de Havilland Sea Vixen
| DH.110 Sea Vixen | |
|---|---|
| | |
| The only remaining airworthy Sea Vixen (civil registration G-CVIX) at the 2009 Yeovilton Air Show | |
| Role | Carrier-based fighter |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | de Havilland |
| First flight | 26 September 1951[1] |
| Introduction | July 1959 |
| Retired | 1972 |
| Primary user | Royal Navy |
| Number built | 145 |
|
| |
The de Havilland DH.110 Sea Vixen is a twin boom, twin-engined 1950s–60s British two-seat jet fighter operated by the Fleet Air Arm. It was designed by de Havilland during the late 1940s at their facility in Hatfield, Hertfordshire. Developed from an earlier first generation jet fighter, the Sea Vixen was a capable carrier-based fleet defence fighter that served into the 1970s. Initially produced by de Havilland, the type was later known as the Hawker Siddeley Sea Vixen after de Havilland became a part of the Hawker Siddeley Group in 1960.
The Sea Vixen had the distinction of being the first British two-seat combat aircraft to achieve supersonic speed, albeit not in level flight. Operating from the decks of various British aircraft carriers, the type was used in combat in Tanganyika and in Yemen during the Aden Emergency. In 1972, the Sea Vixen was phased out in favour of the Mach 2-capable McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II interceptor. A single example remains airworthy today in the UK and is displayed regularly at airshows.
Development
Origins
In 1946, the de Havilland Aircraft Company conducted a series of discussions with officials within the British Admiralty on the topic of its requirements for prospective jet-powered all-weather fighter aircraft.[1] From these talks, it became clear that such an aircraft would have to have a crew of two to make effective use of the radar and navigational facilities, that a twin-engine arrangement was heavily desired for reliability for safe extended operations over the sea, and that there was interest in using a swept wing. It would also possess a moderate wing loading, for manoeuvrability when at altitude as well as for carrier deck take-offs and landings; for the latter role, it was determined that highly effective flaps were necessary.[1] Accordingly, de Havilland decided to pursue development of an appropriate design to conform to the demands of the Royal Navy. The proposed aircraft, which was designated as the DH 110 by de Havilland, was a twin-engined all-weather fighter.[1]

The DH 110's design shared the twin-boom layout of the preceding de Havilland Vampire and Venom, had an all-metal structure, featured a swept wing configuration (swept at an angle of 45°), and adopted an armament of four 30 mm ADEN cannons.[1] It was to be powered by a pair of Rolls-Royce Avon turbojet engines, each capable of generating 7,500 lbf (33 kN) of thrust, which would allow the aircraft to be supersonic in a shallow dive.[1] Once in flight, the DH 110 had the distinction of being the first British two-seat combat aircraft to achieve supersonic speed.[2][3]
In January 1947, specifications N.40/46 and F.44/46 were issued by the British Air Ministry for similar night-fighters to equip the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) and Royal Air Force (RAF); de Havilland submitted their DH 110 proposal to both specifications.[1] In response, nine DH 110 prototypes were ordered for the RAF (together with four of the competing Gloster Javelin) and four prototypes for the Fleet Air Arm.[4][5] In 1949, however, the Royal Navy decided to procured the de Havilland Sea Venom which, as a development of a preexisting aircraft, was cheaper and would be available quicker in order to meet its immediate needs for a jet-powered night fighter to replace its fleet of piston-engined de Havilland Sea Hornets, while the RAF decided to cut its order back to two prototypes.[1] Despite this setback, de Havilland elected to continue work upon the DH 110 while trying to recapture official interest in the type.[1][6]
On 26 September 1951, an initial prototype was completed and conducted its maiden flight from Hatfield Aerodrome, piloted by John Cunningham.[5][7] Early flight tests of the prototype demonstrated the aircraft's performance to have exceeded expectations; by the following year, the prototype was regularly flying in excess of the speed of sound.[1] However, tragedy struck while the DH 110 was demonstrated at the Farnborough Airshow on 6 September 1952.[8] Following a demonstration of its ability to break the sound barrier during a low level flight, the aircraft disintegrated. Debris then landed upon spectators; the accident killed a total of 31 people, including the crew of two, test pilot and record breaker John Derry and Tony Richards.[8][9]
