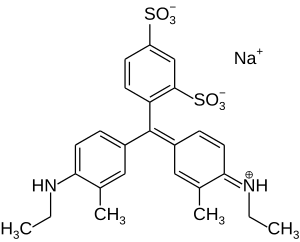
Xylene cyanol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Acid Blue 147 xylene cyanole xylene cyanol FF xylene cyanole FF C.I. 42135 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 2650-17-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 21106494 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.334 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H27N2NaO6S2 | |
| Molar mass | 538.61 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Xylene cyanol can be used as a color marker, or tracking dye, to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Bromophenol blue and orange G can also be used for this purpose.
Once mixed with the sample, concentration of xylene cyanol is typically about 0.005% to 0.03%.
Migration speed
In 1% agarose gels, xylene cyanol migrates at about the same rate as a 4 to 5 kilobase pair DNA fragment [1] (although this depends on the buffer used). Xylene cyanol on a 6% polyacrylamide gel migrates at the speed of a 140 base pair DNA fragment. On 20% denaturating (7 M urea) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), xylene cyanol migrates at about the rate of 25 bases oligonucleotide.
Conjugation
Due to its large number of double bonds separated by single bonds, the molecule is said to be highly conjugated.
References
- ↑ Lela Buckingham & Maribeth L. Flaws. Molecular Diagnostics.- Fundamentals, Methods, & Clinical Applications. F.A. Davis Company, 2007, p. 91