Edmonton Light Rail Transit
|
| |||
 | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Edmonton, Alberta | ||
| Transit type | Light rail | ||
| Number of lines | 2 | ||
| Number of stations | 18 | ||
| Daily ridership | 108,690 (2015)[1] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | April 22, 1978 | ||
| Operator(s) | Edmonton Transit System | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 24.3 km (15.1 mi)[2][3] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (standard gauge) | ||
| Electrification | Overhead lines, 600 volts DC[4] | ||
| |||
| Edmonton LRT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
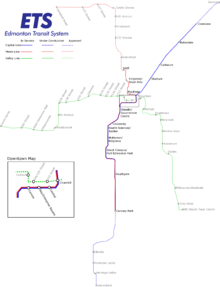
Edmonton Light Rail Transit, commonly referred to as the LRT, is a light rail system in Edmonton, Alberta. Part of the Edmonton Transit System (ETS), the system has 18 stations on two lines and 24.3 km (15.1 mi) of track.
ETS designates the first line as the Capital Line. The 21-kilometre line starts at Clareview in Edmonton's northeast and ends at Century Park in Edmonton's south end.[2] The Metro Line is a 3.3-kilometre (2.1 mi) extension of the system from Churchill LRT Station in downtown Edmonton northwest to NAIT LRT Station.[3] It had been scheduled to open in spring 2014,[5][6] but was delayed to September 6, 2015.[3][7][8] The first phase of the 27 kilometres (17 mi) Valley Line, which is planned to run from downtown Edmonton to Mill Woods, began construction in spring 2016 after the contract was finalized in February 2016.[9][10]
History

In 1962, Canadian Bechtel Ltd. was commissioned to develop a plan for Edmonton's rapid transit system. Construction began in 1974 with a budget of $65 million.[11] Edmonton became the first city in North America with a metropolitan population of less than one million to build a modern light rail system.[12] The population was just over 445,000 when construction started on the route in 1974.[13] It also became the first city in Western Canada to operate a rapid transit system. Testing of the new line started in 1977 with regular service starting April 22, 1978, in time for the 1978 Commonwealth Games. The line followed a CN right-of-way from Belvedere Station to Stadium Station (near Commonwealth Stadium), via an intermediate stop at Coliseum Station (near Northlands Coliseum), and then continued in a tunnel under 99 Street to Central Station, at Jasper Avenue and 100 Street, including an intermediate stop at Churchill Station. The original line was 6.9 km long.[14]
When the line opened, fare collection was modelled on traditional rapid transit lines, with booth attendants. Low volumes of activity at some entrances led to weekend closures of alternate station entrances. In November 1980, Edmonton Transit (as it was then named) switched to a modified European-style "proof of payment" system, retaining the old turnstiles to issue the new receipts.[15] Fares were now collected by automated ticket vending machines with irregular proof of payment inspectors, which permitted keeping all entrances open and required fewer staff.
On April 26, 1981, ETS opened a northeastern-bound extension of 2.2 km on the CN right-of-way to Clareview Station. In June 1983, the light rail tunnel downtown was extended by 0.8 km to Bay and Corona stations. The D.L. MacDonald Yard, between Belvedere and Clareview, opened in December 1983 to store and service the vehicles. The line was extended in September 1989 by 0.8 km to Grandin Station (close to the Alberta Legislature). On August 23, 1992, the next extension opened from Grandin to University Station, partially via the Dudley B. Menzies Bridge, crossing the North Saskatchewan River with a lower level for pedestrians and cyclists, and partially via a tunnel into the station. Major upgrades to the Belvedere and Clareview stations were made in 1998 and 2001 respectively.[14]
On January 1, 2006, the line was extended 0.6 km south through the University Campus to Health Sciences Station, which is located at street level. On April 25, 2009, McKernan/Belgravia and South Campus stations were opened as part of the south LRT expansion, with Southgate and Century Park opening on April 24, 2010. The first of the new Siemens SD-160 light rail vehicle train cars for the new extension were shipped by rail from Florin, California, on April 24, 2008, arriving in Edmonton on May 9, 2008 (37 vehicles in total).[16]
The LRT expansion was developed entirely at surface level with several underpasses after 2006, one at Belgravia Road and the other under 111 Street south of 61 Avenue. A short busway has been constructed from the South Campus station[17] roughly parallel to Belgravia Road in conjunction with the South LRT expansion.
