Decentralized administrations of Greece
The decentralized administrations (Greek: αποκεντρωμένες διοικήσεις, apokentroménes dioikíseis) are the third level of administrative divisions in Greece. They were created in January 2011 as part of a far-reaching reform of the country's administrative structure, the Kallikratis reform (Law 3852/2010).[1]
They enjoy both administrative and financial autonomy[2] and exercise devolved state powers in urban planning, environmental and energy policy, forestry, migration and citizenship.[3] Beyond that, they are tasked with supervising the first and second-level self-governing bodies: the municipalities and regions, in this case the 66 municipalities of Attica and the region itself.
They are run by a government-appointed general secretary, assisted by an advisory council drawn from the regional governors and the representatives of the municipalities.
List of Decentralized Administration
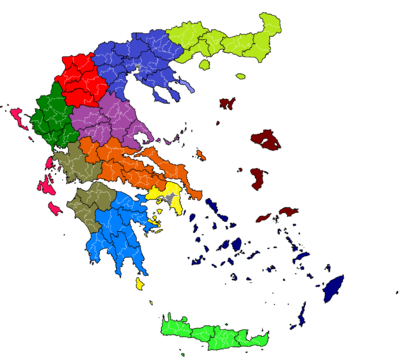
Decentralized Administration of Attica, with the capital of Athens
Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace, with the capital of Thessaloniki
Decentralized Administration of Epirus and Western Macedonia, with the capital of Ioannina
Decentralized Administration of Thessaly and Central Greece, with the capital of Larissa
Decentralized Administration of Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian, with the capital of Patras
Decentralized Administration of the Aegean, with the capital of Piraeus
Decentralized Administration of Crete, with the capital of Heraklion
Autonomous Monastic State of Mount Athos, (excluded from the Kallikratis Plan)
References
- ↑ Ministry of Interior 2013, p. 10 f..
- ↑ Ministry of Interior 2013, p. 12
- ↑ Ministry of Interior 2013, p. 27.
Sources
- Ministry of Interior (January 2013). "Structure and operation of local and regional democracy". Council of Europe.