Subsequent investigation of the accident traced the failure to faulty design of the end sections of the main spar, which resulted in the outer ends of the wings shearing off during a high-rate turn. The subsequent shift in the DH 110's centre of lift caused the aircraft to lurch violently, creating forces of over 12 g, resulting in the cockpit and tail sections breaking away and the engines being torn from the airframe. One of the engines hit an area crowded with spectators at the end of the runway, causing the majority of casualties. Other spectators were injured by debris from the cockpit landing close to the main spectator enclosures alongside the runway. This incident led to a restructuring of safety regulations for air shows in the UK, and no member of the public died as a result of a UK airshow demonstration flight for more than 62 years, until the 22 August 2015 Shoreham Airshow crash of a Hawker Hunter killed eleven.[8]
Redesign and navalisation
In response to the loss of the first prototype, de Havilland enacted a series of modifications to the design, which were implemented upon the remaining second prototype. One of the more obvious aerodynamic changes to the aircraft was the adoption of an all-moving tailplane, the modified prototype did not return to flight until July 1954.[10] By this time, the RAF had announced the abandonment of its interest in the DH 110, having elected to procure the Gloster Javelin instead;[11] however, the Fleet Air Arm had decided that it would adopt the aircraft as a replacement for its interim fleet of Sea Venoms.[12] In February 1955, an order was placed for 110 navalised aircraft, which received the name Sea Vixen.[13]

In addition to tailoring the aircraft specifically to the maritime environment and the requirements of the Royal Navy, de Havilland implemented considerable alterations to the base concept of the Sea Vixen during its redesign.[1] Throughout the 1950s, in which the DH 110 was still being gestated, major advancements in the field of aviation subsystems had occurred in weaponry, fire-control system, radar equipment, and cockpit instrumentation. Critically, the concept of the aircraft being an integrated weapon system had proliferated, under which sensors such as the radar would be more directly tied into navigation and weapon systems.[1] de Havilland elected to implement this concept on the design of the Sea Vixen.[1] According to aviation author David Hobbs, it was the first British fighter aircraft to be designed in this manner.[14]
In June 1955, a semi-navalised prototype, XF828, was completed for the purpose of conducting carrier flight deck suitability trials.[13] For this purpose, XF828 featured several changes, including the alteration of the wing's leading edge profile and the strengthening of the wings, as well as underwing fixture points to perform catapult launches, and a tailhook to conduct arrested landings; however, it lacked a wing folding mechanism or fittings for armaments.[13] On 20 June 1955, this aircraft conducted its first flight from de Havilland's facility at Christchurch Airfield, Dorset. The following year, XF828 performed its first arrested deck landing on the fleet aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal.[15]
In April 1956, the finalised production drawings were formally issued.[13] The fully navalised production Sea Vixen featured a number of improvements over earlier development models; these included the addition of a powered folding wing system, reinforcement of the undercarriage to withstand the additional stresses of carrier landings, a steerable nose wheel, a revised tail unit, and the redesigning of the fuselage to equip armaments and operational equipment.[3][13] On 20 March 1957, the first true Sea Vixen, designated as the Sea Vixen FAW.20 (fighter all-weather, later redesignated FAW.1), performed its first flight. This aircraft was promptly used for clearance trials, in particular for addressing handling problems; the second production aircraft was used for engineering trials and the third aircraft for conducting radar trials.[16] On 2 July 1959, the first Sea Vixen-equipped squadron was formed.[17]
Production Sea Vixens were initially manufactured by de Havilland at the former Second World War Airspeed Ltd. 'shadow factory' at Christchurch near Bournemouth, starting in March 1957.[1] In August 1962, all production activity was transferred to another de Havilland factory located at Hawarden, near Chester.
