Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
| Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
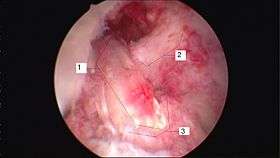 Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction (right knee). The tendon of the semitendinosus muscle was prelevated, folded and used as an autograft (1). It appears through the remnant of the injured original ACL (3). The autograft then courses upwardly and backwardly in front of the posterior cruciate ligament (2). | |
| ICD-9-CM | 81.45 |
| MedlinePlus | 007208 |
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACL reconstruction) is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury.[1] The torn ligament is removed from the knee before the graft is inserted in an arthroscopic procedure. A new technique was introduced in 2015: the "BEAR" procedure, short for bridge-enhanced ACL repair.[2]
Types of grafts
Three sources of replacement material for ACL reconstruction are commonly used:
- Autografts (employing bone or tissue harvested from the patient's body)
- Allografts (using bone or tissue from another body, either a cadaver or a live donor).
- Bridge-enhanced ACL repair (using a sponge filled with the patient's blood to stimulate healing and reconnection of the ACL).
Synthetic tissue for ACL reconstruction has also been developed, but little data exists on its strength and reliability.
Autograft
An accessory hamstring or part of the patellar ligament are the most common donor tissues used in autografts. The quadriceps tendon can also be used if the patellar ligament has been harvested for a previous surgery.
Because the tissue used in an autograft is the patient's own, the risk of rejection is minimal.
Hamstring tendon
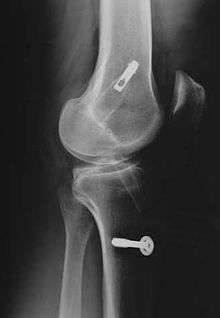
Hamstring autografts are made with the semitendinosus tendon, either alone or accompanied by the gracilis tendon for a stronger graft. The semitendinosus is an accessory hamstring (the primary hamstrings are left intact), and the gracilis is not a hamstring, but an accessory adductor (the primary adductors are left intact as well). The two tendons are commonly combined and referred to as a four-strand hamstring graft, made by a long piece (about 25 cm) removed from each tendon. The tendon segments are folded and braided together to form a tendon of quadruple thickness for the graft. The braided segment is threaded through the heads of the tibia and femur, and its ends are fixed with screws on the opposite sides of the two bones.
Unlike the patellar ligament, the hamstring tendon's fixation to the bone can be affected by motion after surgery. Therefore, a brace is often used to immobilize the knee for one to two weeks. Evidence suggests that the hamstring tendon graft does as well, or nearly as well, as the patellar ligament graft in the long term.[3] Common problems during recovery include strengthening of the quadriceps, T-band, and calf muscles.
The main surgical wound is over the upper proximal tibia, which prevents the typical pain experienced when kneeling after surgery. The wound is typically smaller than that of a patellar ligament graft, and so causes less post-operative pain. Another option first described in 2004, a minimally invasive technique for harvesting from the back of the knee, is faster, produces a significantly smaller wound, avoids the complications of graft harvesting from the anterior incision, and decreases the risk of nerve injury.[4]
There is some controversy as to how well a hamstring tendon regenerates after the harvesting. Most studies suggest that the tendon can be regenerated at least partially, though it will still be weaker than the original tendon.[5][6]
Advantages of hamstring grafts include their high "load to failure" strength, the stiffness of the graft, and the low postoperative morbidity. The natural ACL can withstand a load of up to 2,160 newtons. With a hamstring graft, this number doubles, decreasing the risk of re-injury. The stiffness of a hamstring graft—quadruple that of the natural ACL (Bartlett, Clatworthy and Ngugen, 2001)—also reduces the risk of re-injury.
Patellar tendon
The patellar tendon connects the patella (kneecap) to the tibia (shin). The graft is normally taken from the injured knee, but in some circumstances, such as a second operation, the other knee may be used. The middle third of the tendon is used, with bone fragments removed on each end. The graft is then threaded through holes drilled in the tibia and femur, and screwed into place. It is slightly larger than a hamstring graft.
Disadvantages compared with a hamstring graft include:
- Increased wound pain
- Increased scar formation
- Risk of fracturing the patella during harvesting of the graft
- Increased risk of tendinitis.
- Increased pain levels, even years after surgery, with activities that require kneeling.[7]
Some or all of these disadvantages may be attributable to post-operative patellar tendon shortening.[8]
Allograft
The patellar ligament, tibialis anterior tendon, or Achilles tendon may be recovered from a cadaver and used in ACL reconstruction. The Achilles tendon, because of its large size, must be shaved to fit within the joint cavity.
