Chromosome 3 (human)
| Chromosome 3 (human) | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 3 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 3 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 198,295,559 bp |
| Number of genes | 2,203 |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Metacentric[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| RefSeq | NC_000003 |
| GenBank | CM000665 |
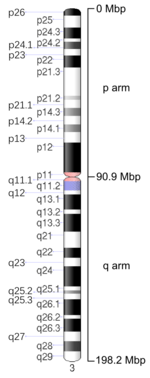
Ideogram of human chromosome 3. Mbp means mega base pair. See locus for other notation.
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans almost 200 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of genetic research. Because researchers use different approaches to predict the number of genes on each chromosome, the estimated number of genes varies. Chromosome 3 likely contains between 1,100 and 1,500 genes.
Genes
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
The following are some of the genes located on chromosome 3:
- AMOTL2: encoding protein]] Angiomotin-like protein 2
- APEH: encoding enzyme Acylamino-acid-releasing enzyme
- AZI2: encoding protein 5-azacytidine-induced protein 2
- C3orf23: encoding protein Uncharacterized protein C3orf23
- C3orf60/NDUFAF3: encoding enzyme NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex assembly factor 3
- C3orf70: encoding protein C3orf70 (Chromosome 3 Open Reading Frame 70)
p-arm
- ALAS1: aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 1
- BTD: biotinidase
- CACNA2D3: calcium channel, voltage-dependent, alpha 2/delta subunit 3
- CCR5: chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5
- CNTN4: Contactin 4
- COL7A1: Collagen, type VII, alpha 1 (epidermolysis bullosa, dystrophic, dominant and recessive)
- C3orf14-Chromosome 3 open reading frame 14: predicted DNA binding protein.
- MITF: microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
- MLH1: mutL homolog 1, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 2 (E. coli)
- OXTR: oxytocin receptor
- PTHR1: parathyroid hormone receptor 1
- SCN5A: sodium channel, voltage-gated, type V, alpha (long QT syndrome 3)
- SLC25A20: solute carrier family 25 (carnitine/acylcarnitine translocase), member 20
- TMIE: transmembrane inner ear
- VHL: von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor
- FOXP1: Forkhead Box Protein P1
- CRBN: Cereblon protein[2]
q-arm
- ADIPOQ: adiponectin
- CAMPD1: Camptodactyly
- CPOX: coproporphyrinogen oxidase (coproporphyria, harderoporphyria)
- HGD: homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (homogentisate oxidase)
- IFT122: intraflagellar transport gene 122
- MCCC1: methylcrotonoyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase 1 (alpha)
- PCCB: propionyl Coenzyme A carboxylase, beta polypeptide
- PDCD10: programmed cell death 10
- PIK3CA: phosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, alpha polypeptide
- RAB7: RAB7, member RAS oncogene family
- RHO: rhodopsin visual pigment
- SOX2: transcription factor
- USH3A: Usher syndrome 3A
- ZNF9: zinc finger protein 9 (a cellular retroviral nucleic acid binding protein)
Diseases and disorders
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
The following diseases and disorders are some of those related to genes on chromosome 3:
- 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency
- 3q29 microdeletion syndrome
- Alkaptonuria
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
- Atransferrinemia
- Autism
- Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy
- ADOA Plus Syndrome
- Biotinidase deficiency
- Blepharophimosis, epicanthus inversus and ptosis type 1
- Breast/colon/lung/pancreatic cancer
- Brugada syndrome
- Castillo fever
- Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency
- Cataracts
- Cerebral cavernous malformation
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 2
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Chromosome 3q duplication syndrome
- Coproporphyria
- Dandy-Walker syndrome
- Deafness
- Diabetes
- Dopamine receptor
- Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- Endplate acetylcholinesterase deficiency
- Essential tremors
- Ectrodactyly, Case 4
- Glaucoma, primary open angle
- Glycogen storage disease
- Hailey-Hailey disease
- Harderoporphyrinuria
- Heart block, progressive/nonprogressive
- Hereditary coproporphyria
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
- HIV infection, susceptibility/resistance to
- Hypobetalipoproteinemia, familial
- Hypothermia
- Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter
- Long QT syndrome
- Lymphomas
- Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
- Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, Murk Jansen type
- Microcoria
- Moebius syndrome
- Moyamoya disease
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Muir-Torre family cancer syndrome
- Myotonic dystrophy, type 2
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Neuropathy, hereditary motor and sensory, Okinawa type
- Night blindness
- Nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal recessive
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Ovarian cancer
- Porphyria
- Propionic acidemia
- Protein S deficiency
- Pseudo-Zellweger syndrome
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Romano-Ward syndrome
- Seckel Syndrome
- Sensenbrenner syndrome
- Septo-optic dysplasia
- Short stature
- Spinocerebellar ataxia
- Sucrose intolerance
- T-cell leukemia translocation altered gene
- Usher syndrome type III
- Usher syndrome (Finland)
- Usher syndrome
- von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- Waardenburg syndrome
- Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group c
References
- ↑ "Table 2.3: Human chromosome groups". Human Molecular Genetics (2nd ed.). Garland Science. 1999.
- ↑ CRBN cereblon [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 3. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/23/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.