Further development


Beyond the initial FAW.1 model, de Havilland proceeded with the development of an improved variant, which was subsequently designated as the Sea Vixen FAW.2. This served as the successor to the FAW.1 and included many improvements. As well as Firestreak missiles, it could carry the Red Top air-to-air missile, four SNEB rocket pods and the air-to-ground Bullpup missile. An enlarged tail boom allowed for additional fuel tanks in the "pinion" extensions above and in front of the wing leading edge, there was an improved escape system and additional room for more electronic countermeasures (ECM) equipment.[3] However, the changes in aerodynamics meant that the 1,000 lb bomb could no longer be carried. Visually the FAW.1 and FAW.2 could be distinguished by the tail booms which extended forward over the leading edge of the wing on the FAW.2.
In 1962, the Sea Vixen FAW.2 conducted its maiden flight; the type entered service with frontline squadrons in 1964. Overall, a total of 29 FAW.2s were newly built along with a further 67 FAW.1s that were rebuilt and upgraded to FAW.2 standard. In 1966, the original FAW.1 begun to be phased out. In 1972, the career of the Sea Vixen FAW.2 came to an end. It had been planned to replace the Sea Vixen with the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, the aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal and Eagle were both intended to be refitted in order to properly accommodate the new aircraft. Due to defence cuts and following the decommissioning of HMS Eagle, only Ark Royal underwent conversion work to take the new Phantom.
A small number of Sea Vixens subsequently saw service in the less glamorous role of drones, in which capacity they were redesignated as the Sea Vixen D.3. Only four aircraft were converted to the D.3 standard,[18] though three more were dispatched to Farnborough to undergo conversion, but ultimately went unconverted.[18] The last remaining airworthy Sea Vixen (XP924) was a D3 conversion.[18] A number of other Sea Vixens became target tugs and were redesignated as the Sea Vixen TT.2.
Design

The de Havilland Sea Vixen was a jet-powered fleet defence fighter, furnished with modern radar and air-to-air armaments to perform its primary mission. Upon entering service, it was the first British aircraft to be solely armed with missiles, rockets and bombs; it was also the first fighter aircraft operated by the FAA to not be equipped with guns of any form.[12][19] The Sea Vixen FAW.1 was armed with four de Havilland Firestreak air-to-air missiles, while the Sea Vixen FAW.2 was additionally equipped with the more capable Red Top missile.[12] The original DH.110 design as offered to the RAF had carried an armament of four cannons; however the cannon were soon removed and an all-missile armament was instead deployed.[13][19] The Sea Vixen FAW.2's ability to use its compliment of air-to-air missiles was greatly enhanced by the presence of the AI18 radar, operated by a dedicated observer.[19]
In addition to its principal fleet defence role, the Sea Vixen could also perform ground attack missions.[12] For this purpose, it was armed with two Microcell unguided 2 inch (51 mm) rocket packs, Bullpup air-to-ground missiles, and four 500 lb (227 kg) or two 1,000 lb (454 kg) bombs.[13][20] The Sea Vixen was furnished with a refuelling probe which enabled the type to conduct aerial refuelling from tanker aircraft, allowing for extended range missions to be performed.[3] In addition, appropriate equipment was developed for the Sea Vixen that allowed it to be used as a tanker for the purpose of refueling other aircraft.[21] The Sea Vixen FAW.1 was also cleared to carry the Red Beard free-fall nuclear bomb in the event of an "extreme operational emergency".[22]
The Sea Vixen was powered by pair of Rolls-Royce Avon 208 turbojet engines, capable of generating 11,230 lbf (50.0 kN) thrust; these enabled a maximum speed of 690 mph (1,110 km/h) and a range of up to 600 mi (1,000 km).[13][19] It had a twin-boom tail configuration, as used on the earlier de Havilland Sea Vampire and Sea Venom fighter aircraft, this was the largest similarity between the Sea Vixen and its predecessors, the former being considerably larger.[12] The internal volume of the tail boom was used to accommodate both fuel and avionics, and were considerably enlarged for this purpose on the improved Sea Vixen FAW.2 variant.[3] The twin boom tail reduced the length and height of the aircraft, both crucial factors to enable its stowage onboard aircraft carriers; it also had the advantages of minimising engine-out asymmetry, shortening of the jetpipes and better facilitated access.[1]

