Airports of London
The metropolitan area of London, United Kingdom is served by six international airports and several smaller airports. Together, they make the busiest airport system in the world by passenger numbers and the second busiest by aircraft movements.[1] In 2011, the six airports handled a total of 133,709,327 passengers. The London airports handle 60% of all the United Kingdom's air traffic. There are 14 domestic destinations served by the airports and 396 international destinations.
International airports
| Airport | Code | Distance to London | Passengers[3][4] | Percentage of passengers | Change from 2011[3][4] | Cargo (Tonnes) | Change from 2010 | Aircraft Movements[5] | Change from 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| London City | LCY | 11 km / 7 mi | 3,016,664 | 2.23% | | 70,781 | | ||
| Heathrow | LHR | 22 km / 14 mi | 70,037,417 | 51.88% | | 1,484,351 | | 475,176 | |
| Gatwick | LGW | 53 km / 33 mi | 34,235,982 | 25.36% | | 88,085 | | 256,987 | |
| Luton | LTN | 46 km / 29 mi | 9,617,697 | 7.12% | | 27,905 | | 96,797 | |
| Stansted | STN | 64 km / 40 mi | 17,472,699 | 12.94% | | 202,593 | | 143,511 | |
| Southend | SEN | 64 km / 40 mi | 617,027 | 0.45% | | 6 | | 27,715 | |
| Total | N/A | N/A | 134,997,486 | 100% | | 1,802,939 | N/A | 1,070,967 | |
City (LCY)
Located in the London Borough of Newham, City Airportmap5 is situated in London's Docklands, and is the closest to central London, which limits its size - the airport has a single runway, which is very short. As a result, no large aircraft are permitted to use the airport, which initially prevented all long-haul flights. However, since 2011, British Airways has operated a flight to New York JFK, via Shannon, using an Airbus A318, which is currently the largest aircraft handled at the airport.
Located only four miles from Canary Wharf, London City Airport is often used by business travellers, with many flights serving destinations across the UK and northern Europe. The airport cannot be expanded due to the docks on either side. It is also the only airport serving London which does not operate at night.
Until the extension of the Docklands Light Railway in 2006, City Airport had poor public transport connections to London.
Heathrow (LHR)
Located in the London Borough of Hillingdon, Heathrowmap1 is by far the largest of London's airports, and considered the international gateway into the United Kingdom. Heathrow has five terminals and two parallel runways. Due to the location in London's western suburbs, Heathrow has been unable to expand (especially since the Cameron ministry scrapped the proposals for a third runway on 12 May 2010[6]), and as a result consistently runs at 99% capacity. This has led to Heathrow being one of the worst rated airports in the world, with lengthy border control queues being a recent problem.[7] The airport is connected to Great Britain's motorway network via the M4 and M25 motorways.
In April 2012, Heathrow announced that for the first time in history it handled 70 million passengers in a calendar year,[8] making it the third busiest airport in the world in terms of passenger numbers, after Atlanta and Beijing. It also comes second behind Dubai International Airport in the list of the busiest airport in the world in terms of international passenger numbers, as well as the busiest airport in United Kingdom and the busiest in Europe, again, both in terms of passenger numbers.
Heathrow serves six continents around the world, and is the base for the flag carrier British Airways in Terminal 5. While it also serves short-haul flights, Heathrow is London's long distance hub and is the most popular arrival point for flights from the United States of America, with 13 million passengers. However, because it is operating at capacity, Heathrow has failed to increase service cities in the newly industrialized countries, like China, falling behind European bases like Frankfurt, Amsterdam, and Paris.
Gatwick (LGW)
Located in West Sussex, Gatwickmap2 is the second busiest airport in the London metropolitan region, and is the busiest single runway airport in the world. It is currently the second busiest airport in the United Kingdom after Heathrow, and the 10th busiest in Europe. It is the second base for British Airways, serving Europe and the Caribbean. It is also the base for low-cost carriers like Monarch, easyJet, Norwegian Air Shuttle and Flybe.
The airport consists of two terminals, North and South, is connected to the motorway network via the M23, and has its own railway station, with Gatwick Express serving Victoria station in Central London.
Luton (LTN)
Located on the Bedfordshire / Hertfordshire border, Luton Airportmap4 is London's fourth largest airport but the closest to the capital after Heathrow and City airports, it is the fifth busiest in the United Kingdom, and the 42nd busiest in Europe. It is the headquarters of the low cost carriers EasyJet, Thomson and Monarch and is a focus airport for other no-frills airlines.
