Beethoven and C minor
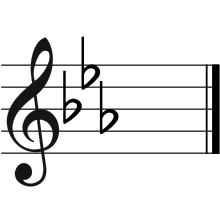 | |
| Relative key | E♭ major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | C major |
| Dominant key | G minor |
| Subdominant | F minor |
| Component pitches | |
| C, D, E♭, F, G, A♭, B♭, C | |
In the compositions of Ludwig van Beethoven, the key of C minor is commonly regarded as significant: works for which he chose this key are felt to be powerful and emotionally stormy.
Background
During the Classical era, C minor was used infrequently and always for works of a particularly turbulent cast. Mozart, for instance, wrote only very few works in this key, but they are among his most dramatic ones (the twenty-fourth piano concerto, the fourteenth piano sonata and the Great Mass in C minor, for instance). Beethoven chose to write a much larger proportion of his works in this key, especially traditionally "salon" (i.e. light and diverting) genres such as sonatas and trios, was a sort of conscious rejection of older aesthetics, valuing the "sublime" and "difficult" above music that is "merely" pleasing to the ear.[1]
The key is said to represent for Beethoven a "stormy, heroic tonality";[2] he uses it for "works of unusual intensity";[3] and it is "reserved for his most dramatic music."[4]
Pianist and scholar Charles Rosen writes:[5]
- "Beethoven in C minor has come to symbolize his artistic character. In every case, it reveals Beethoven as a Hero. C minor does not show Beethoven at his most subtle, but it does give him to us in his most extrovert form, where he seems to be most impatient of any compromise".
A characteristic 19th-century view is that of the musicologist George Grove, writing in 1898:[6]
- "The key of C minor occupies a peculiar position in Beethoven's compositions. The pieces for which he has employed it are, with very few exceptions, remarkable for their beauty and importance."
Grove's view could be said to reflect the view of many participants in the Romantic age of music, who valued Beethoven's music above all for its emotional force.
Not all critics have taken a positive view of Beethoven's habitual return to the tonality of C minor. Musicologist Joseph Kerman faults Beethoven's reliance upon the key, particularly in his early works, as a hollow mannerism: "[T]he 'c-minor mood' in early Beethoven... is one that has dated most decisively and dishearteningly over the years... In this familiar emotional posture, Beethoven seems to be an unknowing prisoner of some conventional image of passion, rather than his own passion's master."[7]
Of the works said to embody the Beethovenian "C minor mood", probably the canonical example is the Fifth Symphony. Beethoven's multi-movement works in C minor tended to have a slow movement in a contrasting major key, nearly always the subdominant of C minor's relative key (E♭ major): A♭ major, providing "a comfortingly cool shadow or short-lived respite",[8] but also the relative key (E♭ major, Op. 1/3), the tonic major (C major, Opp. 9/3, 18/4, 111) and the sharpened mediant major (E major, Op. 37), the last setting a precedent for Brahms' third Piano Quartet, Grieg's Piano Concerto and Rachmaninoff's second Piano Concerto.
In his essay Beethoven's Minority,[9] Kerman observes that Beethoven associated C minor with both its relative (E♭) and parallel (C) majors, and was continually haunted by a vision of C minor moving to C major. While many of Beethoven's sonata-form movements in other minor keys, particularly finales, used the minor dominant (v) as the second key area - predicting a recapitulation of this material in the minor mode[8] - his use of the relative major, E-flat (III) as the second key area for all but two of his C minor sonata-form movements, in many cases, facilitated a restatement of part or all of the second theme in C major in the recapitulation. One exception, the first movement of the Piano Sonata No. 32, uses A-flat major (VI) as its second key area, also allowing a major-mode restatement in the recapitulation - and the other exception, the Coriolan Overture, is only loosely in sonata form and still passes through III in the exposition and major-mode I in the recapitulation. Furthermore, of the final movements of Beethoven's multi-movement works in C minor, three are in C major throughout (Opp. 67, 80, 111), one finishes in C major (Op. 37), and a further four (along with one first movement) end with a Picardy third (Opp. 1/3, 9/3, 10/1, 18/4, 111 i).
List of works
Here is a list of works by Beethoven in C minor that are felt to be characteristic of how Beethoven used this key:[6]
- Cantata on the Death of Emperor Joseph II, WoO 87 (1791)
- Piano Trio, Op. 1, No. 3 (1793)
- Piano Sonata, Op. 10, No. 1 (1795-8)
- Piano Sonata, Op. 13, "Pathétique" (1798)
- String Trio, Op. 9, No. 3 (1798)
- Piano Concerto No. 3 (1800)
- String Quartet, Op. 18, No. 4 (1800)
- Violin Sonata, Op. 30, No. 2 (1802)
- Symphony No. 3, second movement, "Funeral March" (1803)
- 32 Variations in C minor, WoO 80 (1806)
- Coriolan Overture, Op. 62 (1807)
- Fifth Symphony (1808)
- Choral Fantasy, Op. 80 (1808)
- String Quartet No. 10, Op. 74, scherzo movement (1809)
- Piano Sonata No. 32, Op. 111 (his last piano sonata, 1822)
Other minor keys
The works by Beethoven in C minor hardly exhaust the set of emotionally stormy minor-key works by this composer; some useful comparisons would include the piano sonatas Op. 2, No. 1 and Op. 57 (both in F minor), the String Quartet, Op. 95 (also in F minor), the final movements of Beethoven's only two pieces in C-sharp minor (the "Moonlight" Sonata and the String Quartet, Op. 131), and two of his most famous D-minor works: the "Tempest" Sonata and the Ninth Symphony (whose slow movements, like that of many of his C-minor works, are in the subdominant parallel).
See also
References
- ↑ Taruskin, Richard (2005). Oxford History of Western Music. Oxford University Press (USA). ISBN 978-0-19-516979-9. Chapters 30 ("The First Romantics") and 31 ("C-Minor Moods")
- ↑ Wyatt, Henry. "Program Notes: 14 June 2003 — Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (Salzburg, 1756-Vienna, 1791): Overture to Le Nozze di Figaro". Rutgers University (Mason Gross School of the Arts). Archived from the original on 2003-08-27.
- ↑ Bromberger, Eric. http://www.wpas.org/pdf/p147_Midori.pdf
- ↑ (PDF) https://web.archive.org/web/20110716002951/http://www.sandiegosymphony.com/uploads/pdfs/jacobs07.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2006. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Rosen, Charles (2002). Beethoven's Piano Sonatas: A Short Companion. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 134.
- 1 2 Grove, George (1962) [1898]. Beethoven and his Nine Symphonies. New York: Dover Publications (originally Novello, Ewer and Company). p. 181.
- ↑ Kerman, Joseph (1966). The Beethoven Quartets. New York: W. W. Norton. p. 70.
- 1 2 Hepokoski, James and Warren Darcy (2006) [2006]. Elements of Sonata Theory: Norms, Types, and Deformations in the Late-Eighteenth-Century Sonata. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Kerman, Joseph (1994) [1994]. Write All These Down: Essays on Music. Berkeley: University of California Press.