| LRT system construction history[14] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | Capital project | Opening date | Track length | Light rail vehicles |
Stations | Cost (millions) |
Other features |
| Capital | First segment | April 22, 1978 | 6.9 km (4.3 mi) | 14 | 5 | C$64.9 | |
| Capital | Clareview extension | April 1981 | 2.2 km (1.4 mi) | 3 | 1 | C$9.5 | Park and ride lot with 450 stalls |
| Capital | Corona extension | June 1983 | 0.8 km (0.50 mi) | 20 | 2 | C$89.6 | |
| Capital | D.L. MacDonald Yard | December 1983 | C$28.2 | ||||
| Capital | Grandin extension | September 1989 | 0.8 km (0.50 mi) | 1 | C$67.1 | ||
| Capital | University extension (single track from south portal) | August 23, 1992 | 1.6 km (0.99 mi) | 1 | C$79.1 | Dudley B. Menzies Bridge | |
| Capital | University extension (second track from south portal) | May 14, 1994 | |||||
| Capital | Belvedere Station upgrade | September 23, 1998 | C$6.3 | Covered five-car platform Grade-separated pedestrian overpass | |||
| Capital | Clareview Station upgrade | March 4, 2001 | C$11.5 | Covered five-car platform Pedestrian underpass Transit centre on either side Park and ride increased to approximately 1,500 stalls | |||
| Capital | Health Sciences Station extension | January 4, 2006 | 0.6 km (0.37 mi) | 1 | C$100 | ||
| Capital | South Campus Station extension | April 25, 2009 | 2.2 km (1.4 mi) | 37[16] | 2 | C$690 | transit centre pedestrian underpass busway bridge[18] |
| Capital | Century Park Station extension | April 24, 2010 | 5.4 km (3.4 mi) | 2 | two transit centres two overhead pedways one park 'n' ride | ||
| Metro | NAIT Station branch | September 6, 2015 | 3.3 km (2.1 mi) | 20 | 3 | C$665 | overhead pedway at MacEwan one transit centre pedestrian overpass with elevator at Health Sciences[19] |
Every station on the line built since 1983 has been built with full accessibility for persons with disabilities. The 1998 and 2001 upgrades to the Belvedere and Clareview stations involved installation of roofs and lengthening of platforms to accommodate five-car trains.[14]
The LRT system had an estimated 18,220 weekday passenger boardings in 1978.[14] Six stations and 24 years after the University extensions, boardings more than doubled to 39,550 in 2002.[14] The LRT system continues to expand from its current 15 stations and 21 km of double track. LRT ridership has grown to 100,760 in 2013.[20]
Network
The system has two lines. The Capital Line, runs from northeast Edmonton to south Edmonton via Downtown. A second line, the Metro Line, connecting Downtown with northwest Edmonton, began limited operations in September 2015. There are further projects to create a new 27-kilometre line that will extend to Mill Woods Town Centre in the southeast part of the city and to Lewis Farms in the west end of the city.
During construction, surface area was preserved (although costs increased) by tunnelling under the downtown core and the University of Alberta main campus. The underground portions of the LRT connect to the Edmonton Pedway system with links to many buildings. The LRT crosses the North Saskatchewan River between the Grandin and University stations on the Dudley B. Menzies Bridge,[21] a dedicated LRT and pedestrian bridge.
Storage, maintenance and operations of the LRT are controlled from the D.L. MacDonald Yard.
