Dalapon
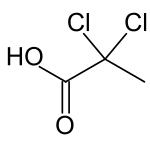 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2-Dichloropropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 75-99-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 6178 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.840 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4Cl2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 142.96 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dalapon is a selective herbicide used to control perennial grasses. The major use of dalapon is on food crops including sugarcane and sugar beets.[1]
Its use is no longer authorized in France.[2]
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health in the United States has identified it as a potential workplace hazard. The recommended time-weighted average exposure limit is 6 milligrams per cubic meter during a 10-hour workday.[3]
Exposure to dalapon affects the eyes, central nervous system, digestive system, respiratory system, and skin. Dalapon can be absorbed through inhalation, eye contact, skin contact, or by ingesting it. The symptoms of dalapon exposure include eye irritation, central nervous system depression, bradycardia, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, fatigue, burn, upper respiratory irritation, and skin irritation. First aid measures for exposure include artificial respiration, immediate eye irrigation, and immediate washing with water. Immediate medical attention should be sought if dalapon is ingested.[3]
References
- ↑ "Dalapon". pmep.cce.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- ↑ "Retrait de l'autorisation de mise sur marché des préparations contenant du Dalapon." (PDF). 18 August 2002. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- 1 2 "CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - 2,2-Dichloropropionic acid". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2016-06-07.