Structural basin
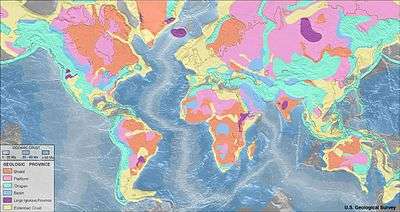
A structural basin is a large-scale structural formation of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat-lying strata. Structural basins are geological depressions, and are the inverse of domes. Some elongated structural basins are also known as synclines. Structural basins may also be sedimentary basins, which are aggregations of sediment that filled up a depression or accumulated in an area; however, many structural basins were formed by tectonic events long after the sedimentary layers were deposited.
Basins appear on a geologic map as roughly circular or elliptical, with concentric layers. Because the strata dip toward the center, the exposed strata in a basin are progressively younger from the outside in, with the youngest rocks in the center. Basins are often large in areal extent, often hundreds of kilometers across.
Structural basins are often important sources of coal, petroleum, and groundwater.
Examples of structural basins
Europe
- Hampshire Basin, United Kingdom
- London Basin, United Kingdom
- Paris Basin, France
- Permian Basin, Poland, northern Germany, Denmark, the Netherlands, the North Sea, and Scotland
North America
Trinidad and Tobago
- Southern Basin, Trinidad
United States
- Albuquerque Basin, New Mexico
- Appalachian Basin, Eastern United States
- Big Horn Basin, Wyoming
- Black Warrior Basin, Alabama and Mississippi
- Delaware Basin, Texas and New Mexico
- Denver Basin, Colorado
- Illinois Basin, Illinois
- Los Angeles Basin, California
- Michigan Basin, Michigan
- North Park Colorado Basin
- Paradox Basin, Utah and Colorado
- Permian Basin, Texas and New Mexico
- Piceance Basin, Colorado
- Powder River Basin, Wyoming and Montana
- Raton Basin, Colorado and New Mexico
- Sacramento Basin, California
- San Juan Basin, New Mexico and Colorado
- Uinta Basin, Utah
- Williston Basin, Montana and North Dakota
- Wind River Basin, Wyoming
Oceania
Australia
South America
- Chaco Basin, Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay
- Magallanes Basin, Chile
- Neuquén Basin, Argentina and Chile
- Paraná Basin, Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay
See also
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Basin. |
References
- Monroe, James S., and Reed Wicander. The Changing Earth: Exploring Geology and Evolution. 2nd ed. Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing Company, 1997. ISBN 0-314-09577-2