The LRT operates between 5:00 am and 1:00 am daily. Trains run on a five-minute frequency during rush hour, ten-minute frequency midday and Saturdays, and on a fifteen-minute frequency in the evening and on Sundays.[22] When the Metro Line is running at full capacity, train frequency will double between Health Sciences/Jubilee station and Churchill station.
On June 25, 2012, the City of Edmonton launched a public contest to name the existing and future lines.[23] On January 31, 2013, the city announced the names: Capital Line, Metro Line, Valley Line, Energy Line, and Festival Line.[24][25]
| Line | Termini | Stations | Length | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 501 | Capital Line | Clareview | Century Park | 15[2] | 21 km (13 mi)[2] | |
| 502 | Metro Line (nights and Sundays) | NAIT | Health Sciences/Jubilee | 10 | 8 km (5 mi) | |
| Metro Line (Monday to Saturday) | NAIT | Century Park | 14 | 16 km (10 mi) | ||
Stations
The system has 18 consecutive stations: Clareview, Belvedere, Coliseum, Stadium, Churchill, Central, Bay/Enterprise Square, Corona, Grandin/Government Centre, University, Health Sciences/Jubilee, McKernan/Belgravia, South Campus/Fort Edmonton Park, Southgate, and Century Park stations. Of these, Churchill, Central, Bay/Enterprise Square, Corona, Grandin/Government Centre, and University are underground. Three newest stations opened in September 2015 for the Metro Line: MacEwan, Kingsway/Royal Alex, and NAIT.
Another 12 stations will be built for the first phase of the Valley Line, which is planned to be opened in 2020.[26]
All existing stations have a centre platform.
Rolling stock
The rolling stock of the Capital Line and Metro Line is composed of trains of either Siemens-Duewag U2 or Siemens SD-160 cars. ETS operates 37 U2 cars, some of which have been in operation since the system opened in 1978. ETS also operates 57 SD-160 cars, of which 37 were ordered between 2005 and 2007, with the first cars entering revenue service on January 27, 2009.[27] An additional 20 cars were purchased in 2010 and 2011 for use in the Metro Line and were delivered from March 2012 to April 2013.[28][29][30]
The Capital Line uses five-car trains during peak hours, and three-car trains are occasionally used for late night service. The Metro Line will operate three-car trains until the permanent NAIT station is opened, as the temporary NAIT Station can only accommodate three-car trains. The permanent station will be 125 metres long to accommodate a five-car train. All other extensions to the Capital and Metro lines will have five-car platforms.[31]
Future lines of the LRT, including the Valley Line will use new low-floor cars.[32]
Safety and security
All LRT stations are monitored by CCTV cameras. All trains are equipped with operator alert systems which will allow passengers to contact the train operator in the event of an emergency. Likewise, all stations are equipped with blue emergency help phones which will connect with ETS Security. The stations are patrolled by ETS Transit Peace Officers.[33]
Despite the security measures put in place, there have been several incidents on the Edmonton LRT or at the LRT stations. In 2008, there were 328 crimes against persons reported on transit property.[34] Some of the most serious incidents include:
- In 1988, a woman was strangled to death in a Churchill Station washroom.[34]
- In 2010, a woman was shot and killed at Stadium Station.[34]
- In 2012, a man was beaten to death on board the LRT between Stadium and Belvedere Station.[35]
Fares
The cash fare for passengers using Edmonton Transit System buses and the LRT, effective February 1, 2016, is $3.25 for adults, seniors and youth. Children five years old and under ride free when accompanied by a fare-paying adult.[36]
| Fare type | Price[36] |
| Cash fare | $3.25 |
| Children 5 and under | Free |
| Day pass | $9.25 |
| Month pass | $91.50 |
Passengers can also purchase books of transit tickets or monthly transit passes. Seniors can purchase an annual transit pass at a discounted rate.