Stansted (STN)
Located in Essex, Stanstedmap3 is London's third busiest airport, being the fourth busiest in the United Kingdom, behind Manchester Airport, 26th busiest in Europe, and is one of the primary operational bases for Europe's largest low-cost carrier, Ryanair. Stansted destinations are largely in Europe, however in the past it has served destinations further afield, like Kuala Lumpur. It is the home of Harrods Aviation, allowing VIP aircraft to land there, such as Air Force One carrying the President of the United States, Barack Obama, in 2009 and also 2016.[9]
Southend (SEN)
Located in Essex, Southend Airportmap6 expanded commercial air transport operations to destinations in Ireland in 2011, and to Europe in 2012 when easyJet commenced operations using the brand new terminal and railway station. Southend claims it only takes 15 minutes to get through arrivals from plane to train with hand luggage. It was once the third busiest airport in the United Kingdom.
Other civil airports
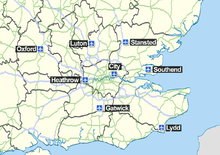
A number of other airports also serve the London area.
Open airports
The following are mainly used by general aviation flights.
- London Biggin Hill Airportmap7, in the London Borough of Bromley
- Blackbushe Airportmap8, in Hampshire
- Damyns Hall Aerodromemap9, in the London Borough of Havering
- Denham Aerodromemap10, in Buckinghamshire
- Elstree Airfieldmap11, in Hertfordshire
- Fairoaks Airportmap12, in Surrey
- Farnborough Airportmap13, in Hampshire
- London Heliportmap14, in the London Borough of Wandsworth
- Lydd Airport (London Ashford Airport)map15, in Kent
- North Weald Airfieldmap16, in Essex
- London Oxford Airportmap17, in Oxfordshire
- Panshanger Aerodromemap18, in Hertfordshire
- Redhill Aerodromemap19, in Surrey
- Rochester Airportmap20, in Kent
- Stapleford Aerodromemap21, in Essex
- White Waltham Airfieldmap22, in Berkshire
- Wycombe Air Parkmap23, in Buckinghamshire
Closed airports
Airports are listed at their current borough, although the area may have been outside London at the time of construction.
- Cricklewood Aerodromemap24, in the London Borough of Barnet
- Croydon Airportmap25, in the London Borough of Croydon
- Great West Aerodromemap26, in the London Borough of Hillingdon
- Hendon Aerodromemap27, in the London Borough of Barnet
- Heston Aerodromemap28, in the London Borough of Hounslow
- Hounslow Heath Aerodromemap29, in the London Borough of Hounslow
- London Air Park (Hanworth Air Park)map30, in the London Borough of Hounslow
- Stag Lane Aerodromemap31, in the London Borough of Barnet
Royal Air Force stations
There were several Royal Air Force stations in London. This list excludes those that are classed as non-flying stations.
Operational
- RAF Northoltmap32, in the London Borough of Hillingdon, also handes civil flights
Non-operational
Station are listed at their current borough, although the area may have been outside London at the time of construction.
- RAF Biggin Hillmap7, in the London Borough of Bromley
- RAF Fairlopmap33, in the London Borough of Redbridge
- RAF Hendonmap27, in the London Borough of Barnet
- RAF Hestonmap28, in the London Borough of Hounslow
- RAF Hornchurchmap34, in the London Borough of Havering
- RAF Kenleymap35, in the London Borough of Croydon
- RAF St Pancrasmap36, in the London Borough of Camden
- RAF Uxbridgemap37, in the London Borough of Hillingdon
Proposed airports
Thames Estuary
Due to London's high capacity, in particular London Heathrow, Boris Johnson, London's former mayor, and Sir Norman Foster have both brought up plans to have a new airport built, either on a man-made island in the Thames Estuary, or on the Isle of Grain in North Kent. Foster's proposed Thames Hub Airport would be very similar to the design of Hong Kong International Airport and Qatar's Hamad International Airport. The plans to have an airport able to handle 110 million passengers a year would require the closure of Heathrow, and probably make the new airport the busiest in the world.
The plans have met with opposition from some people living nearby warning the airport would create a significant increase in bird strikes.[10] Other people and local businesses, recognising the depressed levels of economic activity in North Kent, have been supportive and argue that London needs a new airport in order to be able to compete in the world.
