Azygos vein
| Azygos vein | |
|---|---|
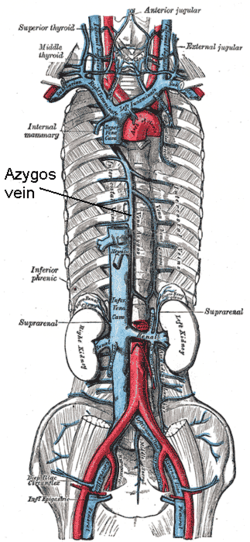 Superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, azygos vein and their tributaries. (Vena azygos labeled at center.) | |
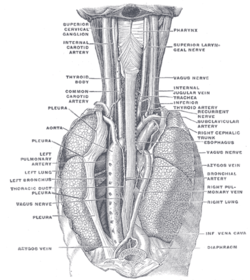 POSTERIOR VIEW: The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind. (Azygos vein labeled at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Right supracardinal vein[1] |
Source | superior intercostal vein |
| Drains to | superior vena cava |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena azygos |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.106 |
| TA | A12.3.07.001 |
| FMA | 4838 |
The azygos vein is a vein running up the side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.[2][3]
Structure
The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava vein. The anatomy of this blood vessel can be quite variable. In some rare variations for example, it also drains thoracic veins, bronchial veins and even gonadal veins. The vein is so named because it has no symmetrically equivalent vein on the left side of the body.
It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending in the posterior mediastinum, and arching over the right main bronchus posteriorly at the root of the right lung to join the superior vena cava. This "arch of the azygos vein" (arcus venae azygos) is an important anatomic landmark. As an anatomical variation in 1-2% of the population, the arch can be displaced laterally, thereby creating a pleural septum separating an azygos lobe from the upper lobe of the right lung.
A major tributary is the hemiazygos vein, a similar structure on the opposite side of the vertebral column. Other tributaries include the bronchial veins, pericardial veins, and posterior right intercostal veins. It communicates with the vertebral venous plexuses.
Azygos venous system
The azygos system of veins is considered to be the azygos vein, along with its left-sided counterparts, the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein.
Etymology
The Greek root zyg refers to a pair. 'A-' means not. Thus, azygos means unpaired. The azygos vein is unpaired in that there is only one in the body, mostly on the right side. While there is the hemiazygos vein and its accessory on the left side of the body, they are considered tributaries of the azygos vein rather than its left-side equivalent.
This terminology is only accurate in some species, such as the human, dog and cat. Ruminants (such as sheep and cows) have paired azygos veins
Imaging
Azygos vein abnormalities can be inferenced on chest radiograph by enlargement of the azygos vein shadow greater than 1 cm. False positives can occur in heart failure causing increased pressures on the right side of the heart, or adjacent lymphadenopathy.[4]
Additional images
-
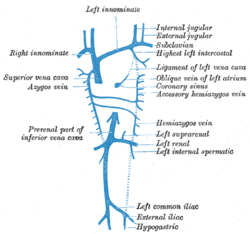
Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
-

Transverse section of thorax at about CC3, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
-
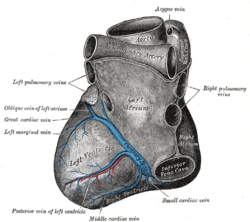
Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart.
-
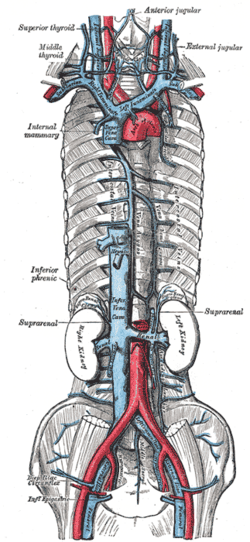
The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries.
-

The thoracic and right lymphatic ducts.
-
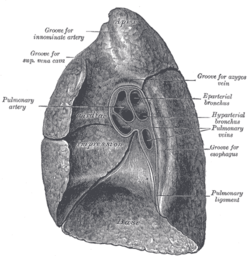
Mediastinal surface of right lung.
-
Azygos vein
-
Azygos vein
See also
- Hemiazygos vein
- Posterior intercostal veins
- Superior vena cava
- Chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency
References
- ↑ Edward Lamperti; Michael Schuenke; Erik Schulte; Udo Schumacher; Ross, Lawrence J. (2006). General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System (Thieme Atlas of Anatomy). Thieme Publishing Group. p. 13. ISBN 3-13-142081-2.
- ↑ http://www.clinicalimaging.org/article/S0899-7071%2899%2900141-2/abstract
- ↑ http://library.prognosisapp.com/case/Emergency/Superior-Vena-Cava-Syndrome[]
- ↑ Berman, Gerald de Lacey, Simon Morley, Laurence (2008). The chest X-ray : a survival guide. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. ISBN 978-0702030468.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 19:03-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Right side of the mediastinum."
- Dissection at lumc.edu
- Radiology at umich.edu
- Function at Knowyourbody.net