Passengers paying a cash fare at a fare machine at an LRT station are issued a transit ticket, which is validated as an LRT ticket after being time-stamped. This ticket is valid both as proof of payment and as a transfer. Transfers allow the passenger to transfer from the LRT to a bus, from a bus to the LRT and between buses, and is valid for 90 minutes from the time it was stamped. Passengers paying a cash fare or validating a ticket on a bus obtain a transfer at the time the fare is paid. Transfers also serve as proof of payment for 90 minutes.[37]
Passengers in an LRT proof of payment area must present proof of payment upon request by an ETS officer. Proof of payment includes LRT tickets, transfers, validated transit tickets and transit passes. Failure to provide proof of payment can result in a $250 fine. Proof of payment areas include all LRT trains and LRT station platforms, unless the ticket vending machines are located on the platform itself.
In 2007, the Edmonton Transit System, the University of Alberta (U of A), and MacEwan University partnered to provide students with a universal transit pass (U-Pass), which is valid on the LRT and all ETS buses as well as on Strathcona County and St. Albert Transit Systems.[38][39] NAIT students voted to join the program in 2010.[40] The U-Pass allows unlimited LRT and bus use to valid pass holders.
Future expansion
The City of Edmonton prioritized completion of the Metro Line to NAIT for 2014, followed by expanding the system to the southeast and west.[41] City council approved funding to begin preliminary engineering on the Valley Line from Mill Woods to Lewis Farms in June 2011.[42]
| Line | Status | Termini | Additional stations | Additional length | Projected opening | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valley Line | Construction[43] | 102 Street (Downtown) | Mill Woods | +11 | +13 km | late 2020 | |
| Valley Line | Priority #1 | 102 Street (Downtown) | Lewis Farms | +16 | +14 km | before 2040 | |
| Metro Line | Priority #2 | NAIT | Blatchford | +1 | before 2040 | ||
| Capital Line | Priority #3 | Century Park | Ellerslie | +1 | before 2040 | ||
| Festival Line | Priority #4 | University | Bonnie Doon | before 2040 | |||
| Metro Line | Priority #5 | Blatchford | Castle Downs | +4[44] | before 2040 | ||
| Capital Line | Approved | Clareview | Gorman | +1[2] | +2.9 km | before 2040 | |
| Metro Line | Approved | Castle Downs | Campbell Road | +3[44] | +11 km (from NAIT to Campbell Road) | before 2040 | |
| Capital Line | Approved | Ellerslie | Desrochers | +3 | before 2040 | ||
| Line | Termini | Additional stations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metro Line | Campbell Road | Neil Ross Road | +4[45] | |
| Energy Line | Lewis Farms | Sherwood Park | ||
| Festival Line | Bonnie Doon | Mill Woods | ||
| Festival Line | University | Sherwood Park (via downtown) | ||
Capital Line expansion
Future plans call for expanding the Capital Line to Gorman in the northeast and Heritage Valley in the south.
Metro Line expansion
On April 27, 2007, the city began detailed planning of a new LRT line that will run north from Churchill Station, to the Northern Alberta Institute of Technology (NAIT), and eventually beyond to north-end neighbourhoods with a terminal station south of St. Albert.
Churchill Station to NAIT
The new line branches off the Capital Line at Churchill Station, runs west along 105 Avenue to the MacEwan University City Centre Campus, then north along 105 Street, Kingsway (Avenue), and 106 Street, to Kingsway Mall and NAIT.