The fuselage comprises several sections, the principal being the one-piece central and stub-wing assembly section.[20] The front fuselage, composed of the pressurized cabin, the brake below the pressure flooring and the radar compartment and its hinged radome are mounted upon four attachments on the forward face of the front spar. Various electrical compartments are located aft of the front spar, above the wing, which are accessible through hatches.[20] The engines are installed within the main fuselage aft of the main box, they could be removed from the fuselage for servicing via detachable panels on the upper fuselage surface.[23] Sections of the fuselage skin were chemical milled while other parts were machine milled. The powered folding wing made use of a pair of wing-fold joints which involved a total of six main attachment points.[24]
The Sea Vixen had a crew of two, a pilot and an observer to operate the radar. The pilot's canopy was offset to the left-hand side of the fuselage, while the observer was housed to the right completely within the fuselage, the latter gaining access to his position through a flush-fitting top hatch, nicknamed the "Coal Hole".[13][25][Note 1] The observer's position was darkened and located deeper down into the fuselage, the former quality been seen to improve the visibility of the radar imagery.[3][26] Both positions were fitted with fully automated height adjustable Martin-Baker Mk.4 ejector seats, which were capable of being deployed under a range of conditions and circumstances, including the aircraft being submerged in water.[3][20] Each crew member had a single centralized service connector comprising circuits that served ventilated g-suits as well as controls for humidity and temperature for crew comfort.[20]
The flying controls of the Sea Vixen were relatively complex, which controlled the fully powered tailplane, ailerons and rudder; these controls remained usable even in the absence of electrical power, such as in the event of a double engine failure.[24] Actuation of the powered flight control surfaces was provided by a pair of independent hydraulic systems and typically featured variable gearing of control movements over differing speeds. An intricate three-section flap arrangement was employed, partially due to the nature of the wing's geometry.[24] The navigation, flight instrumentation and communications equipment included ground and air position indicators, a reference gyro, an autopilot capable of maintaining altitude and speed as well as yaw and pitch damping, tactical air navigation system (TACAN), and ultra high frequency (UHF) radio system.[20]
Operational history

The aircraft did not take part in any true wars during its career with the Fleet Air Arm though it took part in many operations. In 1961, President Abdul Karim Kassem of Iraq threatened to annex the neighbouring oil-rich state of Kuwait. In response to Kuwait's appeal for external help, the United Kingdom dispatched a number of ships to the region, including two fleet carriers. Sea Vixens aboard the fleet carriers flew patrols in the region, and Kassem's aggressive actions wilted in the face of the strong naval presence, thus averting a war over Kuwait.
In January 1964, trouble flared in the East African state of Tanganyika after the 1st and 2nd Tanganyika Rifles mutinied against the British officers and NCOs who, despite Tanganyika being independent, still commanded the regiment. The mutineers also seized the British High Commissioner and the airport at the capital Dar-es-Salaam. The UK responded by sending the light fleet carrier HMS Centaur, accompanied by 45 Commando, Royal Marines. The Sea Vixens, flying off Centaur, performed a number of duties including the providing of cover for the Royal Marines who were landed in Tanganyika by helicopters. The operation "to restore Tanganyika to stability" ended in success. That same year, Sea Vixens of HMS Centaur saw service once again in the Persian Gulf, including the launch of air strikes against rebel forces, this time supporting British forces fighting against locals disgruntled by the loss of tolls in the Radfan. Later in 1964, HMS Centaur's 892 Squadron Sea Vixens stationed off Indonesia, helped to prevent an escalation of President Sukarno's Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation.[27]

Sea Vixens saw further service during the 1960s, performing duties on Beira Patrol, a Royal Navy operation designed to prevent oil reaching landlocked Rhodesia via the then Portuguese colony of Mozambique. The Sea Vixen also saw service in the Far East. In 1967, once again in the Persian Gulf, Sea Vixens helped cover the withdrawal from Aden. There were a number of Royal Navy warships involved, including the carriers HMS Albion, HMS Bulwark and HMS Eagle (carrying the Sea Vixens) and the LPD (Landing Platform Dock) HMS Fearless.
The Sea Vixen also took to the skies in the aerobatic role, performing in two Royal Navy display teams: "Simon's Sircus" (sic) and "Fred's Five".
