Aberrant subclavian artery
| Aberrant subclavian artery | |
|---|---|
|
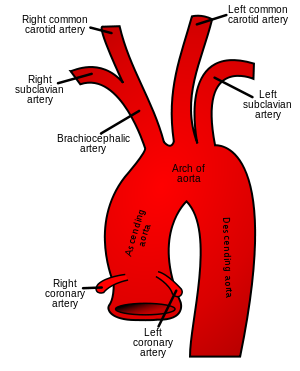
Normal anatomical locations of right and left subclavian arteries | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q27.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 747.21 |
Aberrant subclavian artery, or aberrant subclavian artery syndrome, is a rare anatomical variant of the origin of the right or left subclavian artery. This abnormality is the most common congenital vascular anomaly of the aortic arch.
Presentation

The aberrant artery usually arises just distal to the left subclavian artery and crosses in the posterior part of the mediastinum usually behind the oesophagus on its way to the right upper extremity. Such course of this aberrant vessel may cause a vascular ring around the trachea and oesophagus. Dysphagia due to an aberrant right subclavian artery is termed dysphagia lusoria. Palsy of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is termed Ortner's syndrome.
The aberrant right subclavian artery frequently arises from a dilated segment of the proximal descending aorta, the so-called Diverticulum of Kommerel (which was named for the German Radiologist, Burckhard Freidrich Kommerel (1901–1990), who discovered it in 1936). It is alternatively known as lusorian artery.
Treatment
Surgery is sometimes used to treat the condition.[1]
Images
-

Aberrant subclavian artery at axial CT-scan. (1) trachea, (2) esophagus, (3) Aberrant subclavian artery.
-
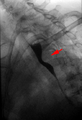
Aberrant right subclavian artery at angiography.
-

Tape-like impression of the esophagus caused by aberrant subclavian artery. Below (arrows) narrowing of the esophagus by a tumor that is causing the swallowing problems.
-
Aberrant subclavian artery seen at swallowing study: Impression of the esophagus from behind.
References
- ↑ Kouchoukos NT, Masetti P (April 2007). "Aberrant subclavian artery and Kommerell aneurysm: surgical treatment with a standard approach". The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 133 (4): 888–92. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.12.005. PMID 17382621.