Cynetes
The Cynetes or Conii were one of the pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, living in today's Algarve and Lower Alentejo regions of southern Portugal before the 6th century BCE (in what was to become the southern part of the Roman province of Lusitania).
Origins and location
They are often mentioned in the ancient sources under various designations, mostly Greek or Latin derivatives of their two tribal names: ‘Cynetas’/’Cynetum’;[2] ‘Kunetes’, ‘Kunetas’, and ‘Kunesioi'[3] or ‘Cuneus’,[4] followed by ‘Konioi’,[5] ‘Kouneon’[6] and ‘Kouneous’/‘Kouneoi’.[7] The Conii occupied since the late Bronze Age most of the present-day Lower Alentejo, Algarve, and the southwestern Huelva province, giving the Algarve its pre-Roman name, the Cyneticum. Prior to the Celtic-Turduli migrations of the 5th-4th Centuries BC the original Conii territories also included upper Alentejo and the Portuguese coastal Estremadura region stretching up to the Munda (Mondego) river valley.
Culture
Their presence in these regions is attested archeologically by the elaborated cremation burial-mounds of their ruling elite, whose rich grave-goods and the inscripted slabs in ‘Tartessian alphabet’ – also referred to as ‘Southwest script’ – that mark the graves, evidence close contacts with North Africa and the eastern Mediterranean since the 9th Century BC.
Inscriptions in the Tartessian language have been found in the area, in a variety often referred to as Southwest Paleohispanic script.[8][9] The name Conii, found in Strabo, seems to have been identical with the Cynesii, who were mentioned by Herodotus as the westernmost dwellers of Europe and distinguished by him from the Celts.[10]
Towns
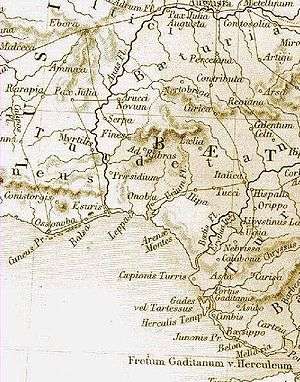
The capital of the Conii was Conistorgis, according to Strabo, who considered the region Celtic.[11] In the local language Conistorgis probably means "City of the Conii". Its precise location has not been determinated. Some authors[12] suggest that Pax Julia might have been founded over the ruins of Conistorgis. Other Conii towns (Oppida) included Ipses (Alvor), Cilpe (Cerro da Rocha Branca – Silves), Ossonoba (near Faro; Iberian-type mint: Osunba), Balsa (Quinta da Torre de Aires, Santa Luzia – Tavira), Baesuris (Castro Marim; Iberian-type mint: Baesuri) and Myrtilis (Mértola; Iberian-type mint: Mrtlis Saidie). According to Pomponius Mela the population of these parva oppida did not surpassed the 6,000 inhabitants.[13] A powerful urban aristocracy of Phoenician and Turdetanian or Turduli colonists dominated all the trade, fishing, and shipbuilding in these same coastal settlements since the 4th Century BC, until the Carthaginians occupied the Cyneticum and founded the Punic colonies of Portus Hannibalis (near Portimão?) and Portus Magonis (Portimão) at the late 3rd Century BC.[14]
History
The Conii seemed to have played no significant role in the 2nd Punic War and subsequent conflicts, even though they were constantly under the pressure from the northerly Celtic tribes throughout the 3rd-2nd Centuries BC, which may explain their willingness to place themselves under the protection of foreign powers such as Carthage and later Rome. Around the 3rd Century BC the Celtici reached the western Algarve, establishing a colony at Laccobriga (Monte Molião, near Lagos) and in 153 BC, during the Lusitanian Wars against Rome, Conistorgis fell to the Lusitani and their Vettones’ allies.[15] The Conii were thence forced to switch their allegiance from the Roman Republic to the Lusitani, being subjected in 141-140 BC to Consul Quintus Fabius Maximus Servilianus’ reprisal campaigns in the Iberian southwest.[16] In 138-137 BC the Cyneticum was aggregated into Hispania Ulterior province, only to become again a battleground during the Sertorian Wars, when Quintus Sertorius seized Conistorgis and Consul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius devastated the region in retaliation,[17] being defeated at the battle of Laccobriga in 78 BC.[18]
Romanization
In 27-13 BC the romanized Conii were incorporated into Lusitania province.
