European Gendarmerie Force
| European Gendarmerie Force | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
| Active | 2006–present |
| Country | |
| Type | Militarized police |
| Size |
~900 (Permanent personnel) 2,300 (Available on standby) |
| Part of | European Union Military Staff |
| Motto(s) | Lex paciferat (Latin for "the law will bring peace") |
The European Gendarmerie Force (EUROGENDFOR or EGF) was launched by an agreement in 2006 between five member states of the European Union (EU): France, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain. Romania joined in 2009; Poland in 2011.[1] Its purpose is the creation of a European intervention force with militarised police functions and specialisation in crisis management, designed after the French Gendarmerie, the Spanish Guardia Civil, and the Italian Carabinieri and its Multinational Specialized Units (M.S.U.).[2][3] Its status is enshrined in the Treaty of Velsen of 18 October 2007.[4]
History
The French Defence Minister Michèle Alliot-Marie first proposed the force in September 2003. Alliot-Marie and the Italian Defense Minister Antonio Martino presented the idea at the Meeting of European Union Defense Ministers in October 2003. The implementation agreement was finally signed by defence ministers of the five participating countries on 17 September 2004 in Noordwijk, Netherlands. On 23 January 2006, the EGF was officially inaugurated during a military ceremony in the Gen. Chinotto barracks in Vicenza.
The EGF was declared fully operational on 20 July 2006, following the High Level Interministerial meeting in Madrid, Spain, and its second successful Command Post exercise (CPX), which took place between 19–28 April 2006. The first CPX was held at the National Gendarmerie Training Center in Saint Astier, France in June 2005.
After Romania's accession to the European Union, the Romanian Gendarmerie sought permanent observer status with the European Gendarmerie Force, as a first step towards full membership.[5] On March 3, 2009, the Romanian Gendarmerie became a full member of the European Gendarmerie Force.[6]
The Polish Military Gendarmerie was originally a partner force and, on 10 October 2006, Poland indicated it would like to join the EGF.[7] In December 2011, Poland applied for full membership in EGF,[8] which was granted in 2011.[1]
Since December 2009, the EGF has taken part in the NATO International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) training operation of the Afghan National Police (ANP) in the War in Afghanistan. As of June 2010, 276 members of the EGF (among which 124 French gendarmes), from France, Spain, Netherlands, Poland and Portugal are training the Afghan National Civil Order Police (ANCOP) officers and non-commissioned officers, while the initial mission was planned to be around 400 to 500 men.[9] They are training them in ANCOP training centers but are also accompanying, advising and helping them during their missions in P-OMLT (Police Operational Mentoring and Liaison Teams),[10][11] where their military experience (even if the mission is strictly speaking civilian since it is "formation") will be useful. As of May 2010, it had trained 50 officers and 250 non-commissioned officers of the ANCOP, and the then French Minister of Defense Brice Hortefeux announced that 40 more French gendarmes would be sent to help this mission.[12]
In early 2010, the EGF was deployed to Haiti to help with post-relief security efforts.[13]
Members
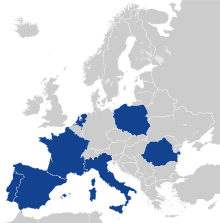
The EGF is based in Vicenza, in northeastern Italy, and has a core of 800 to 900 members ready to deploy within 30 days. The member forces are:[14]
-
 French Gendarmerie
French Gendarmerie -
 Italian Carabinieri
Italian Carabinieri -
 Dutch Royal Marechaussee
Dutch Royal Marechaussee -
 Polish Military Gendarmerie
Polish Military Gendarmerie -
 Portuguese National Republican Guard
Portuguese National Republican Guard -
 Romanian Gendarmerie
Romanian Gendarmerie -
 Spanish Guardia Civil
Spanish Guardia Civil
An additional 2,300 reinforcements are available on standby.
Partners
-
 Lithuanian Viešojo saugumo tarnyba (Public Security Service)[15]
Lithuanian Viešojo saugumo tarnyba (Public Security Service)[15]
Observers
Germany does not take part, as its constitution does not permit the use of military forces for police services. In 2004, Peter Struck, Minister of Defense at the time, clarified that the legal foundation for militarised police forces is different from the expectations underlying the EGF.[17] The paramilitary Bereitschaftspolizei units of the Länder states have no standing patrol order like the German Federal Police. Germany did not sign the Treaty of Velsen on the EGF or any subsequent accord.[18] Instead, there is a tight integration of police forces based on the Prüm Treaty. Originally the Prüm Treaty regulated access to police databases of neighboring countries but it was used multiple times as the legal foundation to exchange riot police equipment and personnel with the participating countries (Germany, Spain, France, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Austria, and Belgium). In 2008 the Prüm Treaty was naturalised as EU law, allowing countries access to police forces regulated under EU law (based on the Schengen agreement). The European Police Forces Training of 2009 (EUPFT 2009) was run in Vicenza (home of EGF headquarters) and the EUPFT 2010 on anti-riot tactics was run in Lehnin in Germany.[19][20]
See also
- Association of the European and Mediterranean Police Forces and Gendarmeries with Military Status
- Common Security and Defence Policy
- EU Battlegroup
- EUFOR
- Eurocorps
- European Defense Agency
- European Maritime Force
- European Security Strategy
- European Union Military Staff
References
- 1 2 "European Gendarmerie Force". Żandarmeria Wojskowa. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ↑ http://www.fiep.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/E-reader-FIEP-Seminarbook.pdf
- ↑ Giovanni Arcudi & Michael E. Smith (2013), The European Gendarmerie Force: a solution in search of problems?, European Security, 22:1, 1-20, DOI: 10.1080/09662839.2012.747511
- ↑ Eurogendfor.org, Treaty establishing the European Gendarmerie Force, accessed on January 24, 2014
- ↑ (Romanian) Politica europeană - Forţa de Jandarmerie Europeană (European Policy - European Gendarmerie Force), Romanian Gendarmerie website, accessed on January 22, 2009
- ↑ Eurogendfor.eu, EGF News, accessed on March 23, 2009
- ↑ "Poland expresses readiness to join European Gendarmerie Force", October 10, 2006
- ↑ "News" section, March 25, 2012
- ↑ (French) Des gendarmes picards bientôt en Afghanistan, Nord Éclair, 12 June 2009
- ↑ http://www.assemblee-nationale.fr/13/cr-cafe/09-10/c0910077.asp (French) report from the commission on Foreign matters of the French Parliament
- ↑ http://www.interieur.gouv.fr/sections/a_la_une/toute_l_actualite/affaires-europeennes/gendarmes-en-afghanistan/view (French), "Gendarmes in Afghanistan", French Internals affairs Ministry website
- ↑ http://www.interieur.gouv.fr/sections/a_la_une/toute_l_actualite/affaires-europeennes/deplacement-afghanistan/view (French) "Brice Hortefeux honours the contribution of French policemen and gendarmes to the Afghan police training", French Internals affairs Ministry website
- ↑ "European gendarmes to beef up Haiti security". euronews. Retrieved 3 September 2010.
- ↑ "Members". European Gendarmerie Force. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ↑ "Partners". European Gendarmerie Force. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ↑ "Observers". European Gendarmerie Force. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
- ↑ "Des gendarmes européens en renfort", 17/09/2004
- ↑ DerStandard.at, Welche Befugnisse hat die Europäische Gendarmerietruppe?, accessed on February 20, 2016
- ↑ "Von Vicenza nach Lehnin", Bundespolizei kompakt (German federal police journal), February 2010
- ↑ http://www.heise.de/tp/blogs/8/147676