30S
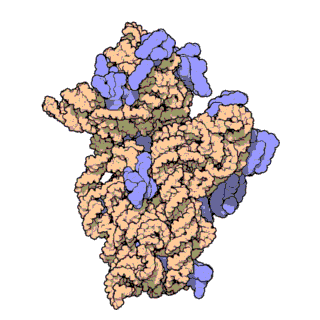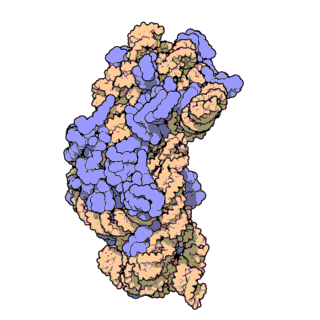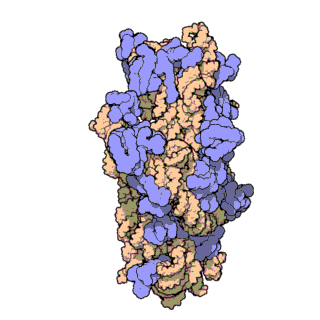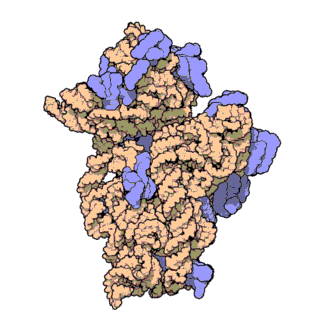
30S is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome found in prokaryotes. It is a complex of the 16S ribosomal RNA and 22 ribonucleoproteins. It complexes with the larger 50S subunit to form the 70S prokaryotic ribosome in the cell.
Function
30S subunit is an integral part of mRNA translation. It binds three Prokaryotic initiation factors: IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3. In addition, a portion of the 30S subunit (the 16S rRNA) guides the initiating (5')-AUG codon of the mRNA into place by lineing up a complementary sequence of RNA on the 16S subunit with the Shine-Dalgarno sequence on the mRNA. This ensures the Ribosome starts translation at the correct location.
Inhibition
The 30S subunit is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as tetracycline, aminoglycosides, macrolides, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and the pleuromutilins.
See also
References
- ↑ Schluenzen F, Tocilj A, Zarivach R, Harms J, Gluehmann M, Janell D, Bashan A, Bartels H, Agmon I, Franceschi F, Yonath A (2000). "Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution". Cell. 102 (5): 615–23. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00084-2. PMID 11007480.
External links
- 16S rRNA, BioMineWiki
- http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mayer/antibiot.htm
- 16S Ribosomal RNA at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)