Traffic and Statistics
Passengers Numbers
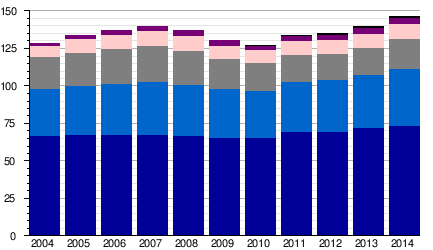 |
| Updated: 28 April 2015.[11] |
| Heathrow, Gatwick, Stansted, Luton, City, Southend |
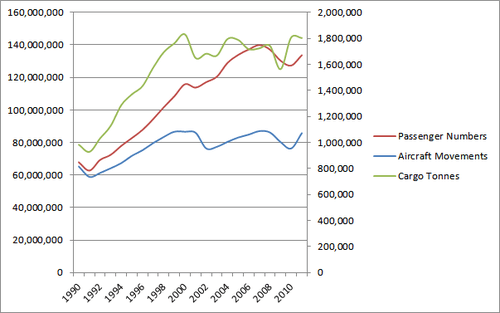
| Year | Aircraft movements | Percentage change | Passenger numbers | Percentage change | Cargo tonnes | Percentage change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 1,074,773[12] | | 113,790,381 | | 1,649,437 | |
| 2002 | 954,570[13] | | 117,138,188 | | 1,682,693 | |
| 2003 | 967,270[14] | | 120,493,239 | | 1,667,803 | |
| 2004 | 1,005,256[15] | | 128,933,753 | | 1,795,326 | |
| 2005 | 1,038,241[16] | | 133,836,827 | | 1,788,671 | |
| 2006 | 1,060,831[17] | | 137,192,958 | | 1,717,360 | |
| 2007 | 1,087,703[18] | | 139,950,593 | | 1,724,040 | |
| 2008 | 1,077,448[19] | | 137,106,041 | | 1,743,028 | |
| 2009 | 1,003,616[20] | | 130,307,938 | | 1,563,783 | |
| 2010 | 954,371[21] | | 127,353,419 | | 1,808,005 | |
| 2011 | 1,072,126[5] | | 133,709,327 | | 1,802,939[22] | |
| 2012 | 1,060,967[5] | | 134,914,412 | | 1,805,761 [23] | |
| 2013 | 1,067,992[5] | | 139,652,261 | | 1,760,690 [23] | |
| 2014 | 1,098,605[5] | | 146,631,158 | | 1,819,587 [23] | |
Busiest routes
In total, there were 30 international destinations from London, and another 3 domestic routes, that handled more than 1 million passengers in 2011:
| Destination | Number of passengers |
|---|---|
| | 3,705,696 |
| | 3,026,082 |
| | 2,700,613 |
| | 2,506,613 |
| | 2,496,921 |
| | 2,376,284 |
| | 2,218,593 |
| | 1,814,682 |
| | 1,678,536 |
| | 1,661,301 |
| | 1,656,818 |
| | 1,642,959 |
| | 1,546,441 |
| | 1,530,810 |
| | 1,526,030 |
| | 1,412,749 |
| | 1,302,237 |
| | 1,299,118 |
| | 1,207,424 |
| | 1,197,847 |
| | 1,189,761 |
| | 1,186,783 |
| | 1,186,358 |
| | 1,185,848 |
| | 1,145,011 |
| | 1,134,396 |
| | 1,069,706 |
| | 1,069,055 |
| | 1,031,320 |
| | 1,003,598 |
Heathrow Airport is a major hub for flights across the North Atlantic. In 2011, 11% of all north Atlantic flights originated or terminated at Heathrow, more than Paris and Frankfurt combined, and Heathrow is the European terminus for 11 of the 25 busiest north Atlantic routes.
The busiest long-haul route in the world is between London (Heathrow and Gatwick) and New York (JFK and Newark), with a total of 3,898,460 passengers travelling between the two cities in 2011.
