CSS Chicora
 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Chicora |
| Ordered: | 1862 |
| Laid down: | March 1862 |
| Commissioned: | November 1862 |
| Decommissioned: | February 18, 1865 |
| Fate: | Burned to prevent capture |
| General characteristics | |
| Displacement: | approximately 850 tons |
| Length: | 172.5 ft (52.6 m) |
| Beam: | 35 ft (11 m) |
| Draft: | 14 ft (4.3 m) |
| Propulsion: | Steam engine |
| Speed: | 5 knots (9.3 km/h; 5.8 mph) |
| Complement: | 150 officers and men |
| Armament: |
|
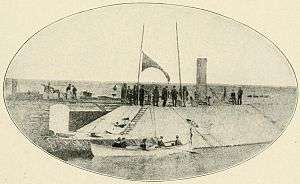
CSS Chicora was a Confederate ironclad ram that fought in the American Civil War. She was built under contract at Charleston, South Carolina in 1862. James M. Eason built her to John L. Porter's plans, using up most of a $300,000 State appropriation for construction of marine batteries; Eason received a bonus for "skill and promptitude." Her iron shield was 4 inches (102 mm) thick, backed by 22 inches (559 mm) of oak and pine, with 2-inch (51 mm) armor at her ends. Keeled in March, she was commissioned in November, Commander John Randolph Tucker, CSN assuming command.
In thick, predawn haze on January 31, 1863, Chicora and CSS Palmetto State raided the Federal blockading force of unarmored ships lying just outside the entrance to Charleston Harbor. With ram and gun, Palmetto State forced USS Mercedita to surrender, then disabled USS Keystone State, who had to be towed to safety. Chicora meanwhile engaged other Union ships in a long-range gun duel, from which she emerged unscathed to withdraw victoriously to shelter inside the harbor.

She took part in the defense of the forts at Charleston on April 7 when they were attacked by a squadron of ironclad monitors under Rear Admiral Samuel Francis du Pont, USN. The Federal ships were forced to retire for repairs and did not resume the action.
Chicora was actively employed in the fighting around Charleston during 1863 and 1864. Her valuable services included the transporting of troops during the evacuation of Morris Island, and the bombardment of Forts Sumter, Gregg, and Wagner. In August 1863 she had the distinction of furnishing the first volunteer officer and crew for the Confederate Submarine Torpedo Boat H. L. Hunley.
"A Lieutenant’s commission in the Confederate States Navy was conferred on me, with orders to report for duty on the ironclad Chicora at Charleston. My duties were those of a deck officer, and I had charge of the first division. On the occasion of the attack upon the blockading squadron ... It was my part, on the memorable morning, to aim and fire one effective shell into the Keystone State while running down to attack us, which (according to Captain LeRoy’s report), killing twenty-one men and severely wounding fifteen, caused him to haul down his flag in token of surrender. The enemy now kept at a respectful distance while preparing their ironclad vessels to sail up more closely. Our Navy Department continued slowly to construct more of these rams, all on the same general plan, fit for little else than harbor defense." -- William T. Glassell, Lt. CSN
She was destroyed by the Confederates when Charleston was evacuated on February 18, 1865.
References
Notes
Bibliography
- Chesneau, Roger; Kolesnik, Eugene M., eds. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Greenwich, UK: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-8317-0302-4.
- Olmstead, Edwin; Stark, Wayne E.; Tucker, Spencer C. (1997). The Big Guns: Civil War Siege, Seacoast, and Naval Cannon. Alexandria Bay, New York: Museum Restoration Service. ISBN 0-88855-012-X.
- Silverstone, Paul H. (2006). Civil War Navies 1855–1883. The U.S. Navy Warship Series. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-97870-X.
- Still, William N., Jr. (1985). Iron Afloat: The Story of the Confederate Armorclads (Reprint of the 1971 ed.). Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 0-87249-454-3.
- Coker, PC, "Charleston's Maritime Heritage 1670–1865", Charleston, CokerCraft Press 1987
- Prisoners of the Civil War; The Paragon Agency, Publishers; 2001
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
External links
 Media related to CSS Chicora (ironclad) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to CSS Chicora (ironclad) at Wikimedia Commons