area: | 78.7 km2 (30.4 sq mi) | ||
| Population density: | 1.4/km2 (3.6/sq mi) | ||
| Median age: | N/A (M: N/A, F: N/A) | ||
| Total private dwellings: | 39 | ||
| Median household income: | $N/A | ||
| References: 2006[4] | |||
- N/A = Data Not Available.
Services
For the Abitibi village of about 25 ha, the First Nation provides the following services:
- band office
- health clinic
- warehouse / fire hall
- public works garage
- community hall
Wahgoshig is policed by the Nishnawbe-Aski Police Service, an Aboriginal-based service.
References
- ↑ "Member Community Page". Algonquin Anishinabeg Nation Tribal Council.
- 1 2 "Abitibi 70 census profile". 2011 Census of Population. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2015-05-12.
- ↑ Francis, Daniel (01/08/07). "Lake Abitibi". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2014-03-17. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "2006 Community Profiles". Canada 2006 Census. Statistics Canada. March 30, 2011. Retrieved 2009-02-24.
External links
- Wahgoshig First Nation Website
- AANDC profile
- Information from Township of Black River-Matheson
- Algonquin Anishinabeg Nation Tribal Council profile
- Abitibi 70 Population Data
 |
Lake Abitibi |  | ||
| Unorganized North Cochrane | |
Unorganized North Cochrane | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Unorganized North Cochrane |
