Zirconium(IV) iodide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
zirconium tetraiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 13986-26-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 75903 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.332 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ZrI4 | |
| Molar mass | 598.842 g/mol |
| Appearance | orange-yellow crystalline hygroscopic |
| Density | 4.914 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 499 °C (930 °F; 772 K) (triple point) |
| Boiling point | 431 °C (808 °F; 704 K) (sublimes) |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mP30 | |
| P2/c, No. 13 | |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
not listed |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
Zirconium(IV) fluoride Zirconium(IV) chloride Zirconium(IV) bromide |
| Other cations |
Titanium tetraiodide Hafnium tetraiodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Zirconium(IV) iodide is the chemical compound with the formula ZrI4. It is the most readily available iodide of zirconium. It is an orange-coloured solid that degrades in the presence of water.The compound was once prominent as an intermediate in the purification of zirconium metal.
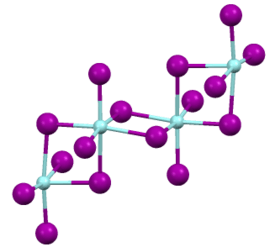
Structure
Like most binary metal halides, it adopts a polymeric structure. As characterized by X-ray crystallography, the compound exists as a polymer consisting of octahedral Zr(IV) centers, each with a pair of terminal iodide ligands and a four doubly bridging iodide ligands. The Zr-I distances of 2.692 (terminal) and 3.030 Å[1][2]
Synthesis and reactions
This compound is volatile, subliming as intact tetrahedral ZrI4 molecules. It is prepared by the direct reaction of powdered zirconium metal and iodine.[3]
Pyrolysis of zirconium(IV) iodide gas by contact of hot wire was the first industrial process for the commercial production of pure ductile metallic zirconium. This crystal bar process was developed by Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer in 1925.[4]
References
- ↑ B. Krebs, G. Henkel und M. Dartmann "Kristallstruktur von Zirkoniumtetrajodid ZrI4: ein neuer AB4-strukturtyp" Acta Crystallogr. 1979, volume B35, pp. 274-278. doi:10.1107/S0567740879003344
- ↑ Troyanov, S.I. "Crystal structure of gamma-ZrI4" Kristallografiya, 1986, volume 31, p446-449.
- ↑ Eberly, K. C. "Zirconium (IV) Iodide" Inorganic Syntheses McGraw-Hill: New York, 1963; Vol. 7, pages 52-54. ISBN 0-88275-165-4.
- ↑ van Arkel, A. E.; de Boer, J. H. (1925). "Darstellung von reinem Titanium-, Zirkonium-, Hafnium- und Thoriummetall". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 148 (1): 345–350. doi:10.1002/zaac.19251480133.
