Arado Ar 95
| Ar 95 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Reconnaissance Biplane |
| Manufacturer | Arado |
| First flight | 1937 |
| Primary users | Chile Kriegsmarine |
| Variants | Arado Ar 195 |
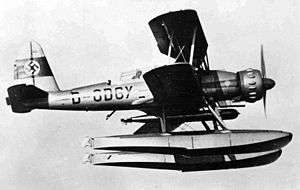
The Arado 95 was a single-engine reconnaissance and patrol biplane designed and built by the German firm Arado in the late 1930s. Ordered by Chile and Turkey, a number were taken over by the Kriegsmarine (German Navy) when World War II started.
Development
The Arado 95 was designed in 1935 as a two-seat seaplane, for coastal patrol, reconnaissance and light attack roles. The first prototype, an all-metal biplane powered by a BMW 132 radial engine, flew in 1936,[1] while a second prototype was powered by a Junkers Jumo 210 liquid-cooled engine. The two prototypes were evaluated against the similar Focke-Wulf Fw 62. The BMW-powered version was considered worthy of further study, and a batch of six were sent for further evaluation with the Legion Condor during the Spanish Civil War.[2]
The Arado Ar 95 was the basis for the prototype Ar 195 carrier-based torpedo bomber, which was proposed for operation from the German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin.[1]
Operational history

The Ar 95 was not ordered by the German armed forces, and so was offered for export in two versions, the Ar 95W floatplane and Ar 95L landplane, with a fixed, spatted undercarriage. Six Ar 95Ls were ordered by the Chilean Air Force, being delivered prior to the start of World War II.[3] Turkey placed an order for Ar 95Ws, but these were taken over by Germany on the outbreak of war.
The requisitioned Ar 95s were designated by the Luftwaffe as the Ar 95A, and were used for training[1] and for coastal reconnaissance operations in the Baltic Sea, operating off the coast of Latvia and Estonia in 1941, and in the Gulf of Finland.[2] They continued operating until late 1944.[1]
Operators
Specifications (Arado 95A-1)
Data from Warplanes of the Luftwaffe.[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: Two
- Length: 11.10 m (36 ft 5 in)
- Wingspan: 12.50 m (41 ft 0 in)
- Height: 3.60 m (11 ft 9¾ in)
- Wing area: 45.4 m² (488.7 ft²)
- Empty weight: 2,450 kg (5,402 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 3,560 kg (7,870 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × BMW 132De Radial engine, 656 kW (880 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 310 km/h (168 kn, 193 mph) at 3,000 m (9,840 ft)
- Cruise speed: 255 km/h (137 kn, 158 mph)
- Range: 1,100 km (594 nmi, 683 mi)
- Service ceiling: 7,300 m (24,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 7.5 m/s (1,476 ft/min [1])
- Wing loading: 78.4 kg/m² (16.1 lb/ft²)
- Power/mass: 184 W/kg (0.112 hp/lb)
Armament
- Guns: 1 × fixed, forward-firing 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine gun and 1 × flexible 7.92 (.312 in) MG 15 machine gun in rear cockpit
- Bombs: 1 × 800 kg (1,764 lb) torpedo or 500 kg (1,102 lb) bomb on underfuselage rack
See also
- Related development
- Related lists
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arado Ar 95. |
- 1 2 3 4 5 Smith, J.R; Kay, Antony L (1972). German Aircraft of the Second World War. London: Putnam. ISBN 0-85177-836-4.
- 1 2 3 Donald, David (Editor) (1994). Warplanes of the Luftwaffe. London: Aerospace Publishing. ISBN 1-874023-56-5.
- ↑ Taylor, Michael J. H. (Editor) (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Jane's Publishing. ISBN 1-85170-324-1.