Bonnethead
| Bonnethead shark | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Superorder: | Selachimorpha |
| Order: | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family: | Sphyrnidae |
| Genus: | Sphyrna |
| Species: | S. tiburo |
| Binomial name | |
| Sphyrna tiburo (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
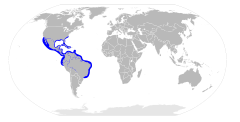 | |
| Range of the bonnethead shark | |
The bonnethead shark or shovelhead (Sphyrna tiburo) is a small member of the hammerhead shark genus Sphyrna, and part of the family Sphyrnidae. It is an abundant species on the American littoral, and the only shark species known to display sexual dimorphism.
Description

Characterized by a broad, smooth, spade-like head, they have the smallest cephalofoil (hammerhead) of all Sphyrna species. The body is grey-brown above and lighter on the underside. On average, bonnethead sharks are about 2–3 ft (0.61–0.91 m) long, with a maximum size of about 5 feet (150 cm). Female Bonnethead sharks tend to be larger than males.
The Greek word sphyrna translates as hammer, referring to the shape of this shark's head; tiburo is the Taino word for shark.
Morpholgy
Sexual dimorphism
Bonnethead sharks are the only sharks known to exhibit sexual dimorphism. In morphology, adult female bonnethead sharks have a broadly rounded head, whereas males possess a distinct bulge along the anterior margin of the cephalofoil. This bulge is formed by the elongation of the rostral cartilages of the males at the onset of sexual maturity and corresponds temporally with the elongation of the clasper cartilages.
Purpose of the hammer
The reasons for cephalofoil has caused scientific debate for more than a decade. Whatever the ultimate purpose, a wing shaped cephalofoil allows hammerhead sharks to swim on a horizontal plane and was thought to give them the ability to execute sharp turns. However, research shows that it is the vertebrae that help them execute sharp turns. The cephalofoil may be responsible for better electroreception (using ampullae of Lorenzini) and heightened olfactory acuity.
Pectoral fins and swimming
The pectoral fins on most fish control pitching (up-and-down motion of the body), yawing (the side-to-side motion) and rolling. Most hammerhead sharks do not yaw or roll and achieve pitch by using their cephalofoil. The smaller cephalofoil of a bonnethead shark is not as successful and they therefore have to rely on the combination of cephalofoil and their large pectoral fins for most of their motility. Compared to other hammerheads, bonnethead sharks have larger and more developed pectoral fins and are the only species of hammerhead to actively use pectoral fins for swimming.
Evolution
Using data from mtDNA analysis, scientist have found that evolution of hammerhead sharks has probably begun with a taxon that had a highly pronounced cephalofoil (most likely that similar to the winghead shark, Eusphyra blochii), and has later been modified through selective pressures. It is thus assumed today that, judging by their smaller cephalofoil, bonnethead sharks are the more recent developments of a 25 million year evolutionary process.
Distribution and habitat
This species occurs off the American coast, in regions where the water is usually warmer than 70 °F (21 °C). It ranges from New England, where it is rare, to the Gulf of Mexico and Brazil, and from southern California to Ecuador. During the summer it is common in the inshore waters of the Carolinas and Georgia; in spring, summer, and fall, it is found off Florida and in the Gulf of Mexico. In the winter, the bonnethead shark is found closer to the equator, where the water is warmer.
It frequents shallow estuaries and bays over grass, mud and sandy bottoms.[1]
Ecology
Behavior
The bonnethead shark is an active tropical shark that swims in small groups of 5 to 15 individuals, although schools of hundreds or even thousands have been reported. Bonnethead sharks move constantly following changes in water temperature and to maintain respiration. The bonnethead shark will sink if it does not keep moving since hammerhead sharks are among the most negatively buoyant of marine vertebrates. The bonnethead shark uses a unique type of cerebrospinal fluid to let others know it is nearby. Like other sharks it is capable of electroreception to detect its preys. This system allows the bonnethead shark to alert other sharks of their presence.
Diet
It feeds primarily on crustaceans, consisting mostly of blue crabs, but also shrimp, mollusks and small fish. Seagrasses have been found in its stomach contents. Their feeding behavior involves swimming across the seafloor, moving its head in arc patterns like a metal detector, looking for minute electromagnetic disturbances produced by crabs and other creatures hiding in the sediment. Upon discovery, they sharply turn around and bite into the sediment where the disturbance was detected. If a crab is caught, the bonnethead shark uses its teeth to grind its carapace and then uses suction to swallow.
To accommodate the many types of animals that it feeds on, the bonnethead shark has small, sharp teeth in the front of the mouth (for grabbing soft prey) and flat, broad molars in the back (for crushing hard-shelled prey).
Reproduction
The bonnethead shark is viviparous. Females reach sexual maturity at about 32 inches, while males reach maturity at around 24 inches. Four to twelve pups are born in late summer and early fall, measuring 12 to 13 inches (330 mm).
Bonnetheads have one of the shortest gestation periods among sharks, lasting only 4.5-5 months.{ref name=iucn/>
A 2001 study showed that a bonnethead female produced a pup by parthenogenesis. The birth took place at the Henry Doorly Zoo in Nebraska and subsequent DNA analysis has shown a perfect match between mother and pup.[2]
Conservation
The bonnethead is an abundant species and is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN. It is heavily targeted by commercial and recreational fisheries and makes up up to 50% of all small shark landings in the eastern US.[1]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sphyrna tiburo. |
- 1 2 3 Cortés, E. (2005). "Sphyrna tiburo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2005: e.T39387A10193033. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ↑ "Captive shark had 'virgin birth'". BBC NEWS.
- "Sphyrna tiburo". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 23 January 2006.
- Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2005). "Sphyrna tiburo" in FishBase. 10 2005 version.