Of the 145 Sea Vixens constructed, 54 were lost in accidents. Two DH.110 development prototypes were also lost.[28]
A small number of Sea Vixens were sent to FR Aviation at Tarrant Rushton airfield for conversion to D.3 drone standard, with some undergoing testing at RAF Llanbedr before the drone programme was abandoned.[29][30] Among them was XP924, now G-CVIX, the only Sea Vixen to remain in flying condition, which has now been returned to 899 NAS colours. Formerly owned and operated by De Havilland Aviation, G-CVIX could be viewed at their hangar at Bournemouth Airport in Dorset, southern England, or at air shows around the UK. The Air Accident Investigation Branch published an enquiry into damage suffered by G-CVIX on landing at Bournemouth on 5 April 2012.[31] On 16 September 2014, G-CVIX was transferred to Naval Aviation Ltd., a subsidiary of Fly Navy Heritage Trust and will be based at the Royal Naval Air Station Yeovilton in Somerset.[32]
Operators
- Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm
| Squadron/Flight | From | First on carrier | To | Codes | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 Sqn Y Flight [33] | November 1958[34] | Never | 2 July 1959 | ? | Intensive Flying Trials Unit (IFTU) based at RNAS Yeovilton.[34] Reformed as 892 Sqn.[35] |
| 892 Sqn[33] | 2 July 1959 | 3 March 1960[35] Ark Royal |
1965 | 208-219 | Flew from: Ark Royal, Victorious, Hermes and Centaur (late 1963 to mid-1965, the fourth and last commission of the ship) |
| 890 Sqn[33] | 1 February 1960 | July 1960 Hermes |
1966[36] | 240-254 | Flew from: Hermes and Ark Royal. Disbanded 1966, reformed September 1967 initially with four FAW.1, and converting to FAW.2.[36] |
| 893 Sqn[33] | 9 September 1960[35] | Ark Royal | 1964 | 455-468 | Flew from: Victorious, with short periods on: Ark Royal and Centaur. |
| 899 Sqn[33] | 1 February 1961[35] | ? | 1965 | 485-489 | Sea Vixen HQ Sqn Yeovilton, with short periods on: Eagle. 899 was the first squadron to evaluate and operate Sea Vixen FAW2 aircraft |
| 766B Training Sqn[33] | October 1959 | 1964 Eagle post refit trials | 1965?[37] | 710-722 | 1962 renamed Naval Air Fighter School; provided a/c and crews for "Fred's Five" aerobatic team, all of whom were instructors on 766 squadron. |
| Squadron/ Flight | From | First on carrier | To | Codes | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 JSTU[38] | April 1964 | Never | February 1966[38] | 13 Joint Service Trials Unit (13 JSTU). Red Top trials at Hatfield and Boscombe Down. | |
| 899 Sqn[37] | December 1963 | December 1964 Eagle |
February 1972 | 120-127 130-137 |
Flew from: Eagle. Last operational carrier embarked Sea Vixen squadron |
| 766 Sqn[37] | 7 July 1965[36] | Never? | 10 February 1970?[Note 2][Note 3] | 700-707 710-717 720-727 |
Naval Air Fighter School, Yeovilton |
| 893 Sqn[37] | 4 November 1965[36] | 19 April 1966 Victorious |
July 1970[39] | 240-247 250-257 |
Flew from: Victorious, Yeovilton, RAF Akrotiri, then Hermes. |
| 892 Sqn[37] | 1963[39] | Hermes | October 1968 | 301-315 | Flew from Hermes. 1968 Simon's Circus aerobatic team from this squadron performed at Farnborough Air Show. |
| 890 Sqn[37] | September 1967[36] | Never | 6 August 1971[39] | 750-755[Note 4] [Note 5] | Trials and operations unit at Yeovilton with mix of FAW.1 and FAW.2. For a short period 1964-5 Ark Royal. |
| FRU[39] | 6 August 1971? | Never | 1 December 1972[37] | 750-755[37][40] | Fleet Requirements Unit (FRU). When 890 Sqn disbanded some aircraft passed to Fleet Requirements Unit (FRU), Yeovilton. FRU became Fleet Requirements and Aircraft Direction Unit (FRADU) on 1 December 1972. |