In April 2008, Edmonton City Council approved $45 million in funding to build a tunnel under the Epcor Tower site immediately, while it was still under construction, with the aim of saving $140 million more than would have been required to dig under the tower once it was completed. This step was taken even though the rest of the project had not yet been approved, because of the time constraint posed by the construction of the new tower.[46] Construction on the tunnel began in August 2009 and was completed by approximately September 2010.[47]
On July 2, 2009, the federal and provincial governments approved the reallocation of funding from the proposed Gorman Station to the line as the city felt that NAIT was a higher priority.[48]
The expansion added three stations to the system; MacEwan Station at MacEwan University, Kingsway/Royal Alex Station near Kingsway Mall and the Royal Alexandra Hospital, and NAIT Station at the Northern Alberta Institute of Technology. MacEwan Station is located just east of the downtown MacEwan University campus, and west of the proposed downtown hockey arena, at 104 Street and 105 Avenue. The Kingsway/Royal Alex Station is located on the north side of Kingsway, to the south of the hospital. As part of the plan, the Kingsway Transit Centre was relocated to the southeast corner of 111 Avenue and 106 Street, to provide service to both Kingsway Mall and the LRT station.[19] The NAIT Station is located north of Princess Elizabeth Avenue, on the south side of NAIT's swimming pool and hockey arena.[47][49][50][51]
The Metro Line was $90 million under its estimated $755 million budget, with a total cost for the project of $665 million.[52]
NAIT to St. Albert
Beyond NAIT, the Metro Line will travel through the new neighbourhood built after the City Centre (Blatchford Field) Airport is dismantled, go over the CN railway yard north of Yellowhead Trail, and continue north along 113A Street, and west along 153 Avenue. The City of St. Albert has also begun preliminary plans to extend the LRT line into their borders.[45]
On May 19, 2010, the transportation department announced its recommendation for an extension of the Metro Line from NAIT station to St. Albert. This extension is expected to eventually serve 42,000 to 45,000 passengers daily.[53]
Valley Line
The Valley Line is a proposed 27 km (17 mi), low-floor urban line running southeast to west from Mill Woods to Lewis Farms, crossing through downtown. The line will be constructed in phases, with phase 1 being the 13.1 km (8.1 mi), 12-station portion between Mill Woods and 102 Street (downtown) allowing passengers to connect with the Capital Line and Metro Line at Churchill. Construction is expected to start in 2016 with completion in 2020.[54][55]
Mill Woods to Downtown
In December 2009, Edmonton city council approved a new low-floor train route that would leave a new ground-level station at Churchill Square on 102 Avenue between 100 and 99 streets before stopping in The Quarters redevelopment on 102 Avenue between 97 street and 96 street. From here the route enters a tunnel and travels beneath 95 street descending into the river valley to cross the North Saskatchewan River on the new Tawatinâ Bridge,[56] which will be constructed east of Louise McKinney Park. The route then proceeds to climb the hill adjacent to Connors Road then proceed east along 95 Avenue and southbound at 85 Street. The route will travel southbound along 85 Street crossing the traffic circle and shifting to 83 Street, continuing south and east towards Wagner Road. Finally the line will proceed south along 75/66 Street until it reaches Mill Woods Town Centre. Within this line the proposed stations are: Quarters, Muttart, Strathearn, Holyrood, Bonnie Doon, Avonmore, Davies (to include a bus terminal and park & ride),[57] Millbourne/Woodvale, Grey Nuns, and Mill Woods Town Centre. The maintenance and storage of vehicles for the line will be at the new Gerry Wright Operations and Maintenance Facility, at Whitemud Drive and 75 Street.[58]
On February 15, 2012, city council approved the Downtown LRT concept plan. The Downtown LRT Project became part of the Southeast to West LRT project.[59] The city hoped to have money in place by the end of 2013 for the $1.8-billion LRT line from downtown to Mill Woods to start construction in 2016. City council committed $800 million, the federal government invested $250 million, and $235 million would come from the provincial government, leaving a $515 million funding gap delaying the project.[60] On March 11, 2014, it was announced that the project would be completely funded[61][62] with an additional $150 million from the federal government and $365 million from the provincial government.[63][64]
Downtown to Lewis Farms
A planned expansion to Lewis Farms, with the West Edmonton Mall en route, is in the engineering phase as part of the 27-kilometre Valley Line.
