Siege of Plevna
| Siege of Pleven | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) | |||||||
 The Capture of the Grivitsa redoubt, by Henryk Dembitzky | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 130,000[3] | 67,000[3] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 40,000 killed or wounded |
25,000 killed or wounded 43,340 surrendered (including non-combatants)[4] [5] | ||||||
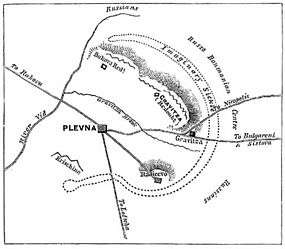
The Siege of Plevna, or Siege of Pleven, was a major battle of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, fought by the joint army of Russia and Romania against the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman defense held up the main Russian advance southwards into Bulgaria for five months, encouraging other great powers actively to support the Ottoman cause. Eventually, superior Russian and Romanian numbers forced the garrison to capitulate. The Russian-Romanian victory on 10 December 1877 was decisive for the outcome of the war and the Liberation of Bulgaria.
Background
In July 1877 the Russian Army, under the command of Grand Duke Nicholas, moved toward the Danube River virtually unopposed, as the Ottomans had no sizable force in the area. The Ottoman high command sent an army under the command of Osman Nuri Pasha to reinforce Nikopol, but the city fell to the Russian vanguard in the Battle of Nikopol (16 July 1877) before Osman reached it. He settled on Plevna, a town among vineyards in a deep rocky valley some twenty miles to the south of Nikopol, as a defensive position. The Ottomans quickly created a strong fortress, raising earthworks with redoubts, digging trenches, and quarrying out gun emplacements. From Plevna Osman's army controlled the main strategic routes to the Balkan Mountains. As the Turks hurried to complete their defenses, Russian forces began to arrive.
Siege
.jpg)
First Battle
General Yuri Schilder-Schuldner, commanding the Russian 5th Division, IX Corps, received orders to occupy Plevna. Schilder-Schuldner arrived outside the town on 19 July and began bombarding the Ottoman defenses. The next day his troops attacked and succeeded in driving Ottoman forces from some of the outer defenses; however, Osman Pasha brought up reinforcements and launched a series of counterattacks, which drove the Russians from the captured trenches, inflicting 3,000 casualties at a cost of 2,000 of his own men.[6]
Second Battle
Osman Pasha strengthened his defences and built more redoubts, his force growing to 22,000 men and 58 guns,[6] while the Russians obtained reinforcements from the army of Prince Carol of Romania (later king Carol I of Romania), who made the stipulation that he be given command of the joint besieging force. General Nikolai Kridener also arrived with the Russian IX Corps. The overall number of Russian troops increased to 35,000 and 176 guns.[6] On 31 July Russian headquarters ordered Kridener to assault the town, attacking from three sides, with every expectation of a Russo-Romanian triumph. General Alexey Schakhovskoy's cavalry attacked the eastern redoubts, while an infantry division under General Mikhail Skobelev assailed the Grivitsa redoubt to the north. Schakhovskoy managed to take two redoubts, but by the end of the day the Ottoman forces succeeded in repulsing all the attacks and retaking lost ground. Russian losses amounted to 7,300, and the Ottomans' to more than 2,000.
Third Battle


After repulsing the Russian attacks, Osman failed to press his advantage and possibly drive off the besiegers; he did, however, make a cavalry sortie on 31 August that cost the Russian 1,300 casualties, and the Ottomans 1,000. The Russians continued to send reinforcements to Plevna, and their army swelled to 100,000 men, now personally led by the Grand Duke. On 3 September Skobelev reduced the Turkish garrison at Lovech, guarding the Ottoman supply lines, before Osman could move out to relieve it (see main article: Battle of Lovcha). The Ottoman army organized the survivors of Lovech into 3 battalions for the Plevna defenses. Osman also received a reinforcement of 13 battalions, bringing his total strength to 30,000—the highest it would reach during the siege.