| FRADU[39] | 1 December 1972[37] | Never | January 1974[Note 6] | 750-755[37][40] | Fleet Requirements and Air Direction Unit (FRADU). Retired Sea Vixen on grounds of cost.[37] January 1974.[39] |
- "Fly Navy Heritage Trust" one former Royal Navy aircraft formerly owned by De Havilland Aviation and flown as a promotional and display aircraft
Surviving aircraft


One Sea Vixen remains airworthy:
- Sea Vixen D.3 G-CVIX, the former XP924, registered until 2014 to DS Aviation (UK) at Bournemouth Airport, Dorset. It has a display of registration mark exemption to fly in its original Royal Navy markings as "XP924" coded "134".[43] It originally flew with 899 Naval Air Squadron Fleet Air Arm as "134" from November 1968 until 1970 from HMS Eagle. The ownership of XP924 moved to the Fly Navy Heritage Trust with a formal donation ceremony at RNAS Yeovilton on 16 September 2014. The Sea Vixen will in future be maintained and operated from Yeovilton by Naval Aviation Ltd., a subsidiary of Fly Navy Heritage Trust.[32]
The following complete airframes are on public display:
- Sea Vixen FAW.1 XJ481, Fleet Air Arm Museum, RNAS Yeovilton, Somerset. Part of the Museum's reserve collection.[44]
- Sea Vixen FAW.1 XJ482, Norfolk and Suffolk Aviation Museum, Suffolk.[45]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ490, Queensland Air Museum, Caloundra, Australia.[46] Airframe complete, but internals removed.
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ494, Bruntingthorpe Aerodrome, Leicestershire.
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ560, Newark Air Museum, Nottinghamshire.[47]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ565, de Havilland Aircraft Heritage Centre, Hertfordshire.[48]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ571, Solent Sky, Hampshire.[49]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XJ580, Tangmere Military Aviation Museum, West Sussex.[50]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XN685, Midland Air Museum, Coventry.[51]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XS576, IWM Duxford, Cambridgeshire.[52]
- Sea Vixen TT.2 XS587 (now G-VIXN), Gatwick Aviation Museum, Surrey.[53]
- Sea Vixen FAW.2 XS590, Fleet Air Arm Museum, RNAS Yeovilton, Somerset.[54]
Specifications (Sea Vixen FAW.2)
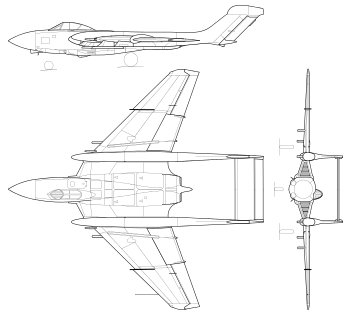
Data from The Great Book of Fighters[55]
General characteristics
- Crew: Two, pilot and Observer
- Length: 55 ft 7 in (16.94 m)
- Wingspan: 51 ft 0 in (15.54 m)
- Height: 10 ft 9 in (3.28 m)
- Wing area: 648 ft² (60.2 m²)
- Empty weight: 27,950 lb (12,680 kg)
- Loaded weight: 41,575 lb (18,860 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 46,750 lb [56] (21,205 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Rolls-Royce Avon Mk.208 turbojets, 50 kN (11,000 lbf) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 0.91 (690 mph, 1,110 km/h) at sea level
- Range: 790 mi (1,270 km) with internal fuel
- Service ceiling: 48,000 ft (14,600 m)
- Rate of climb: 9,000 ft/min (46 m/s)
- Wing loading: 64.2 lb/ft² (313 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.54
Armament
- Hardpoints: 6 and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: 4 × Matra rocket pods with 18 × SNEB 68 mm rockets each
- Missiles: 4 × Red Top or Firestreak air-to-air missiles
- Bombs: 1 × Red Beard freefall nuclear bomb
Avionics
GEC AI.18 Air Interception radar
See also
- De Havilland Aviation
- 1952 Farnborough Airshow DH.110 crash
- de Havilland Aircraft Heritage Centre
- Portal:British aircraft since World War II
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ "Observer" is the FAA term for the navigator/radar operator – the US Navy's equivalent is the radar intercept officer (RIO).