See also
- History of Portugal
- Prehistoric Iberia
- Cyneticum
- Timeline of Portuguese history
- Sefes
- Celtici
- Sertorian Wars
- Southwest Paleohispanic script
- "Tartessian" language (Southwestern or "South-Lusitanian" language)
- Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
Notes
- ↑ Arkeotavira.com map
- ↑ Avienus, Ora Marítima, 200, 205, 223
- ↑ Herodoros of Heracleia, Fragments
- ↑ Pliny the Elder, Natural History, V, 41, 145.
- ↑ Polybius, Istorion, 10: 7, 5.
- ↑ Strabo, Geographikon, III, 1, 4.
- ↑ Appian, Iberiké, 10: 75
- ↑ Koch, John T (2010). Celtic from the West Chapter 9: Paradigm Shift? Interpreting Tartessian as Celtic. Oxbow Books, Oxford, UK. p. 187. ISBN 978-1-84217-410-4.
- ↑ Koch, John T (2011). Tartessian 2: The Inscription of Mesas do Castelinho ro and the Verbal Complex. Preliminaries to Historical Phonology. Oxbow Books, Oxford, UK. pp. 4–5. ISBN 978-1-907029-07-3.
- ↑ Herodotus writes "now the Celtae dwell beyond the pillars of Hercules, being neighbours of the Cynesii, who are the westernmost of all nations inhabiting Europe" (Herodotus, II, 33). In another reference noting the Celts again in the extreme west, he refers to their neighbors the Cynetes: "...the Celts, who, save only the Cynetes, are the most westerly dwellers in Europe." (IV, 49).
- ↑ "In the country of the Celti, Conistorgis is the best known city" (Strabo, III, 2, 2).
- ↑ Ensaio Monográfico de Beja, 1973, Manuel Joaquim Delgado e Beja XX Séculos de História de Uma Cidade,
- ↑ Pomponius Mela, De Chorographia, III, 7.
- ↑ Arruda, O 1.º milénio a.n.e no centro e sul de Portugal (2005), pp. 9-156.
- ↑ Appian, Iberiké, 56-57.
- ↑ Appian, Iberiké, 68-69.
- ↑ Sallust, Excerptae de Historiis, 1, 112-113.
- ↑ Plutarch, Sertorius, 13.
References
- Arruda, Ana Margarida, O 1.º milénio a.n.e no centro e sul de Portugal: leituras possíveis no início de um novo século, in O Arqueólogo Português, série IV, volume 23, Lisboa (2005), pp. 9–156. (in Portuguese)
- Mattoso, José (dir.), História de Portugal. Primeiro Volume: Antes de Portugal, Lisboa, Círculo de Leitores, 1992. (in Portuguese)
- Berrocal-Rangel, Luis (2005). "The Celts of the Southwestern Iberian Peninsula". e-Keltoi: Journal of Interdisciplinary Celtic Studies. 6: 481–96.
- Júdice Gamito, Teresa (2005). "The Celts in Portugal". e-Keltoi: Journal of Interdisciplinary Celtic Studies. 6: 571–605.
- Strabo, Geographika, III, 2, 2.
- Muñoz, Mauricio Pasto: Viriato, A Luta pela Liberdade, Ésquilo, Lisboa 2003 (third edition) ISBN 972-8605-23-4
Further reading
- Ángel Montenegro et alii, Historia de España 2 - colonizaciones y formación de los pueblos prerromanos (1200-218 a.C), Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) ISBN 84-249-1386-8
- Berrocal-Rangel, Luis, Los pueblos célticos del soroeste de la Península Ibérica, Editorial Complutense, Madrid (1992) ISBN 84-7491-447-7
- Philip Matysak, Sertorius and the struggle for Spain, Pen & Sword Military, Barnsley (2013) ISBN 978-1848847873
- Luis Silva, Viriathus and the Lusitanian resistance to Rome 155-139 BC, Pen & Sword Military, Barnsley (2013) ISBN 9781781591284