Arica y Parinacota Region
| Arica and Parinacota Region XV Región de Arica y Parinacota | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Region of Chile | |||
 | |||
| |||
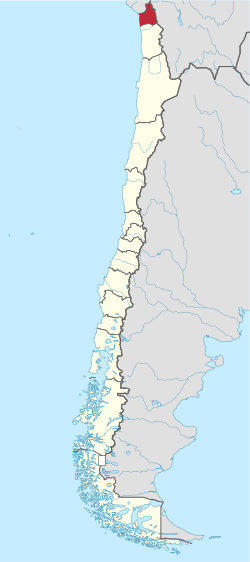 Map of Arica and Parinacota Region | |||
| Coordinates: 18°28′30″S 70°18′52″W / 18.47500°S 70.31444°WCoordinates: 18°28′30″S 70°18′52″W / 18.47500°S 70.31444°W | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Capital | Arica | ||
| Provinces | Arica, Parinacota | ||
| Government | |||
| • Intendant | Gladys Acuña | ||
| Area[1] | |||
| • Total | 16,873.3 km2 (6,514.8 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 12 | ||
| Highest elevation | 6,342 m (20,807 ft) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||
| Population (2012)[1] | |||
| • Total | 213,595 | ||
| • Rank | 13 | ||
| • Density | 13/km2 (33/sq mi) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | CL-AP | ||
| Website | Official website (Spanish) | ||
The XV Arica and Parinacota Region[2][3] (Spanish: XV Región de Arica y Parinacota)[4] is one of Chile's 15 first order administrative divisions. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the east and Chile's Tarapacá Region to the south. It is also the country's newest region, created under Law 20.175. It became operational on October 8, 2007.[1] Chile's former Tarapacá region was a former Peruvian province, which was occupied by Chile under the 1883 Treaty of Ancón at the close of the War of the Pacific, and then formally annexed in 1929 by the Treaty of Lima.
Administration
In 2007, the region was subdivided to create the Arica y Parinacota region and the present day Tarapacá Region to the south. The region is further subdivided into two provinces: Arica and Parinacota.
| Region | Province | Commune | Area (km²)[5][6] |
2002[5][6] Population |
Website[7] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arica and Parinacota | |||||
| Arica | |||||
| Camarones | 3,927 | 1,220 | link | ||
| Arica | 4,799 | 185,268 | link | ||
| Parinacota | |||||
| Putre | 5,903 | 1,977 | link | ||
| General Lagos | 2,244 | 1,179 | link | ||
Demography

According to data from the 2002 Census of INE, the region is populated by 189 644 inhabitants. Its density reaches 11.2 inhabitants per km ².
This region holds the largest population of indigenous peoples of Chile: the Quechua, Aymara, Atacameno, Diaguita, Mapuche and Kaweskar (Alacaluf or Qwakshar) transplanted from Central Chile. A significant number of immigrants from neighboring Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador and Colombia. Included are those of Asian descent, such as Chinese and Japanese; and Arabs from Lebanon, Palestine and Syria. Most of the country's Afro-Chileans live in the Arica province, descended from slaves in the 17th and 18th centuries. There are a large number of Roma people or Gypsies in the Arica province as well, originated from Eastern Europe in the late 19th century.
At the level of cities, the most populated are: Arica, with 175,441 inhabitants and Putre, with 1235 inhabitants.
Geography
The region lies within the Norte Grande (Far North) natural region. It combines deserts, green valleys, the steep and volcanic Andes mountains, and the Altiplano (high plain) to the east. A narrow coastal strip of low-lying land no more than 2 kilometres (1 mi) wide separates the Pacific's Nazca plate from the Andes. Its Parinacota volcano is the region's highest elevation at 6,348 metres (20,827 ft) and lies on the northern border with Bolivia in Lauca National Park.
Hydrology
The region's two main rivers are the Lauca, which drains into Bolivia's Coipasa salt flat (Lago Coipasa), and the Lluta, which flows into the Pacific Ocean. Lake Chungará at 4,517 metres (14,820 ft) above sea level ranks as one of the highest in the world.[1]
Climate
A desert climate dominates the region. Near the coast, cloudiness can limit the temperature swing throughout the day, but in other drier areas, temperatures can vary greatly as is typical in deserts. A marginal desert region can be found over 3,000 m (9,843 ft) above sea level, which sees milder temperatures and summer rains.[1]
Border dispute with Peru
On January 26, 2007, Peru’s government issued a protest against Chile’s demarcation of the coastal frontier the two countries share. According to the Peruvian Foreign Ministry, the Chilean legislatures had endorsed a plan regarding the Arica y Parinacota region which did not comply with the current established territorial demarcation. Moreover, it is alleged that the proposed Chilean law included an assertion of sovereignty over 19,000 m2 (204,514 sq ft) of land in Peru's Tacna Region. According to the Peruvian Foreign Ministry, Chile has defined a new region "without respecting the Concordia demarcation."[8]
For its part, the Chilean government has asserted that the region in dispute is not a coastal site named Concordia, but instead refers to boundary stone No. 1, which is located to the northeast and 200 meters inland.[8] A possible border dispute was averted when the Chilean Constitutional Court formally ruled on January 26, 2007 against the legislation. While agreeing with the court's ruling, the Chilean government reiterated its stance that the maritime borders between the two nations were not in question and have been formally recognized by the international community. . The Peruvian government has stated that it might turn to the international court at The Hague to solve the dispute.[9]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Arica-Parinacota Region". Government of Chile Foreign Investment Committee. Retrieved 13 March 2010.
- ↑ "Iglesias de Arica Parinacota (Churches of Arica Parinacota)". New York, NY: World Monuments Fund. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
However, San Pedro de Esquiña, like many other churches in the Arica y Parinacota region, is at risk.
- ↑ "Journalists and media professionals to participate in awareness-raising workshop on violence against women in Arica". UNESCO. 18 May 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
[...] several women’s public organizations and agencies from the Chilean region of Arica y Parinacota.
- ↑ "Ley 20175. Crea la XV Región de Arica y Parinacota y la Provincia del Tamarugal en la Región de Tarapacá". Ley Chile (in Spanish). Valparaiso, Chile: Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional de Chile. 11 April 2007. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
- 1 2 "National Statistics Institute" (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- 1 2 "Territorial division of Chile" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 November 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ↑ "Asociacion Chilena de Municipalidades" (in Spanish). Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- 1 2 "Peru protests against Chile's new definition of territory". Xinhua People’s Daily online. Retrieved 27 January 2007.
- ↑ "Peru-Chile Sea Dispute May Go to The Hague". Lima: Prensa Latina. 27 January 2007. Retrieved 28 January 2007.
External links
- Constitutional Court sentence (Spanish)