With an allograft, there is a slight chance of rejection, which would necessitate further surgery to remove the graft and replace it. Infection may also require removal of the graft. However, sterilization and redundant donor screening processes make allografts generally safe. Irradiation of donor tissue to remove infectious agents can weaken the tissue, although for ACL surgery, the weakened tendon is generally as strong as the replaced ligament.[9]
Choice of graft
Type
Typically, age and lifestyle help determine the type of graft used for ACL reconstruction.[7] The biggest factors in knee stability are correct graft placement by the surgeon and treatment of other menisco-ligament injuries in the knee, rather than type of graft.
The advantages of an allograft are that the patient does not sustain additional injury through removal of a tendon, thus improving recovery time, and that total procedure time is slightly reduced. Disadvantages are the risk of infection from foreign bodily materials and, potentially, a slightly weaker graft.[10]
Site
No ideal graft site for ACL reconstruction exists. Surgeons have historically regarded patellar tendon grafts as the "gold standard" for knee stability,[7] but the procedure has a slightly higher complication rate, including knee pain when lunging.[11]
Hamstring grafts historically had problems with fixation slippage and stretching out over time. Modern fixation methods avoid graft slippage and produce similarly stable outcomes with easier rehabilitation, less anterior knee pain and less joint stiffness.
Although there is less experience with the use of tibialis anterior grafts, preliminary data has shown no difference in short-term subjective outcomes between tibialis anterior allografts and patellar tendon allografts.[12]
Stem cell treatment
Autologous stem-cell transplantation using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been used to improve recovery time from ACL surgery, especially for athletes.[13] MSCs are multipotent stem cells, meaning they can differentiate into multiple cell types. In the case of mesenchymal stem cells, these cell types include osteoblasts (bone cells), adipocytes (fat cells), and chondrocytes (cartilage cells). Ligament tissue mainly consists of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix. The fibroblasts are in charge of maintaining and regenerating tissue. When introducing MSCs to induce new ligament growth, there are several factors that a tissue engineer must consider.[13] Ligament cells differ in size, respond to different cues in the cell environment, and express different cell surface markers, limiting the number of clinical treatments for accelerated repair of ACL tissue to MSCs and primary fibroblasts obtained from other ACL tissue. One study found that the proliferation rate and collagen production were greater with MSCs than with fibroblasts.[14] Therefore, most modern stem cell injections use MSCs to promote faster repair of the ACL and allow people such as athletes to return to their previous form faster.
In order for MSCs to differentiate into an ACL, they must be placed in a proper scaffold on which to grow, and must be in a bioreactor that maintains a normal physiological environment for the cells to reproduce and proliferate effectively.[15] The scaffold must have the mechanical properties of a healthy ACL to sustain the ligament while it is in its primary form and maintain normal knee movement. It must also be biodegradable so that as the ligament grows, the scaffold degrades proportionally and eventually disappears when the ligament has physiological mechanical properties.[16] Scaffolds that are used for ACL growth include collagen, silk, gelatin, polylactic acid, and glycosaminoglycans.[17] Mechanical properties of the scaffolds are further enhanced through braiding and twisting of the scaffold materials.
The bioreactor must have similar properties to a knee joint so that when the ACL is inserted into the body, it is not rejected as foreign, which could cause infection. Therefore, it has to have compatible pH levels, oxygen concentration levels, metabolite levels and temperature, in addition to being sterile.[18]
Recovery
Initial physical therapy consists of range of motion (ROM) exercises, often with the guidance of a physical therapist. Range of motion exercises are used to regain the flexibility of the ligament, prevent or break down scar tissue from forming and reduce loss of muscle tone. Range of motion exercise examples include: quadriceps contractions and straight leg raises. In some cases, a continuous passive motion (CPM) device is used immediately after surgery to help with flexibility. The preferred method of preventing muscle loss is isometric exercises that put zero strain on the knee. Knee extension within two weeks is important with many rehab guidelines.
Approximately six weeks is required for the bone to attach to the graft. However, the patient can typically walk on their own and perform simple physical tasks prior to this with caution, relying on the surgical fixation of the graft until true healing (graft attachment to bone) has taken place. At this stage, the first round of physical therapy can begin. This usually consists of careful exercises to regain flexibility and small amounts of strength. One of the more important benchmarks in recovery is the twelve weeks post-surgery period. After this, the patient can typically begin a more aggressive regimen of exercises involving stress on the knee, and increasing resistance. Jogging may be incorporated as well.
After four months, more intense activities such as running are possible without risk. After five months, light ball work may commence as the ligament is nearly regenerated. After six months, the reconstructed ACL is generally at full strength (ligament tissue has fully regrown), and the patient may return to activities involving cutting and twisting if a brace is worn. Recovery varies highly from case to case, and sometimes resumption of stressful activities may take a year or longer.