The option approved by Council in 2010 was to have the west LRT extension run from downtown, along 104 Avenue and Stony Plain Road before diverting south on 156 Street towards Meadowlark Health And Shopping Centre, then along an 87 Avenue alignment to West Edmonton Mall and beyond. Proponents of this route cited opportunities for transit-oriented development.[65][66]
Controversy
Since the opening of the Metro Line, the line has been dealing with signalling problems as trains can only run at a maximum of 25 km/h (16 mph) between the Churchill and NAIT stations, creating passenger delays and traffic congestion.[67]
The Valley LRT to Mill Woods has generated opponents particularly on the location of the route. The Edmonton Chinese community opposed the city's plan to lay the tracks on 102 Avenue as it is directly in front of a Chinese elderly care facility. Despite demands to relocate the route to 102a Avenue, the city council voted for the original proposal.[68] An advocacy group opposed the route saying that the new LRT bridge crossing the North Saskatchewan River will have a negative impact on the river valley and the removal of the existing footbridge during construction would leave them with no river crossing. The city however states that impact is minimal and other alternative routes were not suitable.[69][70]
Concerns over community impacts[71] along the proposed West[72] and North[73] LRT extensions have led to a larger debate[74] over the vision[75] guiding the various expansion plans, and the criteria used to select the routes.
A lack of coordination between the extensions and transit-oriented developments as well as integration with other regional transportation nodes, has given rise to proposals for a new LRT master plan to guide it all.[76]
Signalling system
With the opening of the Metro Line, ETS will convert the signalling system for the Capital Line from fixed block to Communications-based train control (CBTC) or moving block. The new Metro Line was built to use only CBTC.[77]
The signalling system will control train traffic to keep it safely spaced and on schedule, share train location information publicly (e.g., digital and audio announcements at LRT stations), and manage intersections by triggering traffic signals and crossing warning systems (warning bells, flashing lights and gates).[77]
The older fixed block system divides the track into sections called blocks protected by signals that maintain at least one empty fixed block between trains. The new CBTC system will instead maintain a fixed distance of empty space (a moving block) between trains. This allows trains to operate closer together, which increases the frequency of trains arriving at stations and increases an LRT system’s overall capacity for ridership.[77]
The CBTC uses computers on trains that report into a central controller to pinpoint the exact location of each train and constantly adjust the speed, spacing and routing of trains to keep trains safe and on schedule. It safely tightens up the spacing between trains so that Metro Line and Capital Line trains can share the same tracks between Health Sciences/Jubilee Station and Churchill Station. Edmonton Transit runs peak-time trains every 5 minutes through downtown, but this frequency will be increased to every 2.5 minutes when the Metro Line is fully operational.[77]
Thales Rail Signalling Solutions is the signalling contractor that installed the system. They have completed systems in many cities including Vancouver (Canada Line) and are also working on Ottawa’s Confederation Line.[77]
References
- ↑ "September 2015 Cumulative Boarding Report" (pdf). City of Edmonton. April 2016. p. 6. Retrieved April 19, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "The Way We Move LRT for Everyone" (pdf). Edmonton Transit System and City of Edmonton. pp. 4–5. Retrieved 2015-09-08.
- 1 2 3 "Metro Line (North LRT to NAIT)". City of Edmonton. September 7, 2015. Retrieved September 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Edmonton Datasheet - SD160 Light Rail Vehicle" (PDF). Siemens. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 26, 2010. Retrieved March 9, 2011.
- ↑ "Metro Line Scheduled to Open in Spring 2015". City of Edmonton. January 21, 2015. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ↑ "Metro LRT delayed, not yet 'reliable' says city". CBC News. May 30, 2015. Retrieved May 31, 2015.
- ↑ Clark, Debra (September 6, 2015). "Highly anticipated Metro LRT line opens to public". CTV News. Retrieved September 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Edmonton opens northern Metro Line". Railway Gazette International. September 8, 2015. Retrieved September 8, 2015.
- ↑ Kent, Gordon (February 11, 2016). "'There's no hidden surprises,' city says, as it signs contract for Edmonton Valley Line LRT". Edmonton Journal. Postmedia Network. Retrieved February 13, 2016.
- ↑ "Bechtel Team Awarded Edmonton Valley Line Light Rail Project in Canada". Bechtel. February 11, 2016. Retrieved February 13, 2016.