In August, Romanian troops led by General Alexandru Cernat crossed the Danube and entered the battle with 43,414 men.[7] On 11 September the Russians and Romanians made a large-scale assault on Plevna. The Ottoman forces were dug in and equipped with German Krupp-manufactured steel breech-loading artillery and American-manufactured Winchester repeaters[8] and Peabody-Martini rifles. For three hours they poured murderous fire into the waves of advancing Russians.[9] Czar Alexander II and his brother Grand Duke Nicolas watched from a pavilion built on a hillside out of the line of fire.[10] Skobelev took two southern redoubts. The Romanian 4th division led by General George Manu took the Grivitsa redoubt after 4 bloody assaults, personally assisted by Prince Carol. The next day, the Turks retook the southern redoubts, but could not dislodge the Romanians, who repelled three counterattacks. From the beginning of September, Russian losses had amounted to roughly 20,000, while the Ottomans lost 8,000–10,000.[11]
Fourth Battle

Growing Russian and Romanian casualties put a halt to frontal assaults. General Eduard Ivanovich Todleben arrived to oversee the conduct of the siege as the army chief of staff. Todleben had proven command experience in siege warfare, having gained renown for his defense of Sevastopol (1854–1855) during the Crimean War. He decided on a complete encirclement of the city and its defenders. Osman requested permission from his superiors to abandon Plevna and retreat, but the Ottoman high command would not allow him to do so. By 24 October the Russians and Romanians had closed the ring. Supplies began to run low in the city, and Osman finally made an attempt to break the Russian siege in the direction of Opanets. On 9 December the Ottoman forces silently emerged at dead of night, threw bridges over and crossed the Vit River, attacked on a two-mile front, and broke through the first line of Russian trenches. Here they fought hand to hand and bayonet to bayonet, with, at first, little advantage to either side; however, outnumbering the Ottoman forces almost 5 to 1, the Russians and Romanians eventually drove them back across the Vit, wounding Osman in the process (he was hit in the leg by a stray bullet, which killed his horse beneath him). Rumours of his death created panic. After making a brief stand, the Ottoman forces found themselves driven back into the city, losing 5,000 men to the Russians' 2,000.[12] The next day Osman surrendered the city, the garrison and his sword to Romanian Col. Mihail Cerchez. He was treated honorably, but his troops perished in the snows by the thousands as they straggled off into captivity.
Results


The Siege of Plevna seriously delayed the main Russian advance into Bulgaria, but its end freed up Russian reinforcements, which were sent to Gen. Joseph Vladimirovich Gourko, who then decisively defeated the Ottoman forces in the fourth battle of Shipka Pass. The siege was widely reported on and followed by the public in Europe and beyond. Although the declining Ottoman Empire was by this time often regarded as "the sick man of Europe", the Ottoman Army's five-month-long resistance against a much larger army earned a degree of admiration, which may have contributed to the unsympathetic treatment of the Russian Empire at the Congress of Berlin.
According to British diplomatic historian A. J. P. Taylor:
- Most battles confirm the way that things are going already; Plevna is one of the few engagements which changed the course of history. It is difficult to see how the Ottoman Empire could have survived in Europe...if the Russians had reached Constantinople in July; probably it would have collapsed in Asia as well. Plevna...gave the Ottoman Empire another forty years of life.[13]
The siege of Plevna also signalled the introduction of the repeating rifle into European warfare.[9] Russian troops at Plevna were largely armed with the M1869 Krnka, a single shot lifting breech block conversion of the muzzle loading M1857 rifled musket even though some units had been reequipped with the more modern, but still single shot, Berdan rifle.[9] The old Krnka was soundly outperformed by the more modern single shot Turkish Peabody-Martini rifles and it became clear that the new Berdan rifle had also been rendered obsolete even as it was being introduced into service, outclassed by the Turkish Winchester repeaters. Reports of the heavy losses suffered by the Russian army at the hands of the Turks at Plevna forced armies across Europe to begin the process of either reequipping with repeating rifles or finding a way to convert their existing single shot rifles into magazine fed weapons.
