Chocolate agar
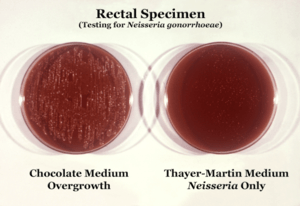
Known as overgrowth, the nonselective chocolate agar medium on the left, due to its composition, allowed for the growth of organismal colonies other than those of N. gonorrhoeae, while the selective Thayer-Martin medium on the right, containing antimicrobials that inhibit the growth of organisms other than N. gonorrhoeae, shows no overgrowth, but is positive for N. gonorrhoeae bacteria. (Enlarge image to see N. gonorrhoeae colonies)
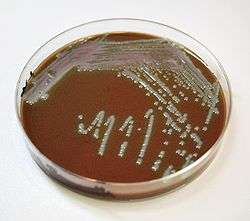
Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA) – is a nonselective, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria.[1][2][3] It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been lysed by slowly heating to 80°C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria meningitidis.[4] In addition, some of these bacteria, most notably H. influenzae, need growth factors such as NAD (factor V) and hemin (factor X), which are inside red blood cells; thus, a prerequisite to growth for these bacteria is lysis of the red blood cells. The heat also inactivates enzymes which could otherwise degrade NAD. The agar is named for the color and contains no actual chocolate.
Variants
Chocolate agar with the addition of bacitracin becomes selective, most critically, for the genus Haemophilus. Another variant of chocolate agar called Thayer-Martin agar contains an assortment of antibiotics which select for Neisseria species.
References
- ↑ Segen. "Chocolate agar: Definition". The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- ↑ "Chocolate Agar (CHOC)". Anaerobe free systems. Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- ↑ Anderson, Cindy (2013). Great Adventures in the Microbiology Laboratory (7th ed.). Pearson. p. 175. ISBN 978-1-269-39068-2.
- ↑ Gunn, B.A. "Chocolate agar: A differential medium for gram positive cocci". PubMed. Retrieved 28 September 2012.