Maps
- ^map1 Heathrow, 51°28′39″N 000°27′41″W / 51.47750°N 0.46139°W
- ^map2 Gatwick, 51°08′53″N 000°11′25″W / 51.14806°N 0.19028°W
- ^map3 Stansted, 51°53′06″N 000°14′06″E / 51.88500°N 0.23500°E
- ^map4 Luton, 51°52′28″N 000°22′06″W / 51.87444°N 0.36833°W
- ^map5 City, 51°30′19″N 000°03′19″E / 51.50528°N 0.05528°E
- ^map6 Southend, 51°34′13″N 000°41′36″E / 51.57028°N 0.69333°E
- ^map7 Biggin Hill, 51°18′51″N 000°01′47″E / 51.31417°N 0.02972°E
- ^map8 Blackbushe, 51°19′26″N 000°50′51″W / 51.32389°N 0.84750°W
- ^map9 Damyns Hall, 51°34′43″N 000°14′44″E / 51.57861°N 0.24556°E
- ^map10 Denham, 51°35′18″N 000°30′47″W / 51.58833°N 0.51306°W
- ^map11 Elstree, 51°39′21″N 000°19′33″W / 51.65583°N 0.32583°W
- ^map12 Fairoaks, 51°20′53″N 000°33′31″W / 51.34806°N 0.55861°W
- ^map13 Farnborough, 51°16′31″N 000°46′39″W / 51.27528°N 0.77750°W
- ^map14 Heliport, 51°28′12″N 000°10′46″W / 51.47000°N 0.17944°W
- ^map15 Lydd, 50°57′22″N 000°56′21″E / 50.95611°N 0.93917°E
- ^map16 North Weald, 51°43′18″N 000°09′15″E / 51.72167°N 0.15417°E
- ^map17 Oxford, 51°50′13″N 001°19′21″W / 51.83694°N 1.32250°W
- ^map18 Panshanger, 51°48′07″N 000°09′30″W / 51.80194°N 0.15833°W
- ^map19 Redhill, 51°12′49″N 000°08′19″W / 51.21361°N 0.13861°W
- ^map20 Rochester, 51°21′07″N 000°30′10″E / 51.35194°N 0.50278°E
- ^map21 Stapleford, 51°39′09″N 000°09′22″E / 51.65250°N 0.15611°E
- ^map22 White Waltham, 51°30′03″N 000°46′28″W / 51.50083°N 0.77444°W
- ^map23 Wycombe, 51°36′42″N 000°48′30″W / 51.61167°N 0.80833°W
- ^map24 Cricklewood, 51°33′47″N 000°12′47″W / 51.56306°N 0.21306°W
- ^map25 Croydon, 51°21′23″N 000°07′02″W / 51.35639°N 0.11722°W
- ^map26 Great West, 51°28′39″N 000°27′41″W / 51.47750°N 0.46139°W
- ^map27 Hendon, 51°36′00″N 000°14′46″W / 51.60000°N 0.24611°W
- ^map28 Heston, 51°29′15″N 000°23′00″W / 51.48750°N 0.38333°W
- ^map29 Hounslow Heath, 51°27′41″N 000°23′20″W / 51.46139°N 0.38889°W
- ^map30 London Air Park, 51°26′18″N 000°23′45″W / 51.43833°N 0.39583°W
- ^map31 Stag Lane, 51°35′49″N 000°16′26″W / 51.59694°N 0.27389°W
- ^map32 RAF Northolt, 51°33′11″N 000°25′06″W / 51.55306°N 0.41833°W
- ^map33 RAF Fairlop, 51°36′16″N 000°06′10″E / 51.60444°N 0.10278°E
- ^map34 RAF Hornchurch, 51°32′19″N 000°12′17″E / 51.53861°N 0.20472°E
- ^map35 RAF Kenley, 51°18′12″N 000°05′41″W / 51.30333°N 0.09472°W
- ^map36 RAF St Pancras, 51°32′01″N 000°07′29″W / 51.53361°N 0.12472°W
- ^map37 RAF Uxbridge, 51°32′29″N 000°28′19″W / 51.54139°N 0.47194°W
See also
- London Airport
- Transport in London
- Airports in the United Kingdom and the British Crown Dependencies
References
- ↑ Beijing to overtake London as world’s largest aviation hub. Massive new airport planned
- ↑ Size of Reporting Airports 2011
- 1 2 Domestic Terminal Passenger Traffic 2012(a)
- 1 2 EU and Other International Terminal Passenger Traffic 2012
- 1 2 3 4 5 Aircraft Movements 2012
- ↑ "Heathrow third runway plans scrapped by new government". BBC News. 12 May 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ↑ Alan Travis, home affairs editor (3 May 2012). "Official waiting time figures reveal scale of Heathrow chaos | World news | guardian.co.uk". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2012-08-21.
- ↑ Lucy Tobin (2012-04-12). "Record 70 million use Heathrow airport - Business News - Business". London: The Independent. Retrieved 2012-08-21.
- ↑ "G20". Harrodsaviation.com. Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ Juliette Jowit (26 January 2012). "Risk of bird strikes would make Thames Estuary UK's 'most dangerous airport' | Environment | guardian.co.uk". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ "UK Airport Statistics" (PDF). Caa.co.uk. 26 March 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ Aircraft Movements 2001
- ↑ Air Transport Movements(a) 2002
- ↑ Air Transport Movements(a) 2003
- ↑ Air Transport Movements(a) 2004
- ↑ "Air Transport Movements 2005" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ "Air Transport Movements 2006" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ "Air Transport Movements 2007" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ "Air Transport Movements 2008" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ "Air Transport Movements 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- ↑ Air Transport Movements 2010
- ↑ Air Transport Movements 2011
- 1 2 3 Air Transport Movements 2004-2014