The reconstructed ACL has a high success rate. Studies show that cases in which the ACL tears again are generally caused by a traumatic impact. Some studies indicate that wearing a brace during athletic activity does not reduce probability of re-injury to the ACL, but a study of active post-ACL replacement skiers shows a 64% reduction in re-injury likelihood by using a knee brace after recovery.[19] A sufficiently traumatic impact to retear the ACL is unlikely to be mitigated by the use of a brace.
Risks
If the proper rehabilitation procedure is not followed out post surgery, the ACL becomes less mobile and the bones begin to rub against each other.The abnormal bone movement can also damage the tissue, this damage can lead to osteoarthritis.[20]
Recovery
Recovery is a four-phase progression.
Phase 1 (0-2 weeks)
The goals of this phase are to:
- Eliminate swelling due to inactivity
- Progress from partial weight bearing to full weight bearing exercises
- Regain normal range of motion
- Increase quadriceps strength
- Increase hamstring strength
- Increase Gastrocnemius strength
Some equipment that can be used and exercises that can be performed are:
- Use of Cryo-cuff
- - provides cold compression
- Isometric Contraction of Quads
- Quad Sets
- - stand against wall, push extended knee against rolled towel
- - progress to straight leg raised to 30deg.
- Wall Slides
- - To increase knee flexion
- Assisted Knee Flexion
- Towel Squeeze
- - Sit in chair, squeeze rolled towel between knees for 5 seconds. Relax & repeat.
- VMO Strengthening Exercise
- Supported Bilateral Calf-Raises
- walk without crutches
- Swimming (Freestyle front crawl)
- -[21] This particular swimming technique encompasses all the muscles in the knee and will increase not only mobility but also the strength of the surrounding muscles, which include the quadriceps, hamstrings, gastrocnemius, tibialis anterior (shin muscle), abductor hallucius, abductor digiti minimi, and flexor digitorum brevis (foot muscles).
Phase 2 (2-12 weeks)
The goals of this phase are to:
- Regain full knee extension
- Restore knee flexion to +130°
- Perform a full squat properly
- Regain good balance and control
- Reestablish proper gait
Some exercises that can be performed are:
- Mini squats
- - Progress to full squats → single-leg half squat
- Mini Lunges
- - Progress to full lunges
- Leg Press
- - Double-leg → single
- Step-ups
- - lateral & forward
- Bridges
- - Double-leg → single
- - Floor → Swiss ball
- Hip Abduction w/ Theraband
- Hip Extension w/ Theraband
- Wobble board
- - Assisted → un-assisted → eyes closed (assisted → unassisted)
- Stork Stand
- - Assisted → un-assisted → eyes closed (assisted → unassisted) → unstable surface
- Static Proprioceptive hold/ball throwing
- Functional Exercises that can be performed at this time include:
- - Walking
- - Bike
- - Roman Chair
Phase 3 (3-6 months)
The goals of this phase are to:
- Regain full range of motion
- Regain full strength and power
- Increase agility
- allows for adaption to direction change, acceleration and deceleration
- Be able to perform restricted sports-specific drills
- Begin plyometric drills
Some exercises that can be performed are:
- Continue exercises from Phase 2, progress as necessary
- Jump & Land drills
- - Jump from block & stick landing
- - Double-leg landing → single-leg
- Plyometric Drills
- - Jumping over blocks, sideways & forward
- - Hopping up & down steps/stairs
Phase 4 (6-15 months)
The goal of this phase is a return to activity, however it requires an ability to perform some functional performance tests such as:
- Agility Tests
- Illinois Agility Test
- Zig Zag Agility Test
- These tests are used to test the ability of the knee to withstand cutting and planting maneuvers
- Standing Vertical Jump
- Here you jump straight in the air from a standing start and land on two feet as stable as possible.
- Heiden Hop Test
- Here you essentially jump as far as possible with the uninjured leg and land on the injured leg. Your ability to stick the landing is indicative of good knee function.
- Isokinetic Testing
- This is used to evaluate muscle strength.
- The individual should have at least 90% quadricep strength of the uninjured leg
- They should also have equal hamstring strength to their uninjured leg as well
Cost of procedure
The average out-of-pocket cost of ACL reconstruction in the United States is $2,339.43, according to a 2010 survey of ACL surgery patients.[22] Insurance companies may or may not cover the various components of ACL reconstruction, which may include: pre-op appointments, pre-op physical therapy, ACL reconstruction by the surgeon, an assistant's charge, anesthesia, the hospital or facility fee, rental fees for cryotherapy, prescriptions, transportation, crutches or wheelchair fees, leg brace fees, post-op visits (such as to remove drain plugs and monitor swelling), and a physical therapy rehab program.