- ↑ Fiddler 1985, Table 4 says that 766 Sqn disbanded 10 February 1970.[37]
- ↑ [35] Birtles 1986, p. 107 says that 766 Sqn disbanded 10 December 1970. It is not known which date for 766 Sqn disbanding is correct.
- ↑ Fiddler 1985, Table 4 says 750-755 initially, with 001-007 and 010-014 during a brief period on Ark Royal in 1964-65, and 701-706 from 1971.[37]
- ↑ Birtles 1986, p. 107 says that 890 Sqn was disbanded in 1966 and reformed in 1967. Further research is required here.[39]
- ↑ [41]
Citations
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Neal 1960, p. 179.
- ↑ "British two-seat fighter to attain speed of sound." Popular Mechanics, March 1955, p. 97.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "de Havilland DH 110 Sea Vixen FAW.2." de Havilland Aircraft Museum, Retrieved: 25 September 2016.
- ↑ Birtles 1991, p. 194.
- 1 2 Jackson 1987, p. 470.
- ↑ Birtles 1991, pp. 195, 198.
- ↑ "British Unveil Twin-Boom Jet." Popular Science, Vol. 159, No. 6. December 1951. p. 123.
- 1 2 3 "On This Day - 1952: Dozens die in air show tragedy." BBC News, 2008.
- ↑ "1952: 'The crowd parted like the Red Sea'." BBC News, Retrieved: 25 September 2016.
- ↑ Jackson 1987, p. 471.
- ↑ Neal 1960, pp. 179–180.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Polmar 2008, p. 183.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Neal 1960, p. 180.
- ↑ Hobbs 2014, p. 256.
- ↑ Birtles 1991, pp. 198–199.
- ↑ Neal 1960, pp. 180, 184.
- ↑ Jackson 1987, p. 472.
- 1 2 3 The aircraft converted to D.3 standard were: XN657, XP924, XS577 and XS587. The aircraft sent to Farnborough for conversion but not converted were: XJ494, XN658, XN688. See "UK Serials." UK Serials.com. Retrieved: 27 September 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 Dyndal 2016, p. 43.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neal 1960, p. 184.
- ↑ Polmar 2008, pp. 184-185.
- ↑ Nicholas Air International July 2005, p. 47.
- ↑ Neal 1960, pp. 180, 184-185.
- 1 2 3 Neal 1960, p. 185.
- ↑ "de Havilland Sea Vixen History." Thunder and Lightnings. Retrieved: 14 July 2014.
- ↑ Ellis 2016.
- ↑ McCart 1997, p. 96.
- ↑ Eacott, John. Accidents." Sea Vixen. Retrieved: 14 July 2014.
- ↑ Birtles 1991, p. 201.
- ↑ Jackson 1987, p. 474.
- ↑ "DH110 Sea Vixen Faw Mk2, G-CVIX." Air Accident Investigation Branch. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- 1 2 Eagles, Sue. "Classic Fleet Air Arm fighter returns to Yeovilton." Fly Navy Heritage Trust. Retrieved: 6 October 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fiddler 1985, Table 3.
- 1 2 Hobbs 1982, p. 20.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Birtles 1986, p. 102.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Birtles 1986, p. 106.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Fiddler 1985, Table 4.
- 1 2 Birtles 1986, p. 103.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Birtles 1986, p. 107.
- 1 2 "History of the FRADU." fradu-hunters.co.uk. Retrieved: 27 September 2010.
- ↑ Birtles, Philip. Postwar Military Aircraft: 5, de Havilland Vampire, Venom and Sea Vixen, p. 107 says January 1974.
- ↑ "Sea Vixen: G-CVIX." airliners.net. Retrieved: 8 August 2010.
- ↑ "G-CVIX". UK Civil Aviation Authority. Retrieved: 14 July 2014.