- ↑
- ↑ "LRT Brochure" (PDF). November 15, 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 4, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ↑ "Historical City of Edmonton Population" (PDF). City of Edmonton. August 2008. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Colin Hatcher (2003). Edmonton's Light Rail Transit – The First 25 Years. Edmonton Transit System.
- ↑ Tingley, Kenneth W. (2011). Ride of the Century: The Story of the Edmonton Transit System. City of Edmonton. p. 239. ISBN 978-0-9809275-0-4.
- 1 2 "LRT Vehicle Arrival and Unveiling". City of Edmonton. May 2008. Archived from the original on June 16, 2011. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ "South LRT Extension". City of Edmonton. 2009. Archived from the original on June 16, 2011. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ↑ "South LRT Fact Sheet" (PDF). City of Edmonton. 2010. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- 1 2 "North LRT Stations". City of Edmonton. 2010. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "2013 LRT Passenger Count Report" (PDF). City of Edmonton. January 2014. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Dudley Menzies Bridge - Light Rail Transit Bridge Over The North Saskatchewan River". PCL. 2005. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- ↑ "LRT Schedule and Map" (pdf). City of Edmonton. 2013. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ↑ City of Edmonton. "Help Name Edmonton's LRT Lines". Retrieved June 25, 2012.
- ↑ Kent, Gordon (January 31, 2013). "City names LRT lines, grumbling follows". Edmonton Journal. Postmedia Network. Archived from the original on February 3, 2013. Retrieved January 31, 2013.
- ↑ "Approved LRT Line Names" (PDF). City of Edmonton. Retrieved January 31, 2013.
- ↑ "Valley Line (SE to West LRT)" (PDF). City of Edmonton. September 2013. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ "New LRT Cars Start in Regular Service". City of Edmonton. 2009-01-26. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ Ho, Clara (July 9, 2010). "City transportation wants more LRT cars". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved October 30, 2013.
- ↑ "More dollars coming for LRT". CBC News. February 8, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2013.
- ↑ "Annual Review of 2010-2013 Council Initiatives Status Update" (PDF). City of Edmonton. July 4, 2012. Retrieved October 30, 2013.
- ↑ "LRT Design Guideline For ETS Edmonton Transit System" (PDF). City of Edmonton. 2011. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ "Valley Line LRT Factsheet" (PDF). City of Edmonton. April 2013. Retrieved October 30, 2013.
- ↑ "Safety and Security". City of Edmonton. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- 1 2 3 Drake, Laura; Warnica, Richard; Sumamo, Yonathan (May 23, 2010). "Woman's murder rattles LRT riders". Edmonton Journal. Canada.com. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Man dies after beating on Edmonton transit train". CBC News. December 31, 2012. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- 1 2 "Fares". City of Edmonton. February 1, 2014. Retrieved March 4, 2014.
- ↑ "Transfer Policy". City of Edmonton. 2010. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "Edmonton university students say yes to U-Pass". CBC News. 2007-03-09. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ Edmonton Journal (2007-03-27). "MacEwan students approve transit pass". Canada.com. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ Jarvis, Kristina (2010-03-27). "NAIT students approve U-Pass". St. Albert Gazette. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "10-Year Capital Investment Agenda 2012-2021" (PDF). City of Edmonton. June 18, 2012. Retrieved November 20, 2012.
- ↑ "City Council Minutes". City of Edmonton. June 1, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2012.
- ↑ "TransEd LRT".
- 1 2 "Northwest LRT to City Limits". The City of Edmonton. Retrieved August 20, 2013.
- 1 2 "St. Alberta LRT" (PDF). City of St. Albert. February 23, 2013. Retrieved September 10, 2013.
- ↑ "LRT line likely to go under Epcor". Edmonton Journal. 2008-04-09. Retrieved 2008-04-12.
- 1 2 "Summer 2010 North LRT Newsletter" (PDF). 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 16, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ↑ "Alberta surges ahead with climate change action plan". Government of Alberta. 2008-07-08. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ "North LRT Making Tracks Fall 2009" (PDF). City of Edmonton. October 2009. Retrieved 2009-12-23.