Legacy

- A large new factory building, completed in 1877, of the Finlayson & Co cotton mill in Tampere, Finland was named Plevna commemorating the battle and the Guard of Finland that took part.[14]
- On 10 December 1977 on the occasion of the celebration of the 100th anniversary of the Liberation of Pleven from Turkish rule a museum was opened in Pleven – the Pleven Panorama built in Skobelev Park and the area of the Kovanlak redoubt where during the 3rd attack on Pleven took place one of the heaviest battles.
- The city of Plevna, Montana in the United States was given its name by Bulgarian immigrants building the railroad there in honor of the battle of Plevna.
- In other countries, there are five cities and towns named after Plevna, and there are eighteen Plevna streets in Britain alone. They were named in praise of the liberation of Christians oppressed by Islam[15]
- The community of Plevna, Missouri was named after the battle.
In popular culture
- The best-selling Russian detective novel The Turkish Gambit, the second book in the Erast Fandorin series, is set at the Siege of Plevna. In 2005 a film of the same name was made.
- A famous Mehteran (Ottoman military band) piece "Osman Paşa Marşı" (Osman Pasha March) honors the courageous defense of the Plevna; and is one of the most well-known marches in Turkey.
- Under the Red Crescent by Charles Snodgrass Ryan, Australian Surgeon at the Siege of Plevna, who later operated in the Gallipoli campaign and negotiated with his old friends for burial armistices.
See also
References
- ↑ Siege of Plevna, Neville G. Panthaki, Ground Warfare: H-Q, Vol. II, ed. Stanley Sandler, (ABC-CLIO, 2002), 690.
- ↑ Drury, Ian The Russo-Turkish War 1877: Men-at-Arms, (1994) p.6
- 1 2 Sandler S. Ground Warfare: An International Encyclopedia, V. 1. ABC-CLIO, 2002. P. 690
- ↑ Clodfelter M. Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500-2000. McFarland, 2002. P. 220
- ↑ Casualties The Siege of Plevna in the English Press (19.07.1877-10.12.1877): P. 11 http://dergipark.ulakbim.gov.tr/vakanuvis/article/download/5000159902/5000163084
- 1 2 3 Dowling T. C. Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond. ABC-CLIO. 2014. P. 645
- ↑ [George Marcu, Enciclopedia bătăliilor din istoria românilor, Editura Meronia, Bucureşti 2011]
- ↑ Keith W. Doyon. "M1866 Turkish Contract Winchester (.44 Henry Rimfire)". Militaryrifles.com. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- 1 2 3 "The Plevna Delay: Winchesters and Peabody-Martinis in the Russo-Turkish War: A small Turkish army is trapped, but with the help of surprising firepower, they hold up the entire Russian Campaign for over five months." by Richard T. Trenk, Sr. originally published in Man At Arms Magazine, Volume 19, Number Four, August 1997
- ↑ Page 107 and 108, Virginia Cowles, The Russian Dagger: Cold War in the Days of the Czars, Harper & Row (1969), hardcover, 352 pages
- ↑ Dowling T. C. Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond. ABC-CLIO. 2014. P. 646
- ↑ Eggenberger D. An Encyclopedia of Battles: Accounts of Over 1,560 Battles from 1479 B.C. to the Present. Courier Corporation. 2012. P. 337
- ↑ A. J. P. Taylor (1963). The Struggle for Mastery in Europe: 1848–1918. p. 245.
- ↑ "Finlayson history (see year 1877)". Finlayson.fi. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ "Plevna Siege". Goldenaer.com. Retrieved 2016-02-02.
Bibliography
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Plevna". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. (vol. 21 pp. 838–840, article by John Henry Verrinder Crowe)
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Plevna". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. (vol. 21 pp. 838–840, article by John Henry Verrinder Crowe)- Compton's Home Library: Battles of the World CD-ROM
- George Marcu (coord.), Enciclopedia bătăliilor din istoria românilor, Editura Meronia, Bucureşti 2011
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Siege of Plevna. |
- The Siege of Pleven – scene from the Russian film The Turkish Gambit
- Enciclopediaromaniei.ro
- Militaryrifles.com
- Memorial Chapel to the Hero Grenadiers of Plevna (Moscow)