- ↑ "de Havilland Sea Vixen FAW1 (XJ481)." Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Our Aircraft: Aircraft Exhibited at Flixton." Norfolk and Suffolk Aviation Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "de Havilland Sea Vixen F.A.W. MK 2 XJ490 C/N 110017." Queensland Air Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Aircraft List." Newark Air Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Aircraft Collection.". de Havilland Aircraft Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Exhibits." Solent Sky Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Museum Aircraft: De Havilland Sea Vixen FAW2". Tangmere Military Air Museum. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Aircraft Listing". Midland Air Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Aircraft at IWM Duxford". (pdf)." Imperial War Museums. 25 November 2011. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "de Havilland Sea Vixen TT.8." Gatwick Aviation Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "de Havilland Sea Vixen FAW2." Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm Museum. Retrieved: 15 March 2014
- ↑ Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. The Great Book of Fighters. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing, 2001. ISBN 0-7603-1194-3.
- ↑ "Sea Vixen FAW Mk.2 Flight Reference Cards AP101B-3002-14." Ministry of Technology, 1968, rev. 1970.
Bibliography
- Birtles, Philip. Postwar Military Aircraft 5: de Havilland Vampire, Venom and Sea Vixen. London: Ian Allan, 1986, ISBN 0-7110-1566-X.
- Birtles, Philip. "Sea Vixen: Britain's first missile specialist". Air International, April 1991, Vol. 40, No. 4, pp. 194–201. Stamford, UK: Key Publishing. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Donald, David and Jon Lake, eds. Encyclopedia of World Military Aircraft. London: AIRtime Publishing, 1996. ISBN 1-880588-24-2.
- Dyndal, Gjert Lage. Land Based Air Power Or Aircraft Carriers?: A Case Study of the British Debate about Maritime Air Power in the 1960s. Routledge, 2016. ISBN 1-31710-840-X.
- Ellis, Guy. Britain's Jet Age: From the Meteor to the Sea Vixen. Amberley Publishing, 2016. ISBN 1-44564-901-2.
- Fiddler, Brian. Sea Vixen. Ilchester, Somerset, UK: The Society of Friends of the Fleet Air Arm Museum, Fleet Air Arm Museum RNAS Yeovilton, 1985, ISBN 0-948251-03-4.
- Gunston, Bill. Fighters of the Fifties. North Branch, Minnesota: Specialty Press Publishers & Wholesalers, Inc., 1981. ISBN 0-933424-32-9.
- Hobbs, Lt Cdr David. Aircraft of the Royal Navy Since 1945. Liskeard, UK: Maritime Books, 1982, ISBN 0-907771-06-8.
- Hobbs, Lt Cdr David. British Aircraft Carriers: Design, Development & Service Histories. Seaforth Publishing, 2014. ISBN 1-84832-138-4.
- Jackson, A.J. De Havilland Aircraft since 1909. London: Putnam,, Third edition 1987. ISBN 0-85177-802-X.
- McCart, Neil. HMS "Centaur", 1943-72. Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, UK: Fan Publications, 1997. ISBN 978-0-9519538-9-1.
- Neal, Molly. "Sea Vixen." Flight, 5 February 1960, pp. 179–186.
- Nicholas, Jack. "Big Bangs For A Buck: Britain's Tactical Nuclear Forces 1960–1998". Air International, Vol. 69, No. 1, July 2005, pp. 45–49. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Phipp, Mike Bournemouth's Airports - A History. Tempus Publishing, Stroud, Gloucs, 2006, ISBN 0 7524 3923 5.
- Polmar, Norman. Aircraft Carriers: A History of Carrier Aviation and Its Influence on World Events, Volume II: 1946-2006. Potomac Books, 2008. ISBN 1-57488-665-7.
- Taylor, John W. R. "De Havilland Sea Vixen". Combat Aircraft of the World from 1909 to the Present. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1969. ISBN 0-425-03633-2.
- Winchester, Jim, ed. "De Havilland DH.110 Sea Vixen." Military Aircraft of the Cold War (The Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2006. ISBN 1-84013-929-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to de Havilland Sea Vixen. |
- De Havilland Aviation Ltd – operates airworthy de Havilland jet aircraft, including the world's last airworthy Sea Vixen
- SeaVixen.org – Contains information on the aircraft, the squadrons and carriers and those that flew them
- The 1952 Farnborough Air Show crash (with pictures)
- Aeroplane Naval Aircraft Archive - De Havilland Sea Vixen
- Thunder & Lightnings - De Havilland Sea Vixen
- Interview with Sea Vixen display pilot - Lt Cdr Matt Whitfield