- ↑ Leduc County Growth Study (October 2008). "Section Five" (PDF). Recommended Growth Strategy. Leduc County. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 13, 2011. Retrieved January 14, 2011.
- ↑ Mackenzie Sinclair (May 21, 2009). "Lovin' The LRT". See Magazine. Archived from the original on May 26, 2011.
- ↑ Tumilty, Ryan (April 10, 2014). "NAIT LRT Line comes in $90 million under budget, money could be moved to south east". Metro News. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ↑ Ho, Clara (May 19, 2010). "City announces planned LRT route to St. Albert". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ↑ "Valley Line (SE to West LRT): Mill Woods to Lewis Farms". Edmonton Transit System. 2015. Retrieved 2015-06-16.
- ↑ "Valley Line LRT Animation". City of Edmonton. 2013-12-03. Retrieved 2015-06-16.
- ↑ "Southeast LRT (Valley Line) Names Approved". City of Edmonton Naming Committee. Retrieved November 14, 2013.
- ↑ "Southeast to West LRT - Approved Concept Plan Amendment" (PDF). City of Edmonton. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Operations and Maintenance Facility" (PDF). City of Edmonton. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ "Southeast to West LRT: Mill Woods to Lewis Farms". City of Edmonton. Retrieved May 27, 2012.
- ↑ Dykstra, Matt (November 13, 2013). "Federal government projects a $3.7 billion budget surplus which could help Edmonton LRT line". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved November 14, 2013.
- ↑ Tumilty, Ryan (March 11, 2014). "Southeast LRT funding includes $200 million interest-free provincial loan". Metro News. Retrieved March 12, 2014.
- ↑ Kent, Gordon (March 11, 2014). "Southeast LRT on track after province promises to fill $600 million funding gap (with video)". Edmonton Journal. Retrieved March 12, 2014.
- ↑ Simons, Paula (May 26, 2014). "Cash for Valley Line is fine, but transit funding must be consistent". Edmonton Journal. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ↑ Dykstra, Matthew (May 26, 2014). "Edmonton gets a final piece of funding for southeast portio of Valley LRT line". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ↑ Kent, Gordon (September 3, 2009). "Edmonton unveils west and south LRT plans". Archived from the original on November 7, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ↑ "City Proposes Southeast and West LRT Routes". September 3, 2009. Archived from the original on June 16, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ↑ Querengesser, Tim (December 15, 2015). "Edmonton's Metro Line LRT still a troubled machine: Report". Metro News Edmonton. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ↑ "Edmonton approves Chinatown route for LRT". Cbcnews.ca. 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2012-02-15.
- ↑ Ramsay, Caley (May 25, 2014). "City prepares for major changes to popular River Valley trails, footbridge". Global News. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ↑ Hampshire, Gareth (April 22, 2016). "Group wants river valley protected against LRT development". CBC News. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ↑ "West LRT opposition heats up". Edmonton Journal. 2008-04-12. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ "Mandel slams city staff over LRT route". Edmonton Journal. 2008-04-30. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ "Residents fume over LRT's 'path of destruction'". Edmonton Journal. 2008-05-15. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ "Sparks fly as councillors delay LRT hearing". Edmonton Journal. 2009-05-06. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ↑ Jordan Schroder (June 26, 2008). "No, No, No: The LRT Needs To Go Here!". See Magazine. Archived from the original on May 26, 2011.
- ↑ Jordan Schroder (June 19, 2008). "Train To Nowhere". See Magazine. Archived from the original on May 26, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Metro Line: Delay FAQ" (PDF). City of Edmonton. 4 May 2015. Archived from the original (pdf) on June 30, 2015. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
The City is replacing this traditional fixed block system with a modern CBTC (moving block) system
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Edmonton Light Rail Transit. |
- Edmonton Transit System (Official website)
- Edmonton Transit System–Future LRT