Despite the complexity of the procedure and numerous doctor's visits involved, 80–90% of patients who have had the surgery said they had favorable results.[23]
References
- ↑ "Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries". www.webmd.com. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "ACL Program - Bridge-Enhanced ACL Repair (BEAR) Clinical Trial". www.childrenshospital.org. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ Pinczewski, Lyman, Leo, Jeffrey, Lucy, Vivianne, Justin, James; Salmon, Russell; Roe, Linklater (2007). "A 10-Year Comparison of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstructions With Hamstring Tendon and Patellar Tendon Autograft". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. doi:10.1177/0363546506296042. Retrieved 2015-04-13.
- ↑ Kodkani, Pranjal S.; Govekar, Deepak P. (October 2004). "A new technique of graft harvest for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with quadruple semitendinosus tendon autograft". Arthroscopy. 20 (8).
- ↑ Okahashi K, Sugimoto K, Iwai M, et al. (June 2006). "Regeneration of the hamstring tendons after harvesting for arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a histological study in 11 patients". Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 14 (6): 542–5. doi:10.1007/s00167-006-0068-z. PMID 16525795.
- ↑ "Semitendinosus Regrowth: Biochemical, Ultrastructural, and Physiological Characterization of the Regenerate Tendon". The American Orthopedic Society for Sports Medicine. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- 1 2 3 Kraeutler MJ, Bravman JT, McCarty EC. Bone-patellar tendon-bone autograft versus allograft in outcomes of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis of 5182 patients. American Journal of Sports Medicine 2013;41(10):2439-2448. PMID 23585484
- ↑ Marrale, Jonathan; Morrissey, Matthew C.; Haddad, Fares S. (12 April 2007). "A literature review of autograft and allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction". Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 15 (6): 690–704. doi:10.1007/s00167-006-0236-1.
- ↑ "About OA: Southern Maine orthopedic specialists for foot pain, ankle pain, hand pain, shoulder pain, back pain, bone fractures, MRI, physical therapy, and sports medicine.". Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "Patellar vs Hamstring". Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ Biau DJ, Katsahian S, Kartus J, Harilainen A, Feller JA, Sajovic M, Ejerhed L (December 2009). "Patellar Tendon Versus Hamstring Tendon Autografts for Reconstructing the Anterior Cruciate Ligament". Am J Sports Med. 37 (12): 2470–8. doi:10.1177/0363546509333006. PMID 19709991.
- ↑ O'Brien, DF; Kraeutler MJ; Koyonos L; Flato RR; Ciccotti MG; Cohen SB (2014). "Allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in patients younger than 30 years: A matched-pair comparison of bone-patellar tendon-bone and tibialis anterior". Am J Orthop. 43 (3): 132–136. PMID 24660179.
- 1 2 Hui,James. "Use of Stem Cells in Graft Osteo-Integration, Tendon and Muscle Healing" (PDF). Cartilage Repair Program at Nation University Health System of Singapore.
- ↑ Z. Ge; J.C.H. Goh; E.H. Lee. "Selection of cell source for ligament tissue engineering" (PDF). Cell Transplantation. 14 (8): 573–583.
- ↑ Coutu, DL; et al. (August 2007). "Hierarchical scaffold design for mesenchymal stem cell-based gene therapy of hemophilia B.". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 11 (4): 394–8. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.05.034. PMC 2038982
 . PMID 17656148.
. PMID 17656148. - ↑ King, James; Miller, William (January 2011). "Bioreactor Development for Stem Cell Expansion and Controlled Differentiation". Biomaterials. 32 (1): 295–305. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.094. PMID 20864158.
- ↑ Farrell, E; et al. (March 2006). "A collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffold supports adult rat mesenchymal stem cell differentiation along osteogenic and chondrogenic routes.". Tissue Engineering. 12 (3): 459–68. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.12.459. PMID 16579679.
- ↑ E.W. Yates; A. Rupani; G.T. Foley; W.S. Khan; S. Cartmell; S.J. Anand. "Ligament Tissue Engineering and Its Potential Role in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction". Stem Cells International. 2012: 6. doi:10.1155/2012/438125.
- ↑ Sterett WI, Briggs KK, Farley T, Steadman JR (October 2006). "Effect of Functional Bracing on Knee Injury in Skiers With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction". Am J Sports Med. 34 (10): 1581–5. doi:10.1177/0363546506289883. PMID 16870823.
- ↑ "Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries - Topic Overview". www.webmd.com. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "Muscles Used Swimming.". www.swimstoslim.com. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "ACL Survey Results". Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Surgery". WebMD. Retrieved 25 April 2016.